Theory – PASCO ME-9891 Flexible I-beam User Manual
Page 3
®
M o d e l N o . M E - 9 8 9 1
T h e o r y
3
Theory
The deflection of a beam depends on how it is supported, the location and magnitude
of the load, the beam’s elastic modulus (E), and its second moment of area (I).
The vertical deflection of a beam (y) can be found using the formula
(eq. 1)
where M is the internal bending moment at horizontal position x. The product EI is
the beam’s flexural rigidity.
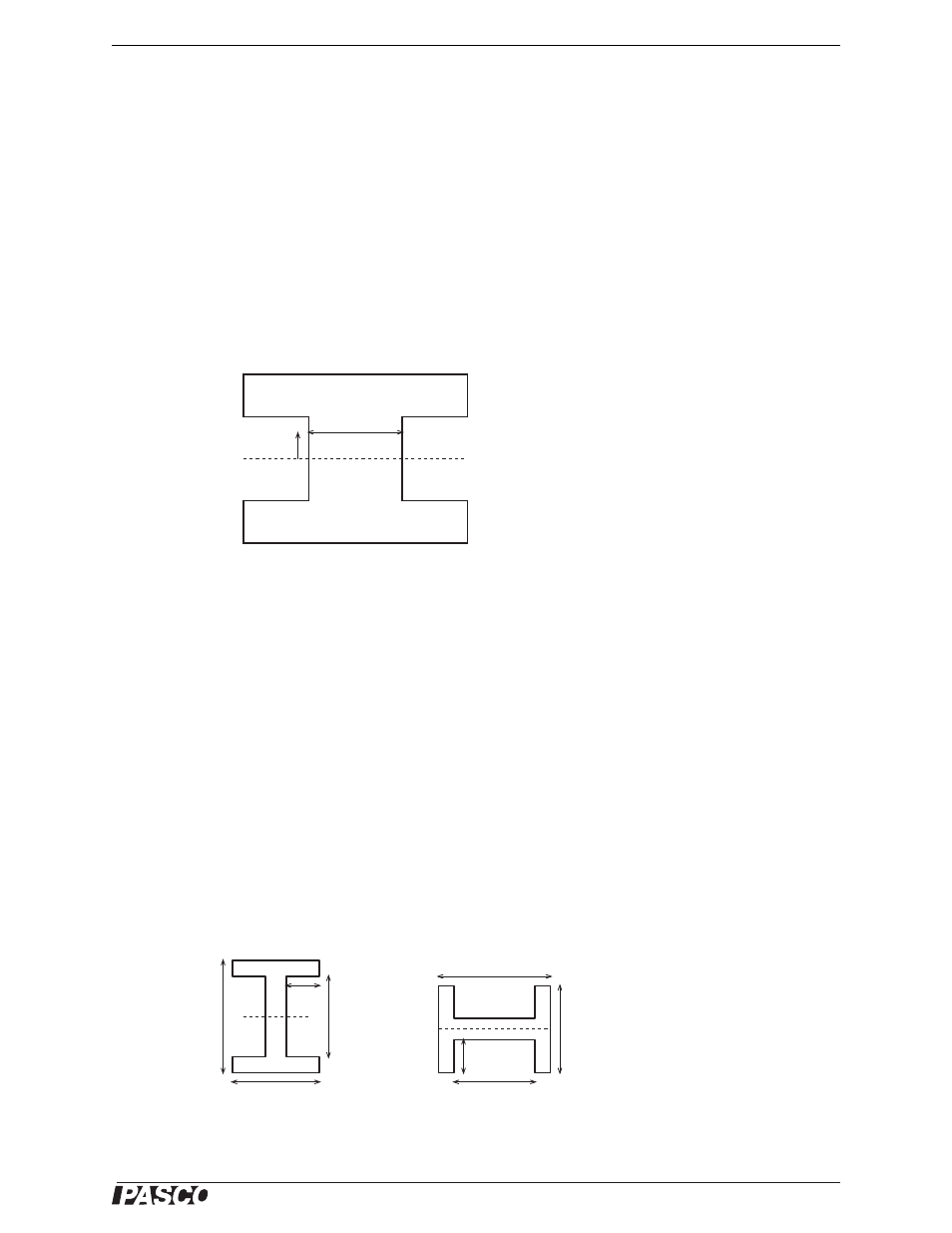
Second Moment of Area
Figure 4
The second moment of area for a beam of constant cross section is
(eq. 2)
where b(y) is the width of the section at a distance y from the neutral axis (Figure 4).
For the upright I-beam in Figure 5a, the second moment of area is
(eq. 3)
For the same I-beam turned on its side (Figure 5b), the second moment of area is
(eq. 4)
Note that these formulas for I are for calculating vertical deflection.
Figure 5
d
2
y
dx
2
--------
M
EI
------
=
y
neutral axis
b(y)
I
y
2
b y
( ) y
d
∫
=
I
WH
3
wh
3
–
12
----------------------------
=
upright
I
H
h
–
(
)W
3
h W
w
–
(
)
3
+
12
----------------------------------------------------------
=
side
H
W
h
w/2
(a) upright
H
W
h
w/2
(b) sideways
- UI-5000 850 Universal Interface Quick Start (1 page)
- UI-5000 850 Universal Interface Instruction Manual (24 pages)
- PS-2193 High Current Sensor (2 pages)
- ME-8979 Mass and Hanger Set (1 page)
- ME-9498A Photogate Head (3 pages)
- ME-6821A Photogate Mounting Bracket (2 pages)
- ME-6825A MINI LAUNCHER (39 pages)
- ME-6810 Time of Flight Accessory (24 pages)
- ME-8574 DISCOVER FRICTION ACCESSORY (4 pages)
- PS-2103A Motion Sensor (4 pages)
- PS-2189 High Resolution Force Sensor (2 pages)
- ME-9448B Super Pulley with Clamp (2 pages)
- ME-6955 1.2 m PAScar Dynamics System (27 pages)
- PS-2104 Force Sensor (2 pages)
- ME-8998 Elastic Bumper Kit (2 pages)
- ME-6843 Spring Cart Launcher (9 pages)
- ME-6950 PAScar with Mass (29 pages)
- PS-2120A Rotary Motion Sensor (9 pages)
- PS-2120A Rotary Motion Sensor (17 pages)
- ME-9821 Centripetal Force Pendulum (18 pages)
- ME-8088 Centripetal Force Apparatus (20 pages)
- ME-8735 Large Rod Stand (2 pages)
- CI-6545 Force Accessory Bracket (3 pages)
- ME-9806 Photogate Brackets (1 page)
- CI-6692 IDS MOUNT ACCESSORY (2 pages)
- ME-6569 RMS_IDS KIT (36 pages)
- ME-6829 Mini Launcher Ballistic Pendulum (18 pages)
- ME-9889 Discover Free Fall System (10 pages)
- SE-7256 Motion Sensor Guard (2 pages)
- ME-8973 Discover Collision Bracket (2 pages)
- AP-8214A Stress_Strain Apparatus (12 pages)
- CI-6691 MINI-ROTATIONAL ACCESSORY (2 pages)
- ME-9833 Physical Pendulum Set (30 pages)
- OS-8473 POLARIZER SET (2 pages)
- PS-2343 USB Camera (2 pages)
- AP-8215A Gravitational Torsion Balance (20 pages)
- OS-8526A X-Y ADJUSTABLE DIODE LASER (2 pages)
- Xplorer-GLX Users’ Guide (152 pages)
- PS-2150 Broad Spectrum Light Sensor (2 pages)
- PS-2164 Quad Pressure Sensor (3 pages)
- PS-2200 Load Cell, 100 N (3 pages)
- PS-2205 Dual Load Cell Amplifier (5 pages)
- PS-2107 Absolute Pressure Sensor (2 pages)
- PS-2102 pH Sensor (3 pages)
- PS-2119 Acceleration Sensor (2 pages)
