Questions c, Optional equipment, Data and calculations c – PASCO ME-9215B Photogate Timer User Manual
Page 22
18
Photogate Timer
012-06379B
®
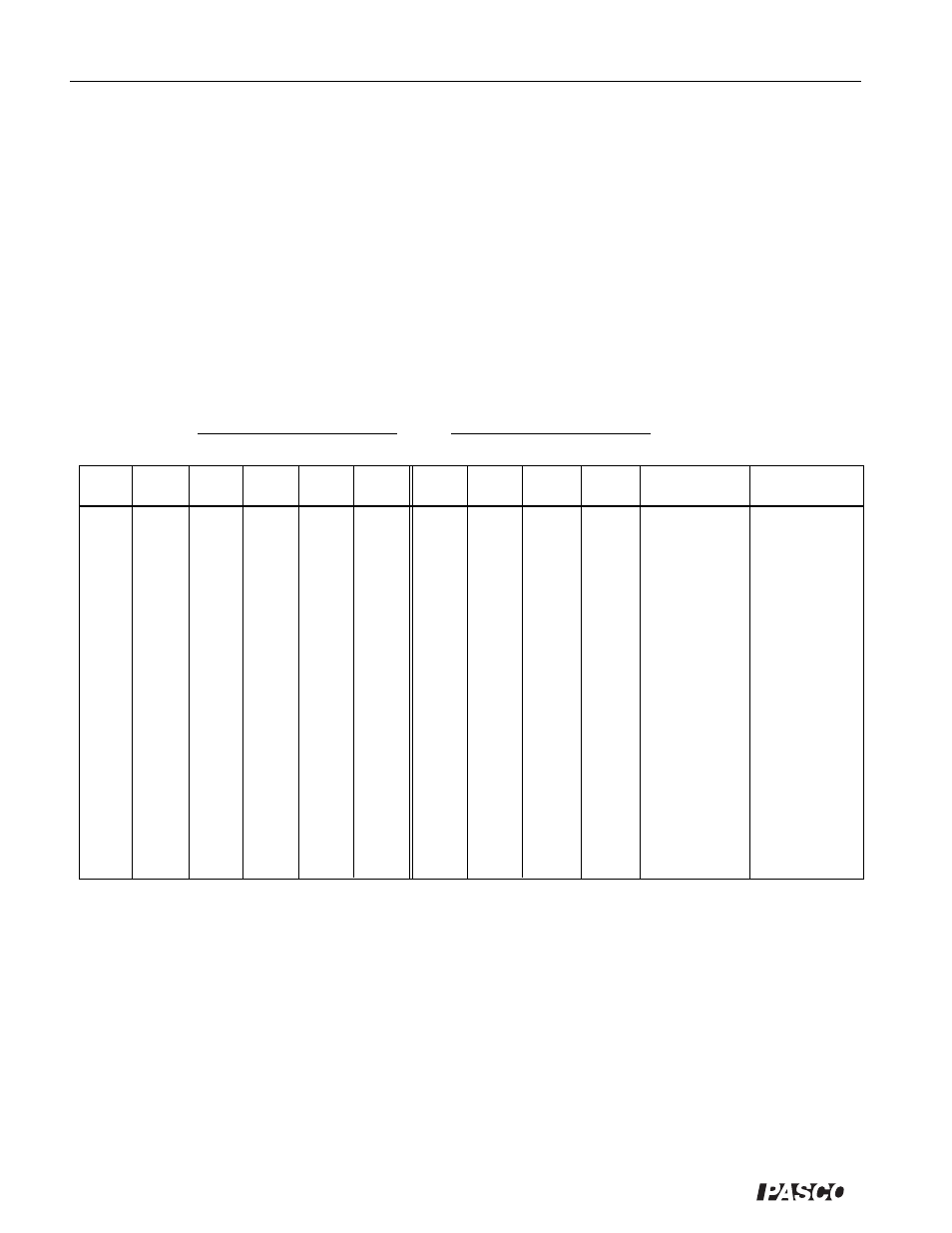
Table 7.1 Data and Calculations
L
1
=
L
2
=
m
1
m
2
t
1i
t
2i
t
1f
t
2f
v
1i
v
2i
v
1f
v
2f
E
ki
E
kf
Questions
c
Was kinetic energy conserved in each of your collisions?
d
If there were one or more collisions in which kinetic energy was not conserved, where
did it go?
Optional Equipment
Design and conduct an experiment to investigate conservation of kinetic energy in an inelastic
collision in which the two gliders, instead of bouncing off each other, stick together so that
they move off with identical final velocities. If you are using a PASCO air track, replace the
bumpers with the wax and needle. Otherwise, velcro fasteners can be used with most gliders.
h
Repeat the experiment several times, varying the mass of one or both gliders and varying the
initial velocity of glider
1
.
i
Try collisions in which the initial velocity of glider
2
is not zero. You may need to practice a bit
to coordinate the gliders so the collision takes place completely between the photogates.
Data and Calculations
c
For each time that you measured, calculate the corresponding glider velocity (e.g., v
1
, = L
1
/t
1i
).
d
Use your measured values to calculate E
ki
and E
kf
, the combined kinetic energy of the gliders
before and after the collision. Record your results in the table.
