Optional, Data and calculations c, Questions c – PASCO ME-9215B Photogate Timer User Manual
Page 10
6
Photogate Timer
012-06379B
®
Optional
You can continue using smaller and smaller distances for D by changing your timing tech-
nique. Tape a piece of cardboard on top of the glider, as shown in Figure 1.2. Raise the pho-
togate so it is the cardboard, not the body of the glider, that interrupts the photogate. Use just
one photogate and place it at x
1
. Set the timer to GATE. Now D is the length of the card-
board. Measure D by passing the glider through the photogate and noting the difference in
glider position between where the LED first comes on, and where it goes off again. Then
start the glider from x
0
as before, and make several measurements of the time it takes for the
glider to pass through the photogate. As before, record your times as t
1
through t
5
. Continue
decreasing the value of D, by using successively smaller pieces of cardboard.
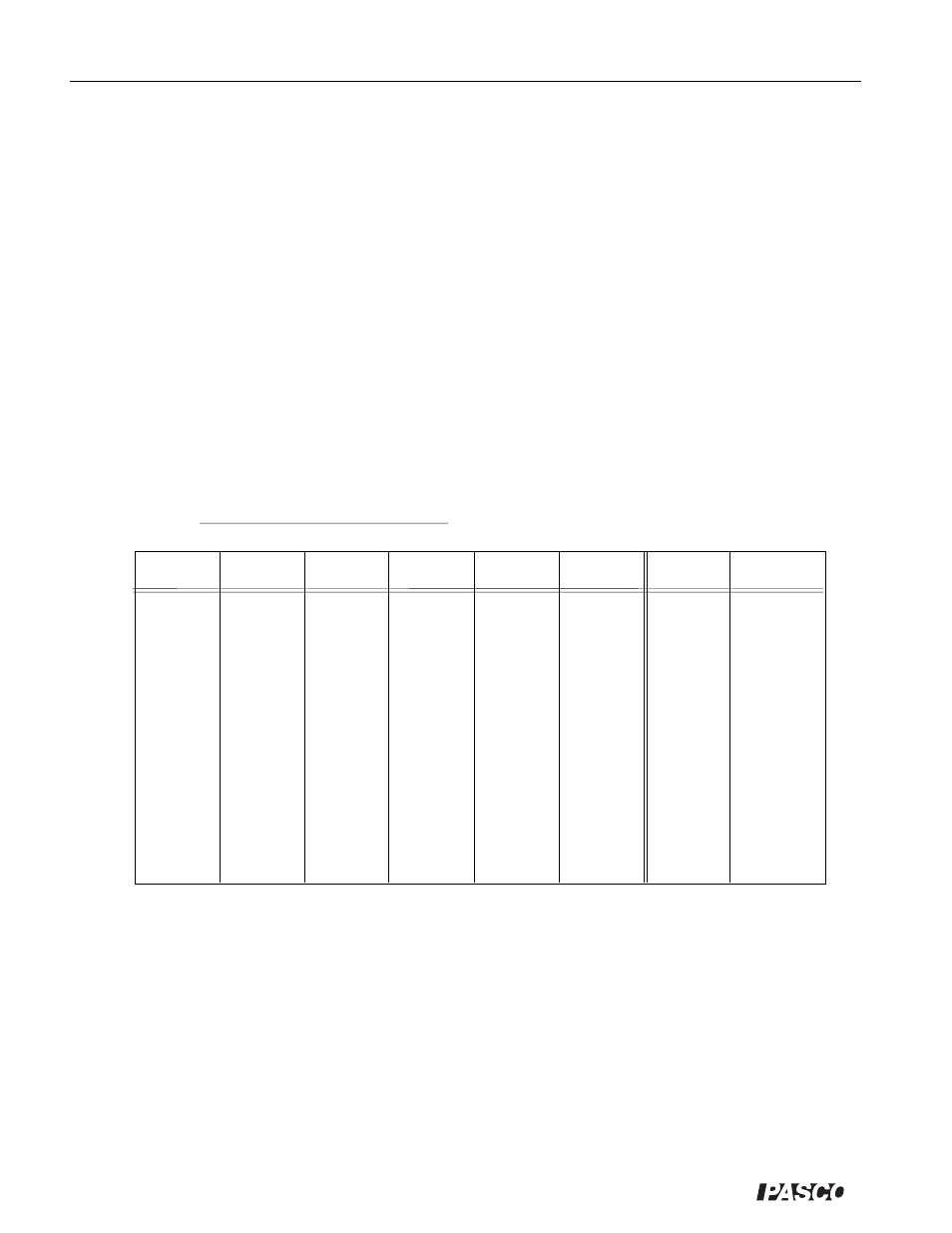
Data and Calculations
c
For each value of D, calculate the average of t
1
through t
5
. Record this value as t
avg
.
d
Calculate v
avg
= D/t
avg
. This is the average velocity of the glider in going between the two
photogates.
e
Plot a graph of v
avg
versus D with D on the x-axis.
x
1
=
D
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
avg
v
avg
Questions
c
Which of the average velocities that you measured do you think gives the closest approximation
to the instantaneous velocity of the glider as it passed through point x
1
?
d
Can you extrapolate your collected data to determine an even closer approximation to the in-
stantaneous velocity of the glider through point x
1
? From your collected data, estimate the
maximum error you expect in your estimated value.
e
In trying to determine an instantaneous velocity, what factors (timer accuracy, object being
timed, type of motion) influence the accuracy of the measurement? Discuss how each factor
influences the result.
f
Can you think of one or more ways to measure instantaneous velocity directly, or is an instanta-
neous velocity always a value that must be inferred from average velocity measurements?
Table 1.1 Data and Calculations
