PASCO CI-6630 BROAD SPECTRUM LIGHT SENSOR User Manual
Broad spectrum light sensor, Instruction sheet for the pasco model ci-6630, Introduction
10
1
100
GAIN
TARE
BR
OAD SPECTR
UM
LIGHT SENSOR
CI-6630
300nm -10,000nm
Instruction Sheet
for the PASCO
Model CI-6630
BROAD SPECTRUM LIGHT SENSOR
012-08541B
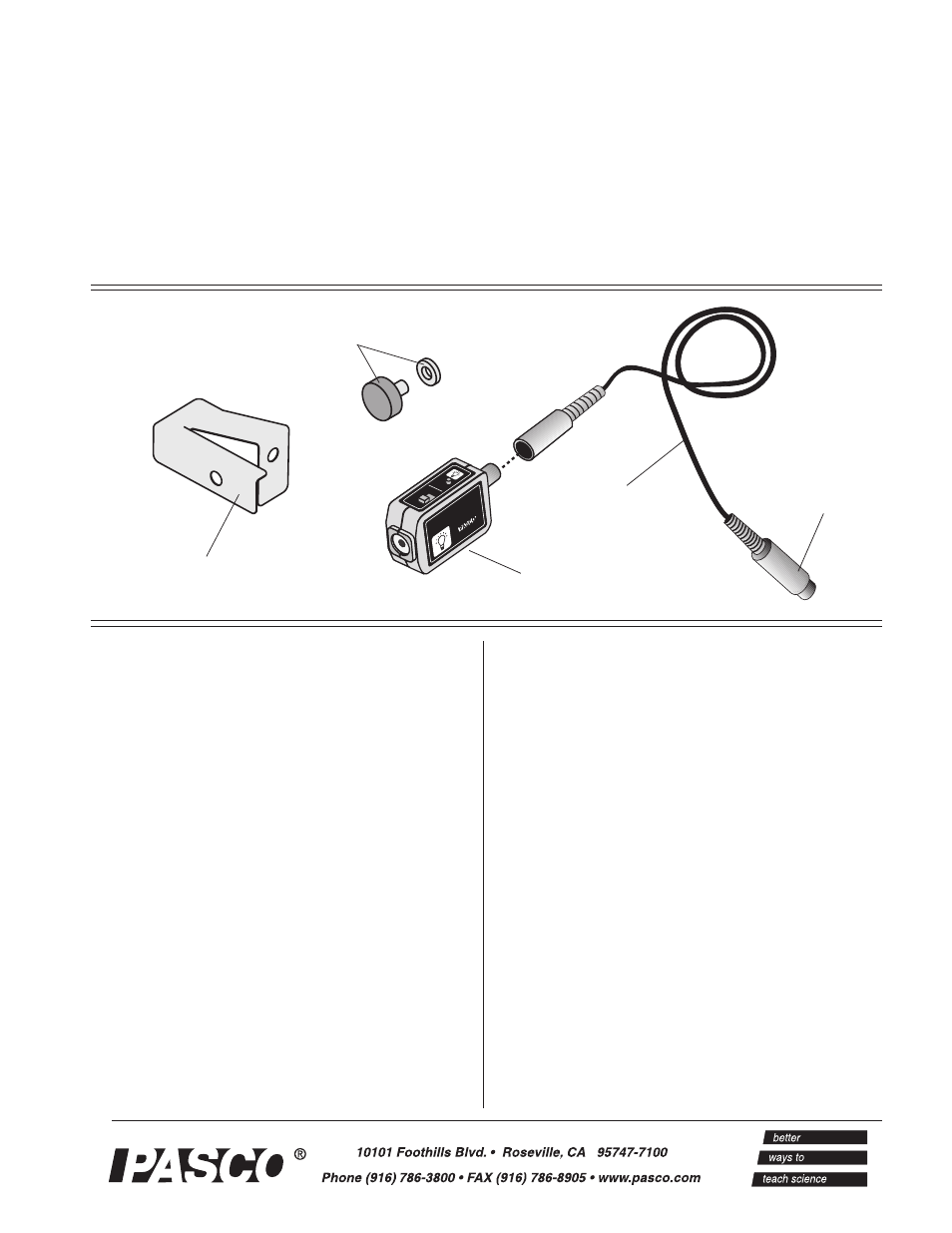
shutter bracket
CI-6630
Light Sensor
to computer
interface
cable with DIN
connectors
thumbscrew
with washer
Introduction
The sensing element of the Broad Spectrum Light
Sensor (CI-6630) uses a thermopile as a detecting
element. Thermopile detectors are voltage-
generating devices that act like a miniature array of
thermocouples. The thermopile is a high output, thin
film, silicon-based device which has 48 thermopile
junctions. The active or “hot” junctions are
blackened to efficiently absorb radiation. The
reference or “cold” junctions are maintained at the
ambient temperature of the detector.
The blackening material used on the “hot” junctions
is capable of absorbing radiant energy from the ultra
violet to the far infrared range. To limit the spectral
sensitivity, optical filters and windows may be placed
in front of the detector. The window installed in the
Broad Spectrum Light Sensor’s detector is BaF
2
,
which has a spectral response from 300 to 10,000
nanometers. The hermetically-sealed detector is heat
treated and filled with argon gas to improve long-term
stability.
The absorption of radiation by the blackened area
causes a temperature rise in the “hot” junctions, as
compared to the “cold” junctions of the thermopile.
This temperature difference across the thermocouple
junction causes the detector to generate a positive
voltage. If the active or “hot” junction cools to a
temperature less than the reference or “cold” junction,
the voltage output becomes negative.
The output of the thermopile detector is presented to a
gain selectable amplifier. The GAIN switch on the top
of the sensor is used to change the signal output (voltage)
of the sensor in experiments where the output signal is too
low, such as in dim light conditions, or when the signal
is too high, such as in bright light conditions.
