Inspections and spare parts, Periodic service, Periodic services – Delta Controls DPR-2000 User Manual
Page 34: Principle of operation
A
32 IOM-DPCDPR-A: FEB 2014
10.2.9. Configuration of the DPR-2200YALW smart level probes
11. INSPECTIONS AND SPARE PARTS.
11.1. Periodic service
Periodic inspections should be made in accordance with the regulations to which the user is subject. During
inspection, the pressure connectors should be checked for loose connections and leaks, the electrical
connectors should be checked with regard to tightness and the state of the gaskets, packing glands, and the
diaphragm seals should be checked for tarnishing and corrosion.
Check the characteristic conversion curve by following the procedures for “Calibration” and, where appropriate,
“Configuration”.
11.2. Periodic services
If the transmitters are installed in a location where they may be exposed to mechanical damage, excess
pressure, hydraulic impulses or excess voltage, or the diaphragm may be in danger from sedimentation,
crystallization or erosion, inspections should be carried out as required.
Where it is found that the signal in the transmission line is absent or its value is incorrect, a check should
be made on the line and its terminal connections.
Check whether the values of the supply voltage and load resistance are correct.
If a communicator is connected to the power supply line of the transmitter, a fault in the line may be
indicated by the message “No response” or “Check connection”.
If the line is in order, check the operation of the transmitter.
i
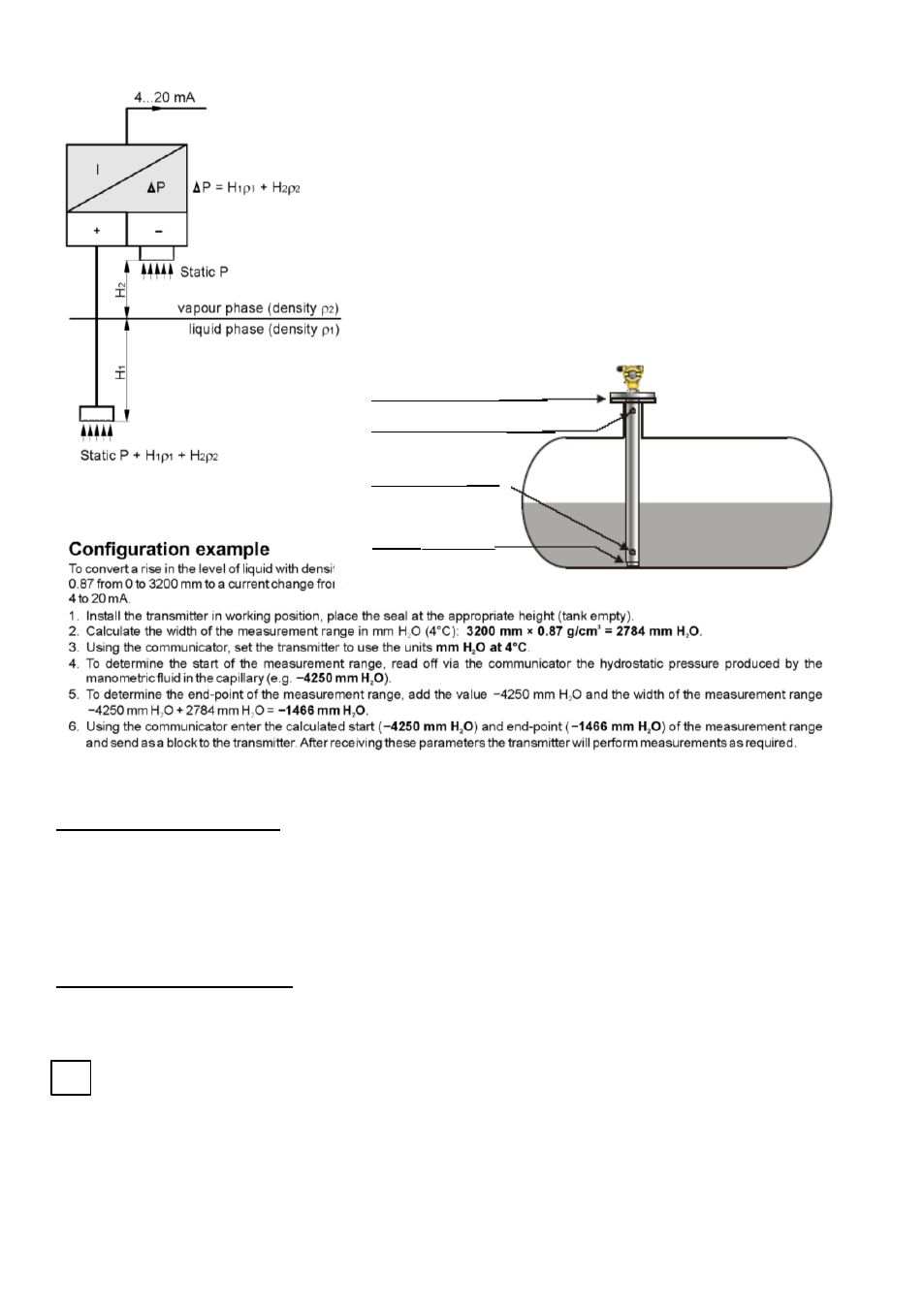
Mechanical installation
On the flange of the tank
Upper equalization hole
Lower
equalization hole
.
Diaphragm
seal unit
Principle of operation
Measurement is carried out using a DPR-2000 differential
pressure transmitter, enabling compensation for static pressure
in the tank. The value processes is just the hydrostatic
pressure of the medium measured at the level of the
diaphragm of the lower seal. This pressure is the sum of the
hydrostatic pressure of the liquid and vapour phases of the
medium. In most practical measurement situations the density
of the vapour phase is negligibly small, and therefore the
measured hydrostatic pressure relates only to the height of the
liquid phase is significant (e.g. propane) the level found by the
method described can be treated as the theoretical level of the
liquid level obtained by adding the actual liquid phase to the
condensed vapour phase.
