Atec Agilent-53132A-53131A-53181A User Manual
Page 9
9
1E + 02
1E + 00
1E – 02
1E – 04
1E – 06
1E – 08
1E – 10
10
100
1000
10000
1E + 05 1E + 06 1E + 07 1E + 08 1E + 09 1E + 10
Input frequency (Hz)
10
100
1000
10000
1E + 05 1E + 06 1E + 07 1E + 08 1E + 09 1E + 10
Input frequency (Hz)
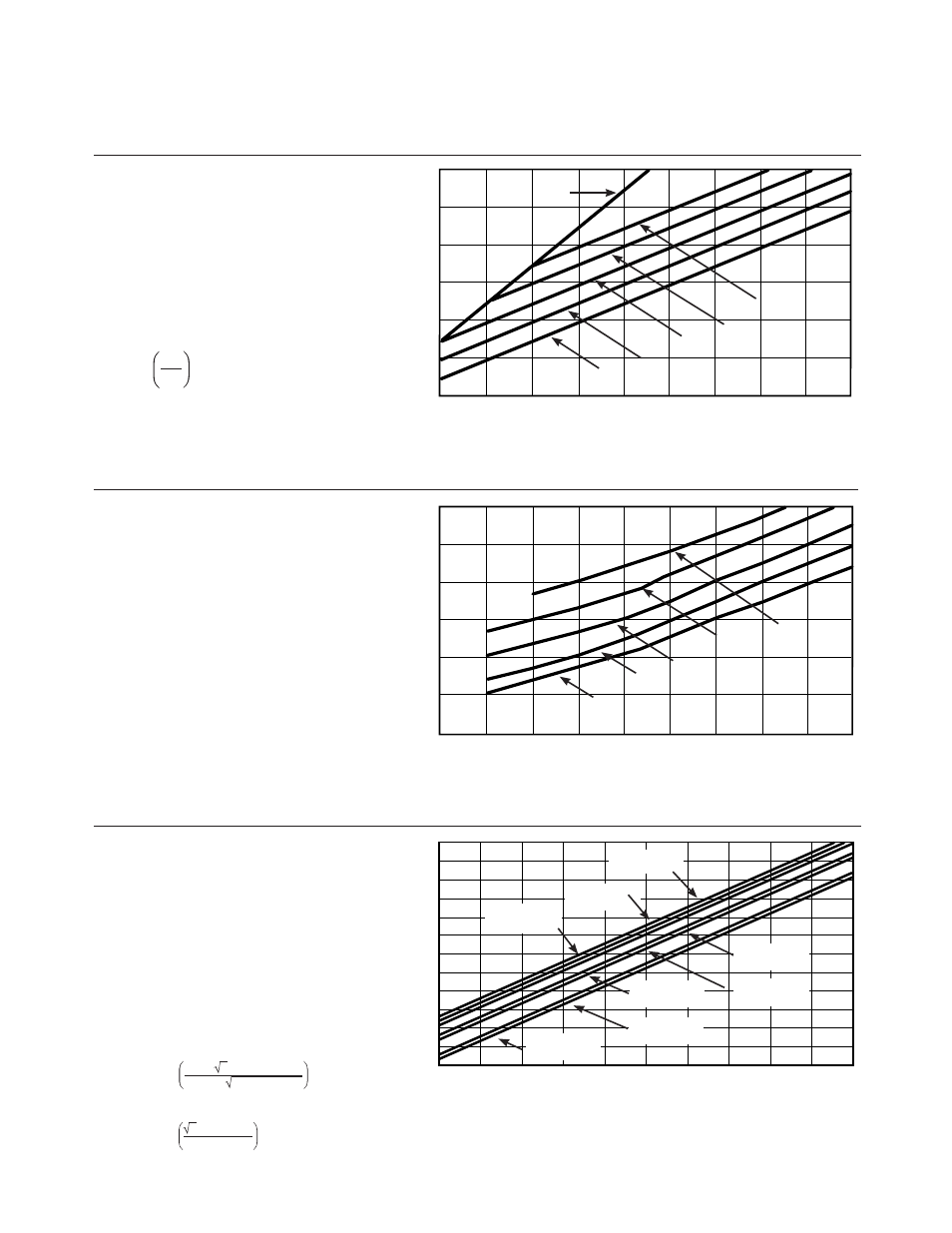
Graph 1:
Agilent 53131A/181A–Worst case
RMS resolution
7
(Automatic or external arming)
The graphs may also be used to compute errors
for period measurements. To find the period
error (DP), calculate the frequency of the input
signal (F = 1/P) and find the frequency error
(DF) from the chart.
Then calculate the period error as:
Graph 2:
Agilent 53131A/181A–Worst case
RMS resolution
7
(Time or digits arming)
Graph 3:
Timebase error
Frequency error (Hz)
Auto armed
1 ms
10 ms
Gate
time
100 ms
1 s
10 s
∆
∆
F
P
×
P
F
=
Time or digit arming
Gate time
Number of samples
4
Ч
2
Ч
Trigger error
×
Frequency
or
period
Frequency error +
×
Automatic or external arming
Gate time
2
×
Trigger error
×
Frequency
or
period
Frequency error +
7. Graphs 1, 2, 4 and 5 do not reflect the effects of
trigger error. To place an upper bound on the added
effect of this error term, determine the frequency
error from the appropriate graph and add a trigger
error term as follows:
E + 02
1E + 00
1E – 02
1E – 04
1E – 06
1E – 08
1E – 10
Frequency error (Hz)
1 ms
10 ms
100 ms
1 s
10 s
1 Hz
10 Hz
100 Hz
1 kHz
10 kHz 100 kHz
1 MHz 10 MHz 100 MHz 1 GHz
1 ns
10 ns
100 ns
1 µs
10 µs
100 µs
1 ms
10 ms
100 ms
1 sec
Input signal frequency or time
10 kHz
1 kHz
100 Hz
10 Hz
1 Hz
100 mHz
10 mHz
1 mHz
100 µHz
10 µHz
1 µHz
100 nHz
10 nHz
10 µs
1 µs
100 ns
10 ns
1 ns
100 ps
10 ps
1 ps
100 fs
10 fs
1 fs
100 as
10 as
Frequency error
Time error
Gate
time
Standard T.B.
1 year after cal
Medium T.B.
1 year after cal
High stability T.B.
10 years after cal
High stability T.B.
1 year after cal
Ultra stability T.B.
1 year after cal
High stability T.B.
1 month after cal
Standard T.B.
1 month after cal
Medium T.B.
1 month after cal
