Tcp service configuration – SENA Parani-MSP1000 User Manual
Page 25
25
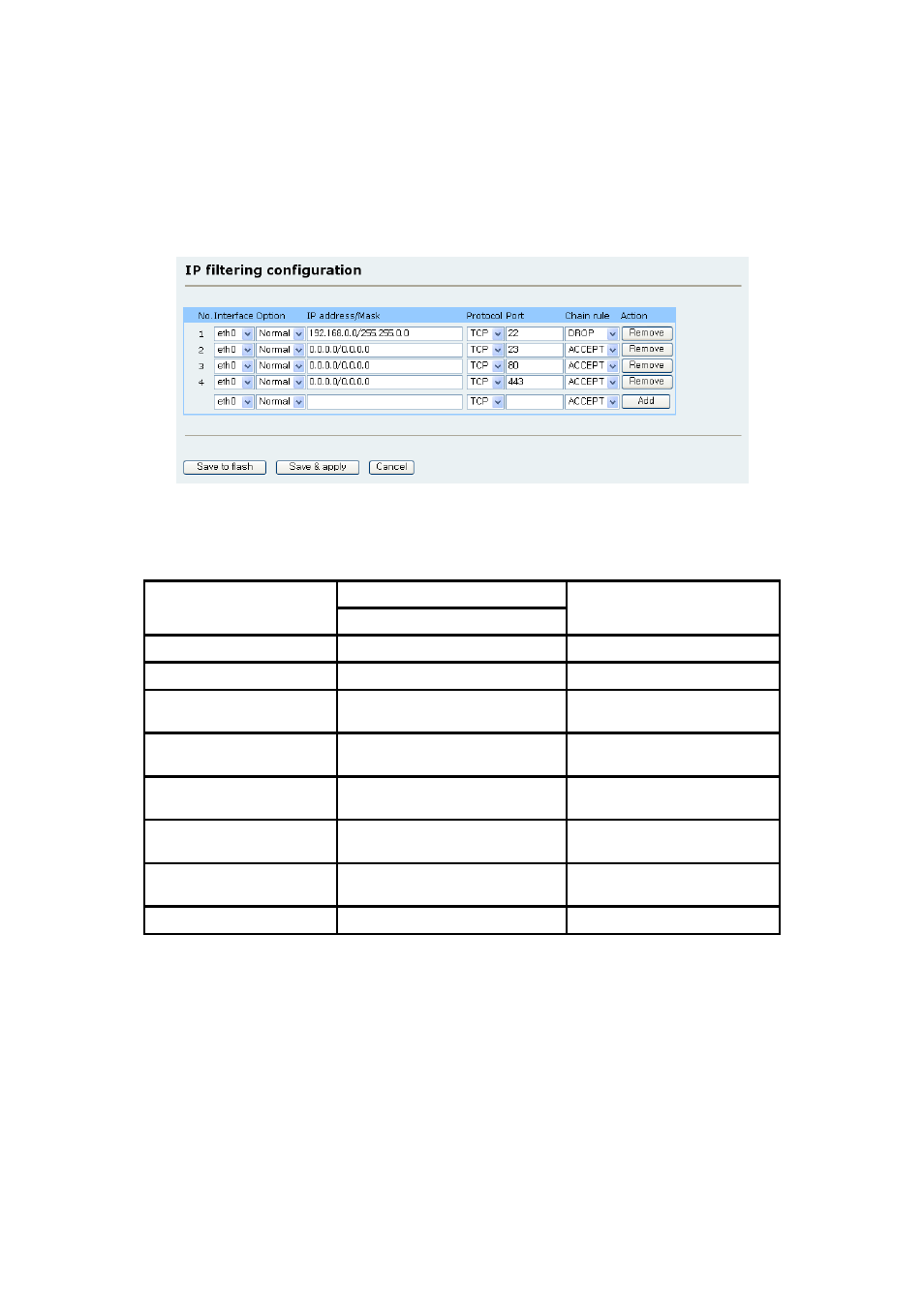
23(Telnet), 22(SSH), 80(HTTP), 443(HTTPS) or each Serial Port Profile session.
Chain rule
Set the basic rule for the host to access the Parani-MSP1000 as one of Accept or Drop.
Figure 3-4 IP filtering Configuration
Table 3-2 Input examples of Option and IP address/mask combination
Input format
Allowable Hosts
IP address/mask
Option
Any host
0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
Normal
192.168.1.120
192.168.1.120/255.255.255.255
Normal
Any host except
192.168.1.120
192.168.1.120/255.255.255.255
Invert
192.168.1.1 ~
192.168.1.254
192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0
Normal
192.168.0.1 ~
192.168.255.254
192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0
Normal
192.168.1.1 ~
192.168.1.126
192.168.1.0/255.255.255.128
Normal
192.168.1.129 ~
192.168.1.254
192.168.1.128/255.255.255.128
Normal
None
0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
Invert
3.5. TCP service Configuration
If a TCP session is established between two hosts, the connection should be closed (normally or
abnormally) by either of the hosts to prevent the lock-up of the corresponding TCP port. To prevent
this type of lock-up situation, the Parani-MSP1000 provides a TCP “keep-alive” feature. The Parani-
MSP1000 will send packets back and forth through the network periodically to confirm that the network
exists. The corresponding TCP session is closed automatically if there’s no response from the remote
host.
