4 a closer look at cobranet – Crown Audio IQ-PIP-USP2_CN User Manual
Page 47
IQ-PIP-USP2/CN
Page 47
IQ-PIP-USP2/CN Reference Manual
10.4 A Closer Look at
CobraNet
CobraNet is a licensed technology
developed by Peak Audio, Inc. con-
sisting of proprietary communica-
tions protocol, firmware and hard-
ware. It allows reliable, determinis-
tic transmission of digital audio over
a 100Base-T Fast-Ethernet network.
This section provides an overview of
CobraNet. Peak Audio has provided
a number of technical papers that
describe CobraNet in detail. These
papers are available at:
http://www.PeakAudio.com/CobraNet/.
10.4.1 Fast Ethernet
(100Base-T)
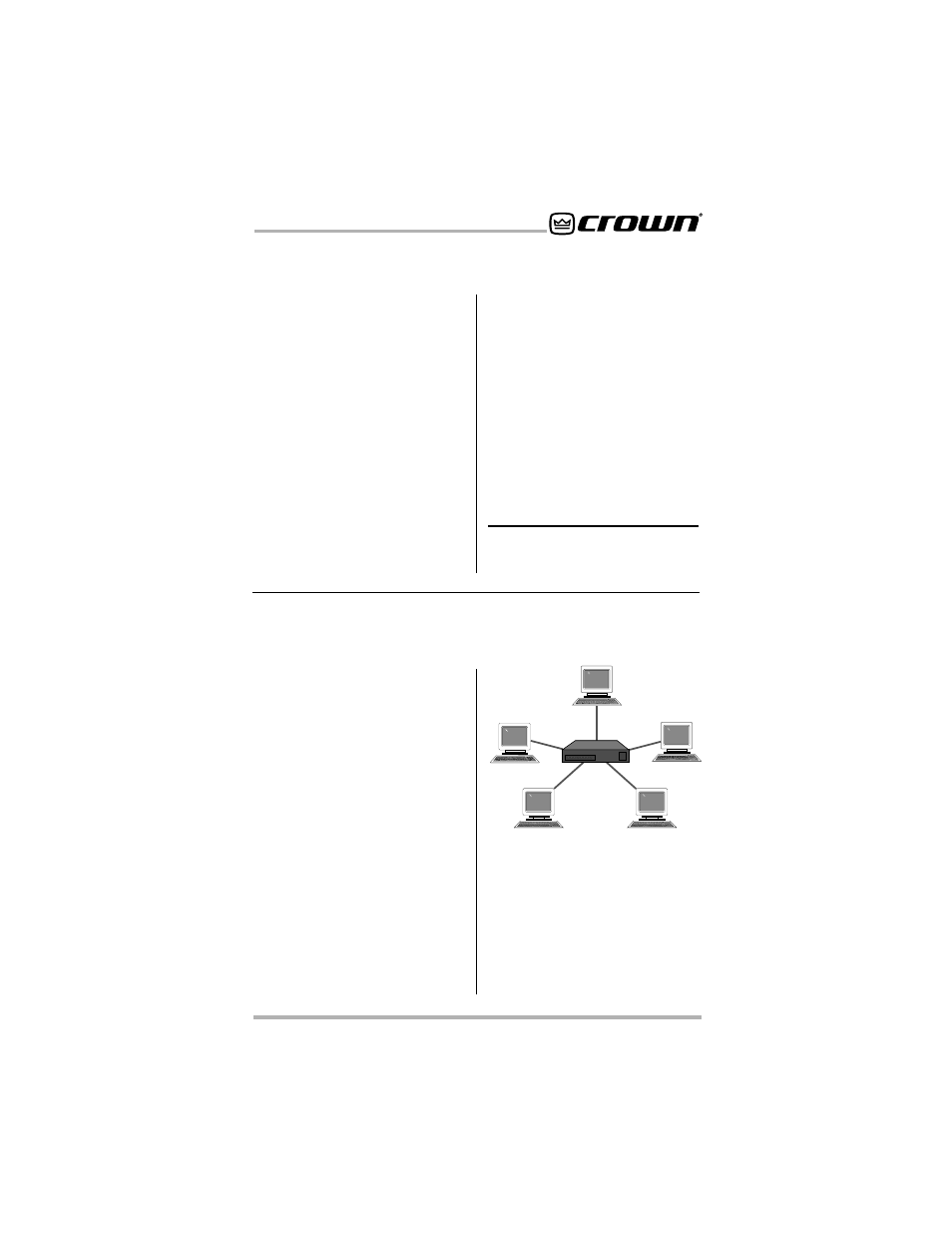
Fast Ethernet (100Base-T) uses a
hub to interconnect all network
nodes to form a star topology (see
Figure 10.10). In the star topology
all PCs are connected to a central-
ized hub. Messages are sent from
the originating PC to the hub, which
then transmits the message either
to the whole network or, if a switched
hub is used, to the destination PC
only. Hubs may be active or
switched.
* Because typical mic cables have high
capacitance, the maximum possible
IQ Bus loop distance will be less.
Lower capacitance allows longer
loops. Unshielded wire usually
has less capacitance.
•
Never use the ground wire in a
mic snake line.
It may
sometimes be convenient to run
IQ Bus data signals to and from
stage monitor amplifiers along
unused wire pairs in a mic snake.
Do not use the ground wire which
is normally connected to pin 1 on
an XLR connector or data noise
will be added to the audio lines.
Use only the signal lines which
normally connect to pins 2 and 3
of the XLRs.*
Outside RF interference is seldom a
problem for a IQ Bus loop—espe-
cially if shielded twisted-pair wire is
used. However, there are extreme
situations when fiber optic wiring is
recommended. For example, locat-
ing a IQ Bus loop next to an AM radio
transmission line may require fiber
optic cabling. An extremely long IQ
Bus loop distance may also require
fiber optic cabling.
Figure 10.10 Star Network Topology
