Internal clock – Rainbow Electronics MAX188 User Manual
Page 13
Internal Clock
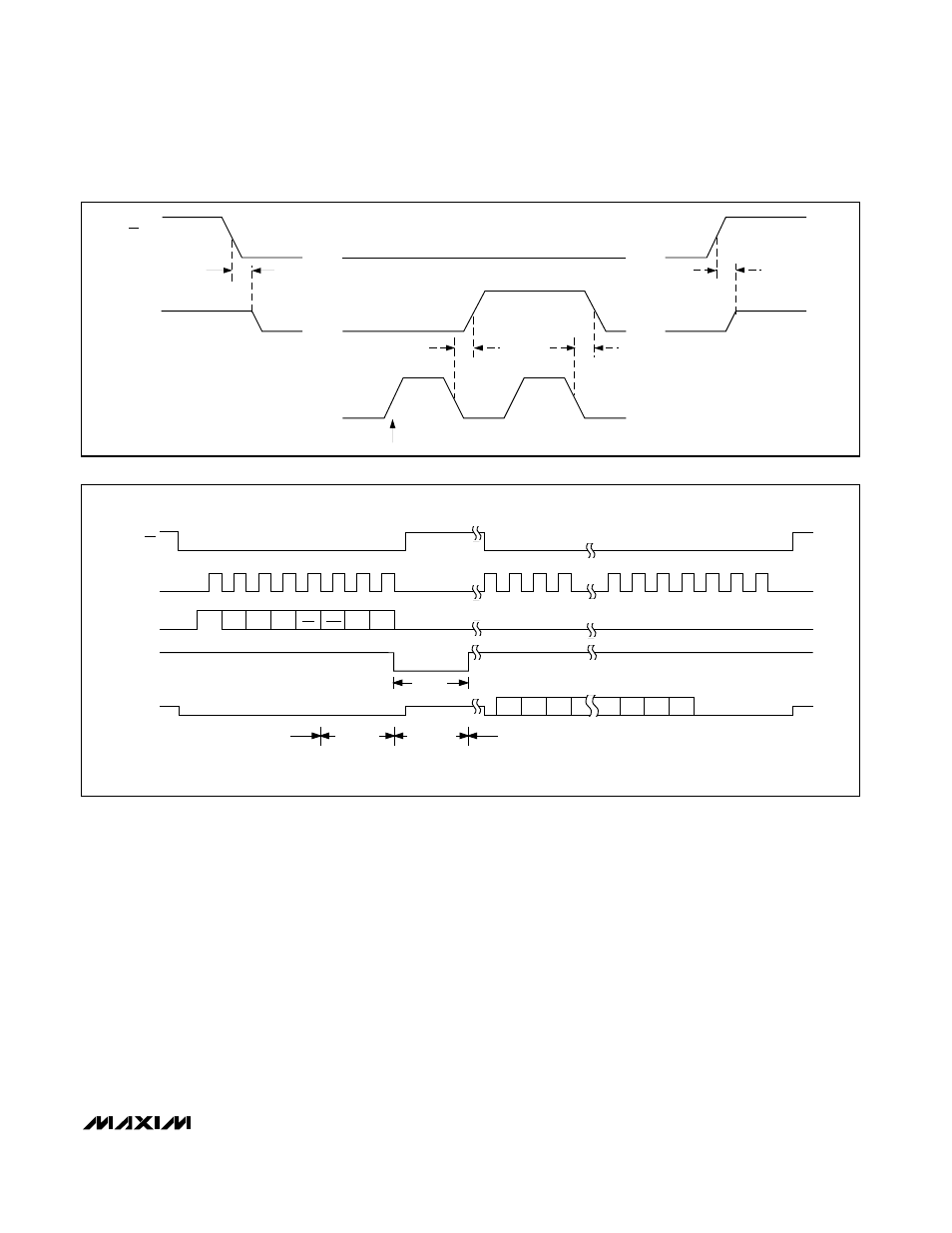
In internal clock mode, the MAX186/MAX188 generate
their own conversion clock internally. This frees the
microprocessor from the burden of running the SAR con-
version clock, and allows the conversion results to be
read back at the processor’s convenience, at any clock
rate from zero to typically 10MHz. SSTRB goes low at the
start of the conversion and then goes high when the con-
version is complete. SSTRB will be low for a maximum of
10µs, during which time SCLK should remain low for best
noise performance. An internal register stores data when
the conversion is in progress. SCLK clocks the data out
at this register at any time after the conversion is com-
plete. After SSTRB goes high, the next falling clock edge
will produce the MSB of the conversion at DOUT, fol-
lowed by the remaining bits in MSB-first format (see
Figure 9).
CS does not need to be held low once a con-
version is started. Pulling
CS high prevents data from
being clocked into the MAX186/MAX188 and three-
states DOUT, but it does not adversely effect an internal
clock-mode conversion already in progress. When inter-
nal clock mode is selected, SSTRB does not go into a
high-impedance state when
CS goes high.
Figure 10 shows the SSTRB timing in internal clock
mode. In internal clock mode, data can be shifted in and
out of the MAX186/MAX188 at clock rates exceeding
4.0MHz, provided that the minimum acquisition time, t
AZ
,
is kept above 1.5µs.
MAX186/MAX188
Low-Power, 8-Channel,
Serial 12-Bit ADCs
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
t
SDV
t
SSTRB
PD0 CLOCKED IN
t
STR
SSTRB
SCLK
CS
t
SSTRB
• • •
• • • •
•
SSTRB
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
1
4
8
12
18
20
24
START SEL2 SEL1 SEL0
UNI/
DIP
SCL/
DIFF PD1 PD0
B11
MSB B10
B9
B2
B1
B0
LSB
ACQUISITION
1.5µs (CLK = 2MHz)
IDLE
FILLED WITH
ZEROS
IDLE
CONVERSION
10µs MAX
A/D STATE
2
3
5
6
7
9
10
11
19
21
22
23
t
CONV
Figure 8. External Clock Mode SSTRB Detailed Timing
Figure 9. Internal Clock Mode Timing
