3 sl series pump operating parameters, 2 rotary lobe pump principle – Viking SLAL User Manual
Page 5
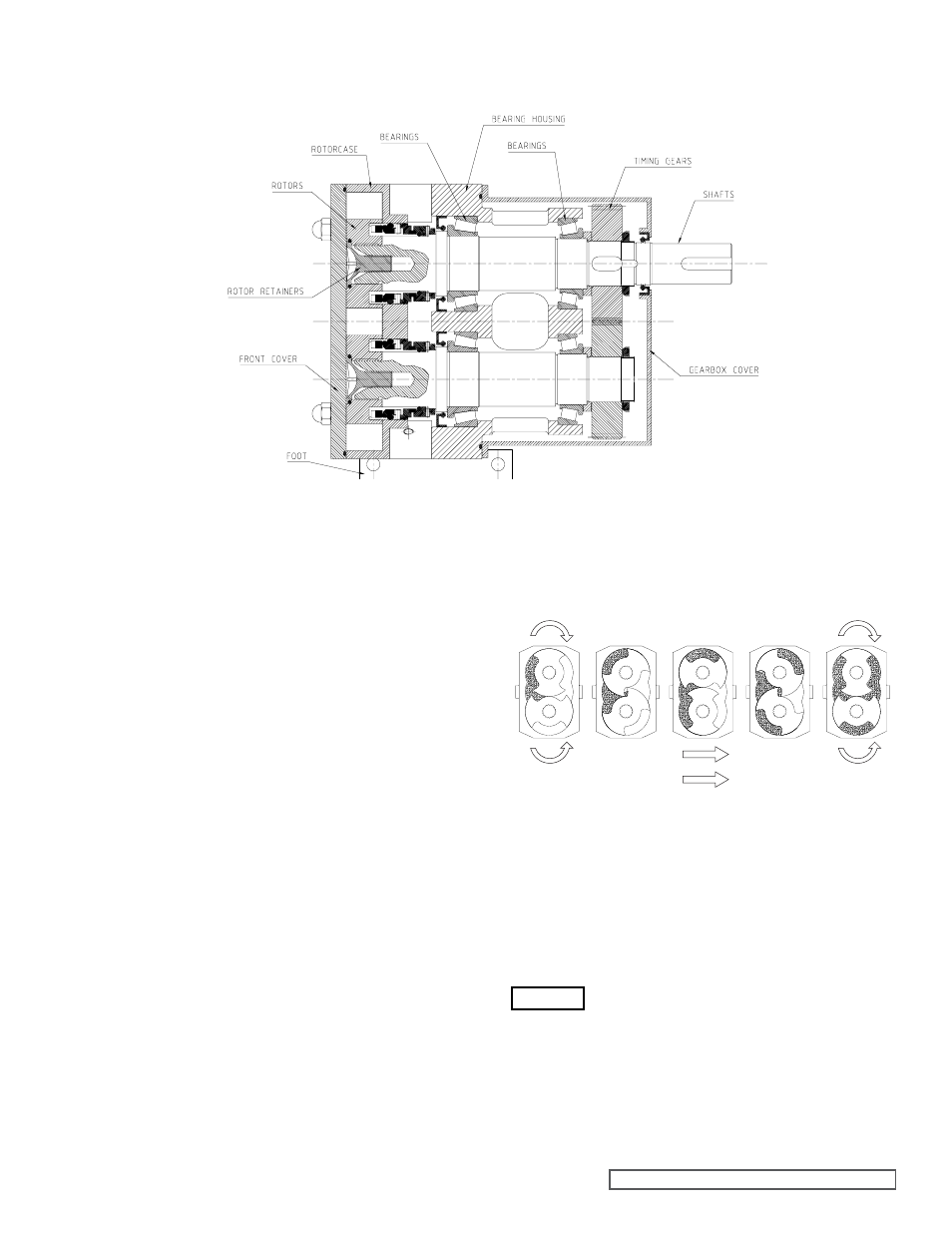
fIGURE 5
fIGURE 6
6a
6b
6c
6d
6e
flOW
SECTION TSM 288
ISSUE
A
PAGE 5 OF 36
3.3 sl sERIEs PUMP OPERaTING
PaRaMETERs
The maximum pressure and speed operating parameters are
given in Figure 7, page 6. In practice these may be limited due
to the nature of the product to be pumped and/or design of the
system in which the pump is to be installed. Consult Viking
Pump or your distributor for assistance.
If the system or product characteristics are to be changed
from the original application for which the pump was
selected, Viking Pump or their authorized distributor should
be consulted to ensure the pump is suitable for the new
application.
The pump should not be subjected to sudden temperature
changes to avoid the risk of damage from sudden
expansion/contraction of components. Care should be
taken when selecting pumps for handling liquids containing
abrasive particles as these may cause wear of pump head
components. For advice or assistance contact your Viking
Pump distributor.
2.8 sTaNdaRd PUMP
COMPONENT TERMs
3.0 GENERal
3.1 sl sERIEs PUMPING
PRINCIPlE
The pumping action of the rotary lobe pump principle is
generated by the contra-rotation of two pumping elements
(rotors) within a chamber (casing) see Figure 6.
The rotors are located on shafts that in turn are held within a
bearing housing mounted to the back of the casing. The shaft
assemblies comprise of, the shaft support bearings and the
timing gears. The gears transfer the energy from the drive
shaft to the driven shaft, synchronizing the rotors such that
they rotate without contact with each other.
As the rotors pass the suction port, Figure 6a, the cavity
increases creating a pressure decrease, which induces the
pumped medium to flow into the casing.
The pumped medium is carried around the casing by the
rotors, Figure 6b and 6c, to the discharge side of the pump,
Figure 6d. Here the cavity decreases and the pumped medium
is discharged from the casing, Figure 6e.
For pump component terms see Figure 5.
3.2 ROTaRY lObE PUMP
PRINCIPlE
WaRNING
