Rapid spanning tree protocol – NetComm IP DSLAM NCT480 User Manual
Page 87
YML856 Rev3
NCT480 IP DSLAM User Guide
NCT480 IP DSLAM User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au
8
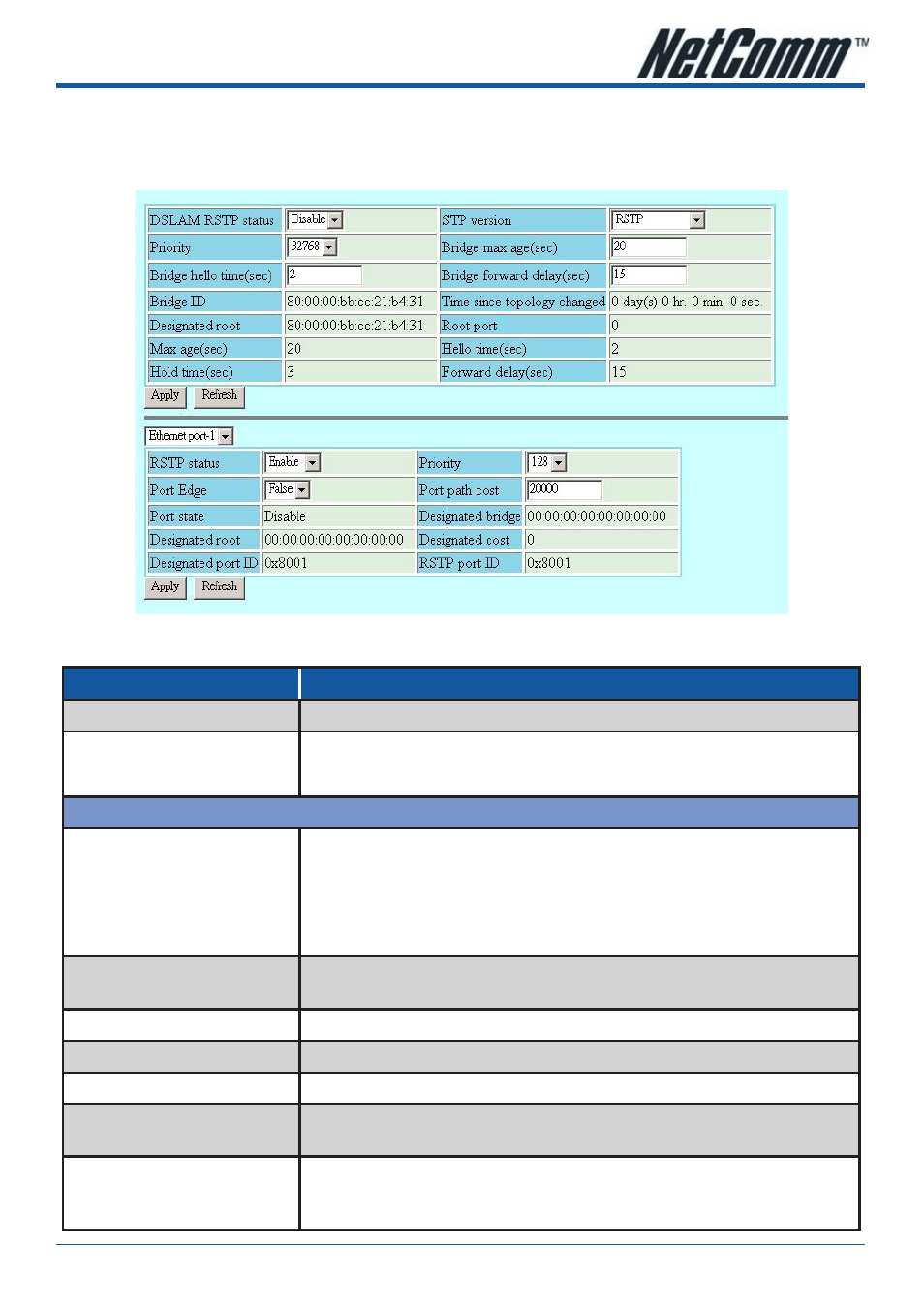
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an evolution of the Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1D standard) and
provides for faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change.
Figure 6-8 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Setting Dialog
Item
Description
DSLAM STP status
Spanning Tree Protocol to be enabled on the Bridge or not.
ethernet Port STP status
This specifies the STP status of Gigabit Ethernet interface.
Press the ‘Apply’ button to confirm the setting.
Set Spanning Tree Protocol Status
STP Priority
This value can determine if the IP-DSLAM will be root switch among all known
switches. The switch with the highest priority (lowest numeric value) becomes the
Spanning Tree root switch. MAC address (the lowest numeric value) is used to decide
root switch if priority is the same.
Valid values: 0 ~ 61440 in steps of 4096
Time Since Top Changed
The time elapsed since the root node of the Spanning Tree has changed. The change of
the root node will cause the Spanning Tree to reconfigure.
Top Changed
The count which the root node has changed in the existing Spanning Tree.
Designated Root
The root of current Spanning Tree indicating by its MAC address.
Root Cost
The cost configured in the DSLAM contributing to the path cost leading to the root
Root Port
The port number of the port which offers the lowest cost path from this bridge to the
root bridge.
Max Age
The maximum age of Spanning Tree Protocol information learned from the network on
any port before it is discarded, in units of seconds, when this bridge is the root of the
spanning tree.
