6 nat/dmz – NetComm G.SHDSL 4-port Security Modem Routers NB712 User Manual
Page 45
NB712 / NB714 User Guide
45
YML829 Rev1
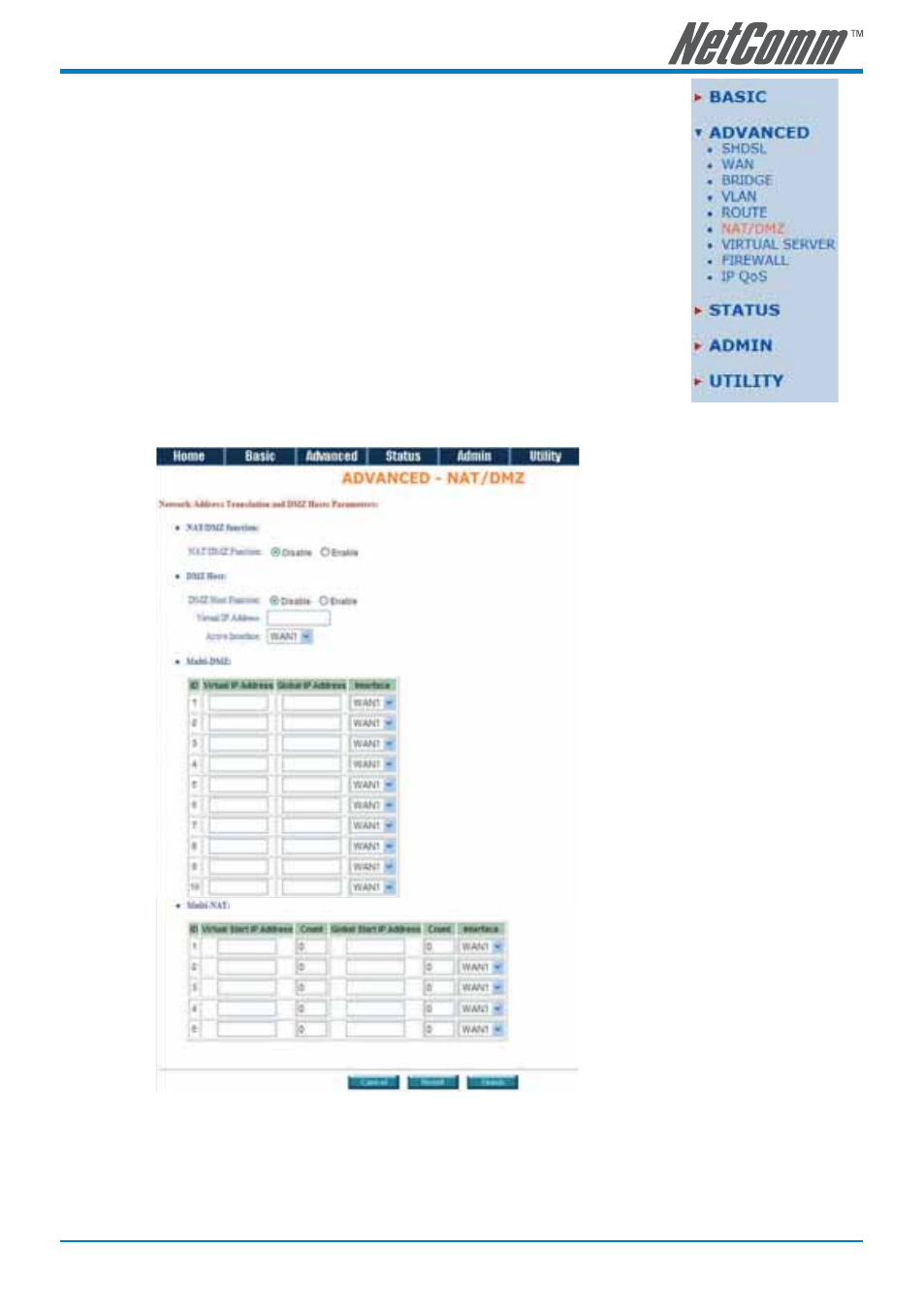
8.6 NAT/DMZ
NAT (Network Address Translation) is the translation of an Internet Protocol address
(IP address) used within one network to a different IP address known within another
network. One network is designated as the inside network and the other is the
outside. Typically, a company maps its local inside network addresses to one or more
global outside IP address and changes the global IP addresses of incoming packets
back into local IP addresses. This ensures security since each outgoing or incoming
request must go through a translation process that also offers the opportunity
to qualify or authenticate the request or match it to a previous request. NAT also
conserves the number of global IP addresses that a company needs and lets the
company use a single IP address for its communication in the Internet world.
DMZ (demilitarized zone) is a computer host or small network inserted as a “neutral
zone” between a company private network and the outside public network. It prevents
outside users from getting direct access to a server that has company private data.
In a typical DMZ configuration for an enterprise, a separate computer or host receives requests from users within
the private network to access Web sites or other companies accessible on the public network. The DMZ host then
initiates sessions for these requests to the public network. However, the DMZ host is not able to initiate a session
back into the private network. It can only forward packets that have already been requested.
