GarrettCom DS8016 User Manual
Page 31
Magnum DS8016 Dual-Speed Stackable Hubs Installation and User Guide (07/06)
23
www GarrettCom com
.
.
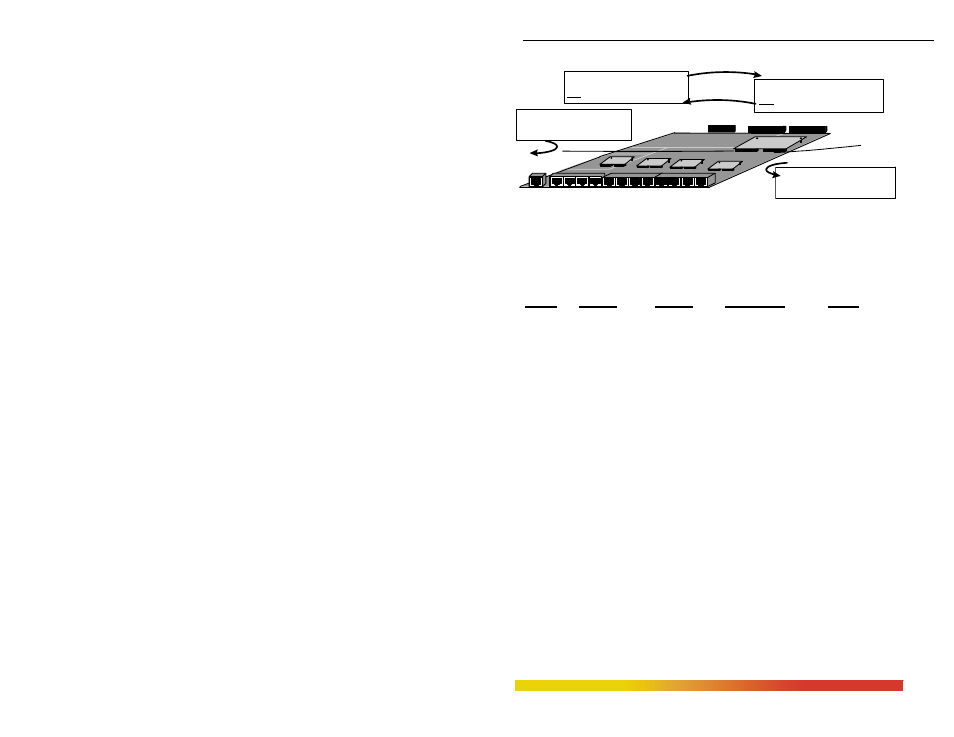
Bridge
Module
10 BUS
100
10 Mbps Domain
100 Mbps Traffic
10Mb Domain : 10Mbps packets
forwarded when the destination addresse
NOT
are
is
in the 10Mb domain address table.
100Mbps Domain :
100Mbps packets are
forwarded when the destination address is
NOT in the 100Mb domain address table.
10Mbps Domain :
10Mbps packets are
filtered when the destination address is
in the 10Mbps domain address table.
100Mbps Domain :
100Mbps packets are
filtered when the destination address is
in the 100Mbps domain address table.
10 Mbps Traffic
100 Mbps Domain
Fig 4.1 Filtering vs Forwarding in Domain Switched Hubs with an internal
Bridge or Switch
1.
Filter / Forward logic for both 10Mb and 100Mb domains
Packet
Source
Destination
Address Table
Filter/Forward
Source Address Address Maintenance Action
10 Mb
Not in table
Not in table
Add source to table
Forward
10 Mb
Not in table
In table
Add source to table
Filter
10 Mb
In table
Not in table
None
Forward
10 Mb
In table
In table
None
Filter
100 Mb
Not in table
Not in table
Add source to table
Forward
100 Mb
Not in table
In table
Add source to table
Filter
100 Mb
In table
Not in table
None
Forward
100 Mb
In table
In table
None
Filter
Table 4.1: DS8016-B Domain-Switched Hub Functionality
2.
Address Learning (Address Table Maintenance)
The Magnum DS8016-B bridge module is a state machine design which has a
total address table capacity of 8K addresses. With a large address table, a Magnum DS8016
can serve the needs of a medium-sized to large network. Table 4.1 shows what filter /
forward action the Magnum DS8016-B will take in each packet-processing situation, and
when a new node address will be added to the internal Address Table. When a new node-
address packet comes into a port for the first time, then the new source address is “learned”
at the same time that the packet is forwarded. After learning, subsequent packets from the
same node address are routinely processed. The address tables are flushed periodically to
update the network status and to purge any inactive stations from the tables of both domains.
3. Throughput Increase
