Guardian Technologies 4758 User Manual
Page 73
SECTION 4.1
DESCRIPTION AND COMPONENTS
PART 4
Page 4.1-1
3DC CONTROL
GENERAL
This section will familiarize the reader with the various
components that make up the DC control system.
Major DC control system components that will be
covered include the following:
❏ A Terminal Strip / Interconnection Terminal
❏ A Transformer (TX)
❏ A Circuit Board.
❏ An AUTO-OFF-MANUAL Switch.
❏ A 15 Amp Fuse.
❏ A 5 Amp Fuse.
TERMINAL STRIP / INTERCONNECTION
TERMINAL
The terminals of this terminal strip are connected to
identically numbered terminals on a prepackaged
transfer switch terminal board. The terminal board
connects the transfer switch to the circuit board and
transformer.
The terminal board provides the following connection
points:
A. Utility 1 and Utility 2
1. Connect to identically marked terminals on a
prepackaged transfer switch terminal board.
2. The circuit delivers "Utility" power source
voltage to the transformer (TX) located in the
control panel assembly.
B. 23 and 194
1. Connect to identically numbered terminals on
the terminal board of the prepackaged transfer
switch.
2. This circuit connects the circuit board to the
transfer relay coil in the prepackaged transfer
switch.
Figure 1. Terminal Board
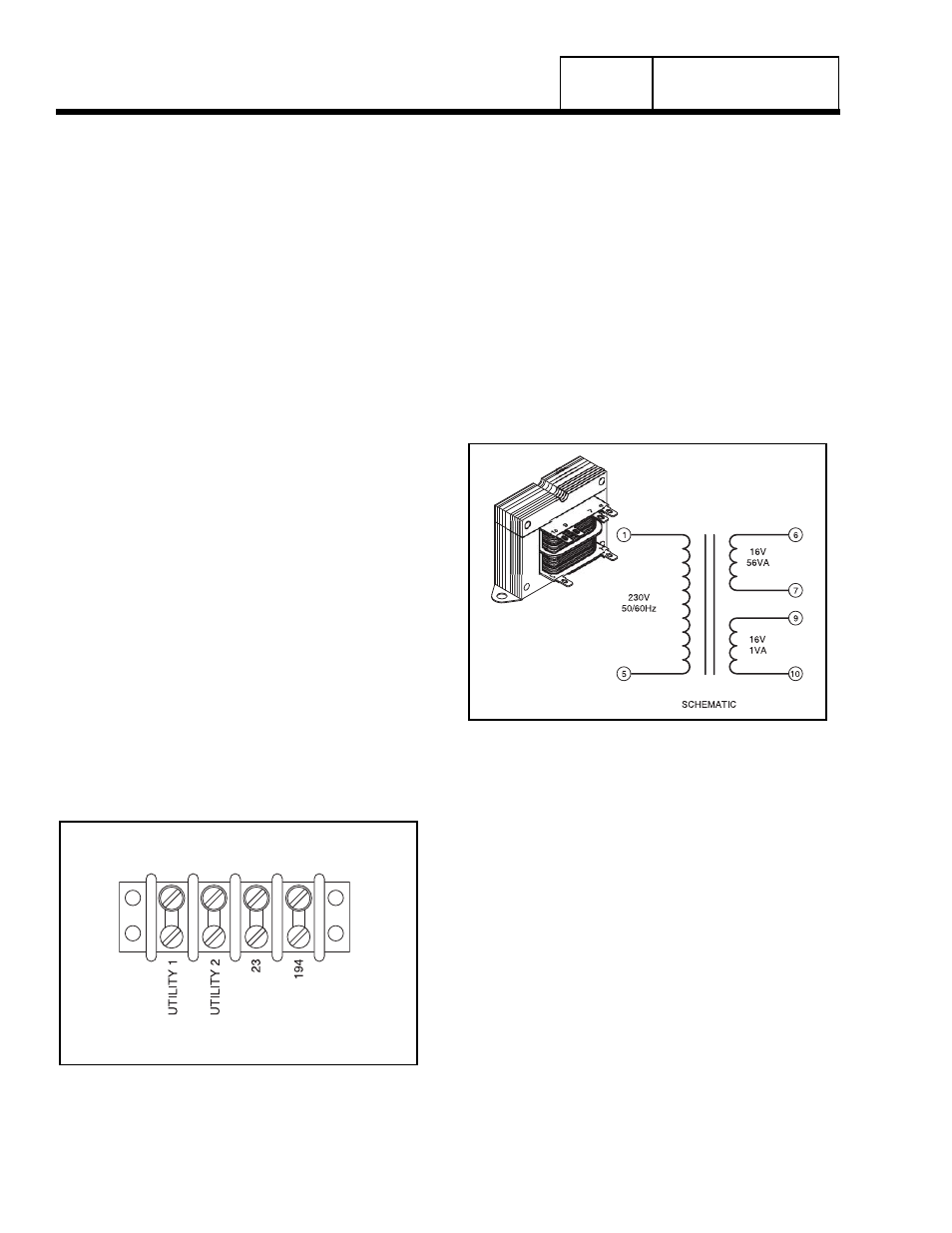
TRANSFORMER (TX)
The control panel assembly’s transformer is a step-
down type. The line-to-line voltage from the Utility
1/Utility 2 terminals is delivered to the transformer’s
primary winding. Transformer action then induces a
reduced voltage (about 12 to 16 volts) into both
secondary transformer windings. Reduced voltage
from one secondary winding is delivered to the circuit
board as "Utility" source sensing voltage. Reduced
voltage from the other secondary winding is delivered
to the battery charger for trickle charging.
If the Utility sensing voltage drops below a preset
value, circuit board action will initiate automatic
generator startup and transfer to the "Standby"
source side.
The sensing transformer is shown in Figure 2, both
pictorially and schematically.
Figure 2. The Transformer
CIRCUIT BOARD
The circuit board controls all standby electric system
operations including (a) engine startup, (b) engine
running, (c) automatic transfer, (d) automatic
retransfer, and (e) engine shutdown. In addition, the
circuit board performs the following functions:
❏ Delivers "field boost" current to the generator rotor
windings (see "Field Boost Circuit" on Page 2.2-1).
❏ Starts and "exercises" the generator once every
seven days.
❏ Provides automatic engine shutdown in the event of
low oil pressure, high oil temperature, or overspeed.
A 17-pin and a 5-pin connector are used to
interconnect the circuit board with the various circuits
of the DC systems. Connector pin numbers,
associated wires and circuit functions are listed in the
CHART on the next page.
