GE GFK-1852 User Manual
Page 56
GFK-1852
Chapter 6 Serial Line Interfaces
6-9
Serial Line Interfaces
6
Using the VMSE on an RS-422/485 Multidrop Network
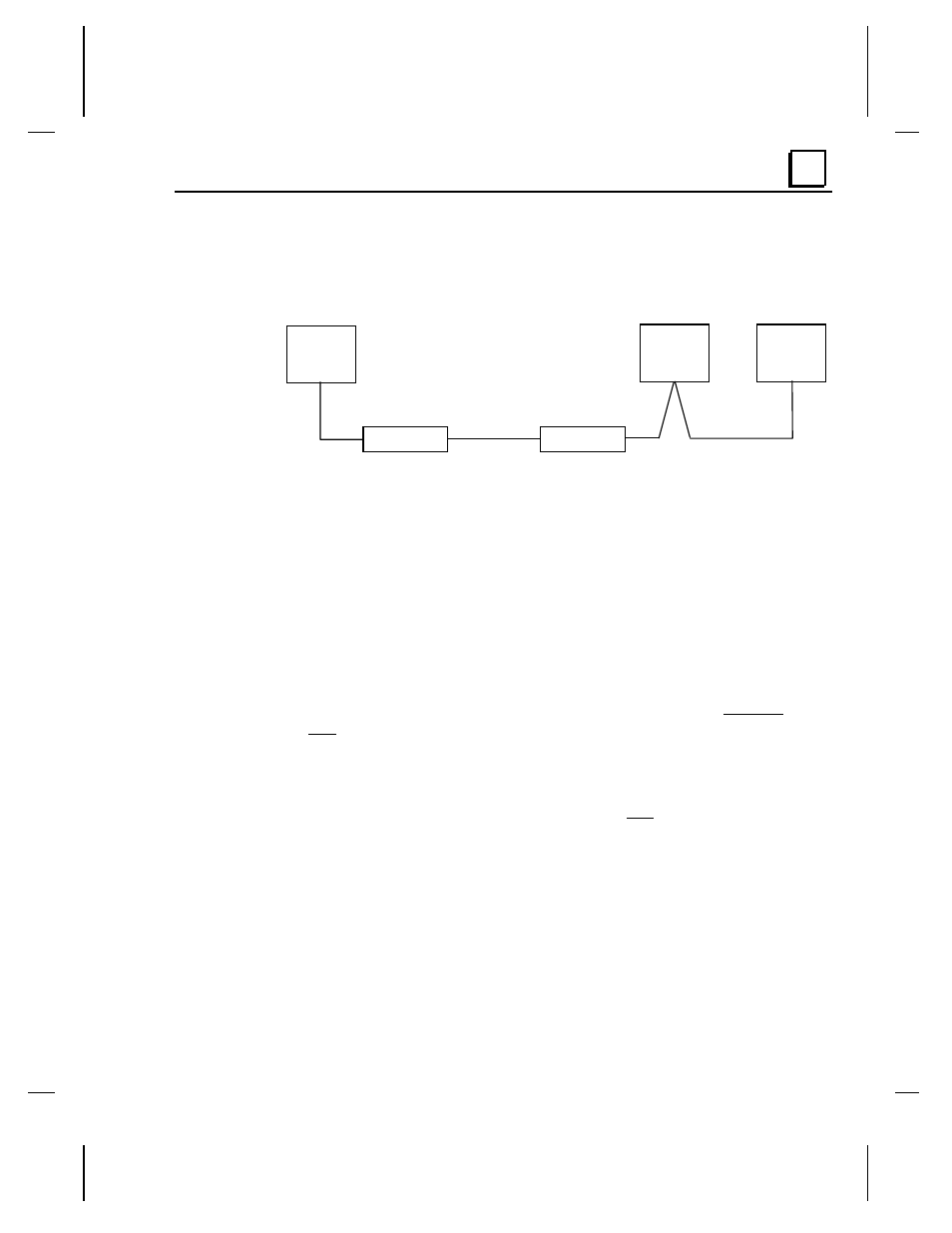
The following figure shows an acceptable configuration for a multidrop network.
This example shows only two slave devices; if additional slaves were added,
termination would be required at the last slave device instead of at Slave #2.
Master
Slave #1
Slave #2
VMSE #1
Switch=**
Termination is required across RD or RX terminals at these locations if the serial line is
greater than 6 feet (2 meters) long
Serial
Serial
Line 2
VMSE #2
Switch=RS-422
Ethernet Cable
VMSE #1 must be set to the configuration (RS-232 or RS-422) that matches the Master
Figure 6-14. Using the VMSE in a Multidrop Arrangement
Multidrop Application Notes
•
Any serial line longer than 6 feet (2 meters) must have a termination resistor
across its receive terminals (RD or RX) at the end of each receive line.
•
The serial port on the VMSE #2 screw terminals must be used since it is the only
VMSE port that supports RS-422. The VMSE’s RJ-45 Serial port cannot be
used since it is an RS-232 port only, and RS-232 does not support multidrop.
•
The switch on the front of the VMSE #2 must be set to RS-422 position to
enable RS-422 on the VMSE screw terminals. Also, the “Interface Type”
configuration parameter must be set to RS-422 (no other setting is acceptable).
•
Serial Line 1 may be RS-232 or RS-422 as long as both Master and VMSE #1
are configured accordingly.
•
For Serial Line 2, which must be an RS-422 line, match the specifications and
basic wiring scheme for User-Built Cable #4. All multidrop connections must
be made at the nodes inside the connectors (thus, each connector terminal would
have two wires attached), in a parallel “daisy-chain” style. No line stubs or
intermediate terminal blocks are permitted.
•
Each serial cable’s shield must be grounded at one end of the cable only.
•
The VMSE can be the only device connected to the master on Serial Line 1
shown in Figure 6-14 above.
