Recommended pcb routing, Supply bypassing, layout, and grounding – Rainbow Electronics MAX98088 User Manual
Page 120
Stereo Audio Codec
with FLEXSOUND Technology
MAX98088
120
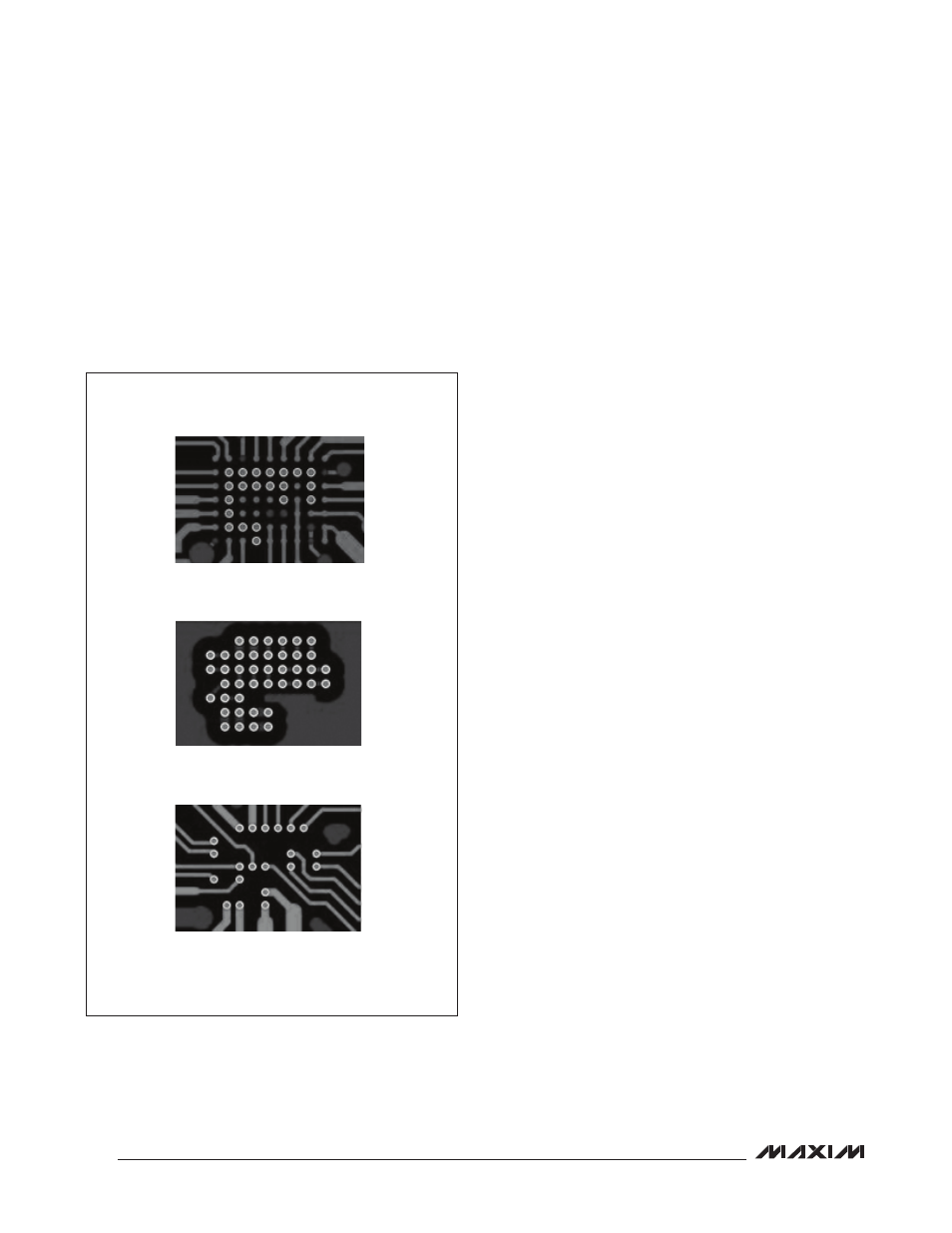
Recommended PCB Routing
The IC uses a 63-bump WLP package. Figure 42
provides an example of how to connect to all active
bumps using 3 layers of the PCB. To ensure uninter-
rupted ground returns, use layer 2 as a connecting layer
between layer 1 and layer 2 and flood the remaining area
with ground.
Supply Bypassing, Layout, and Grounding
Proper layout and grounding are essential for optimum
performance. When designing a PCB for the ICs, parti-
tion the circuitry so that the analog sections of the IC are
separated from the digital sections. This ensures that the
analog audio traces are not routed near digital traces.
Use a large continuous ground plane on a dedicated
layer of the PCB to minimize loop areas. Connect AGND,
DGND, HPGND, SPKLGND, and SPKRGND directly to
the ground plane using the shortest trace length pos-
sible. Proper grounding improves audio performance,
minimizes crosstalk between channels, and prevents any
digital noise from coupling into the analog audio signals.
Ground the bypass capacitors on MICBIAS, REG, PREG,
and REF directly to the ground plane with minimum
trace length. Also be sure to minimize the path length to
AGND. Bypass AVDD directly to AGND.
Connect all digital I/O termination to the ground plane
with minimum path length to DGND. Bypass DVDD,
DVDDS1, and DVDDS2 directly to DGND.
Place the capacitor between C1P and C1N as close as
possible to the ICs to minimize trace length from C1P to
C1N. Inductance and resistance added between C1P
and C1N reduce the output power of the headphone
amplifier. Bypass HPVSS with a capacitor located close
to HPVSS with a short trace length to HPGND. Close
decoupling of HPVSS minimizes supply ripple and maxi-
mizes output power from the headphone amplifier.
HPSNS senses ground noise on the headphone jack and
adds the same noise to the output audio signal, thereby
making the output (headphone output minus ground)
noise free. Connect HPSNS to the headphone jack shield
to ensure accurate pickup of headphone ground noise.
Bypass SPKLVDD and SPKRVDD to SPKLGND and
SPKRGND, respectively, with as little trace length as
possible. Connect SPKLP, SPKLN, SPKRP, and SPKRN
to the stereo speakers using the shortest traces pos-
sible. Reducing trace length minimizes radiated EMI.
Route SPKLP/SPKLN and SPKRP/SPKRN as differential
pairs on the PCB to minimize loop area, thereby the
inductance of the circuit. If filter components are used
on the speaker outputs, be sure to locate them as close
as possible to the IC to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Minimize the trace length from any ground-connected
passive components to SPKLGND and SPKRGND to
further minimize radiated EMI.
Figure 42. Suggested Routing for the MAX98088
LAYER 1
LAYER 2
LAYER 3
