Intel AS/400 RISC Server User Manual
Page 322
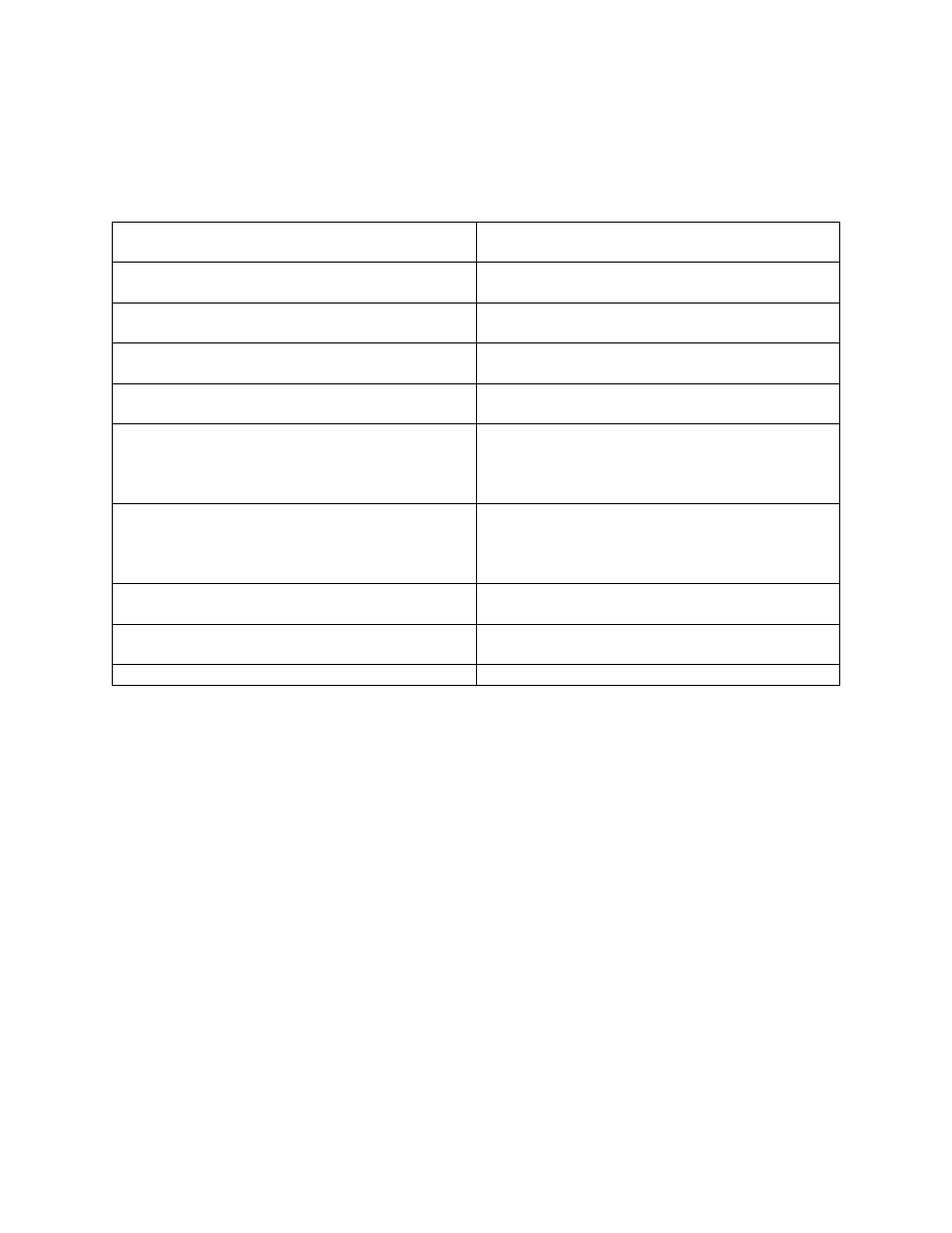
HMT and SMT Compared and Contrasted
Some key similarities and differences are:
ySMT can improve throughput up to 40 per cent,
in rare cases, higher.
yHMT typically improves throughput by 10 to 25
per cent.
ySMT can allow QPRCMLTTSK to change at any
time.
yHMT needs a full IPL for the change to
QPRCMLTTSK to be activated.
ySMT has three values for QPRCMLTTSK ("0"
for off, also called "ST mode", "1" for on, and "2"
for "controlled" where OS/400 decides,
dynamically, whether to be in ST or SMT mode.
yHMT operation is controlled by the system value
QPRCMLTTSK ("1" means active, "0" means
inactive)
ySMT machines continue to report data on a
physical processor basis, but some of the
measurements are harder to interpret (reporting on
a logical CPU basis would be no better).
ySystem performance counters and CPU
utilization values continue to be reported on a
physical CPU basis.
ySMT complicates the question of measuring
CPU utilization.
yCPU utilization measurements are not greatly
affected by HMT.
ySMT allows multiple streams of execution
simultaneously.
yHMT executes only one instruction stream at a
time.
ySMT, because it is more dynamic, the SMT state
need not be identical across partitions.
yAll partitions have the same value for HMT
ySMT can be turned on and off dynamically at
any time. No IPL required
yHMT is can be turned on and off only by a
whole system IPL.
SMT Feature
HMT Feature
Models With/Without HMT
Not all prior models have HMT. In fact, some recent models have neither HMT nor SMT.
The following models have HMT available:
y
270, 800, 810, 820, 830, 840
The following have neither SMT nor HMT:
y
825, 870, 890
Earlier models than the 270 or 820 series (e.g. 170, 7xx, etc.) did not have either HMT nor SMT.
IBM i 6.1 Performance Capabilities Reference - January/April/October 2008
©
Copyright IBM Corp. 2008
Chapter 20 - General Tips and Techniques
322
