8 ret and rets instructions, 9 stack considerations for call instructions – Epson 6200A User Manual
Page 13
S1C6200/6200A CORE CPU MANUAL
EPSON
7
2 MEMORY AND OPERATIONS
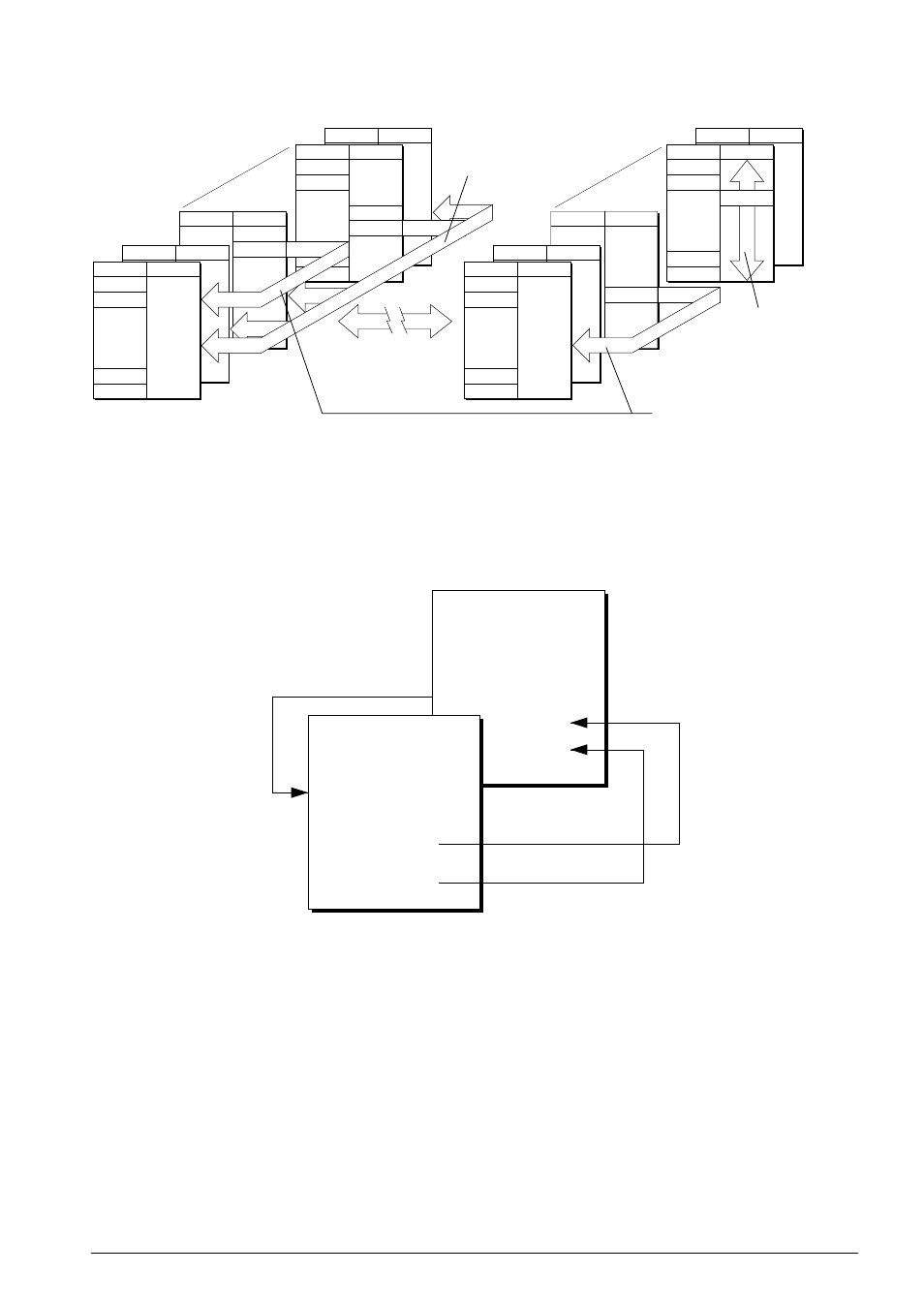
The difference between CALL and CALZ is shown in Figure 2.1.7.2.
Page 15
Bank 0
Page 14
PSET
CALL
Bank 0
Step 0
Step 1
Step 254
Step 255
Bank 0
Page 1
Bank 0
Page 0
Bank 0
Step 0
Step 1
Step 254
Step 255
Page 15
Bank 1
Bank 1
Step 0
Step 1
Step 254
Step 255
Page 3
CALZ
Bank 1
Bank 0
Bank 1
Page 1
Bank 1
Page 0
Bank 1
Step 0
Step 1
Step 254
Step 255
Page 14
CALL
CALL without PSET
can go anywhere
in a page
CALZ can only go to page 0
of the current bank
CALL with PSET
can go anywhere
within a bank
CALL and CALZ
cannot go
between banks
Page 3
CALZ
Fig. 2.1.7.2 The difference between CALL and CALZ instructions
2.1.8 RET and RETS instructions
The RET instruction causes a return from a subroutine to the address immediately following the address
from where that subroutine was called. The RETS instruction causes a return to the address following this
address. Proper use of RET and RETS allows simple conditional exits subroutines back to the main routine.
See Figure 2.1.8.1.
Bank 0 Page 0
Program memory
PSET
CALL
LD
LD
Bank 0 Page 10
Program memory
DDD....................
RET
RETS
0AH
DDD
A,0
B,0
Fig. 2.1.8.1 Difference between RET and RETS instructions
2.1.9 Stack considerations for call instructions
When a subroutine is called, the return address is loaded into the stack and retrieved when control is
returned to the calling program. Nesting allows efficient usage of the stack area.
As the stack area resides in the data memory, care should be taken to ensure that the stack area is not
corrupted by other data.
