ProSoft Technology MVI69-MCM User Manual
Page 112
Reference
MVI69-MCM ♦ CompactLogix or MicroLogix Platform
User Manual
Modbus Communication Module
Page 112 of 167
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 22, 2011
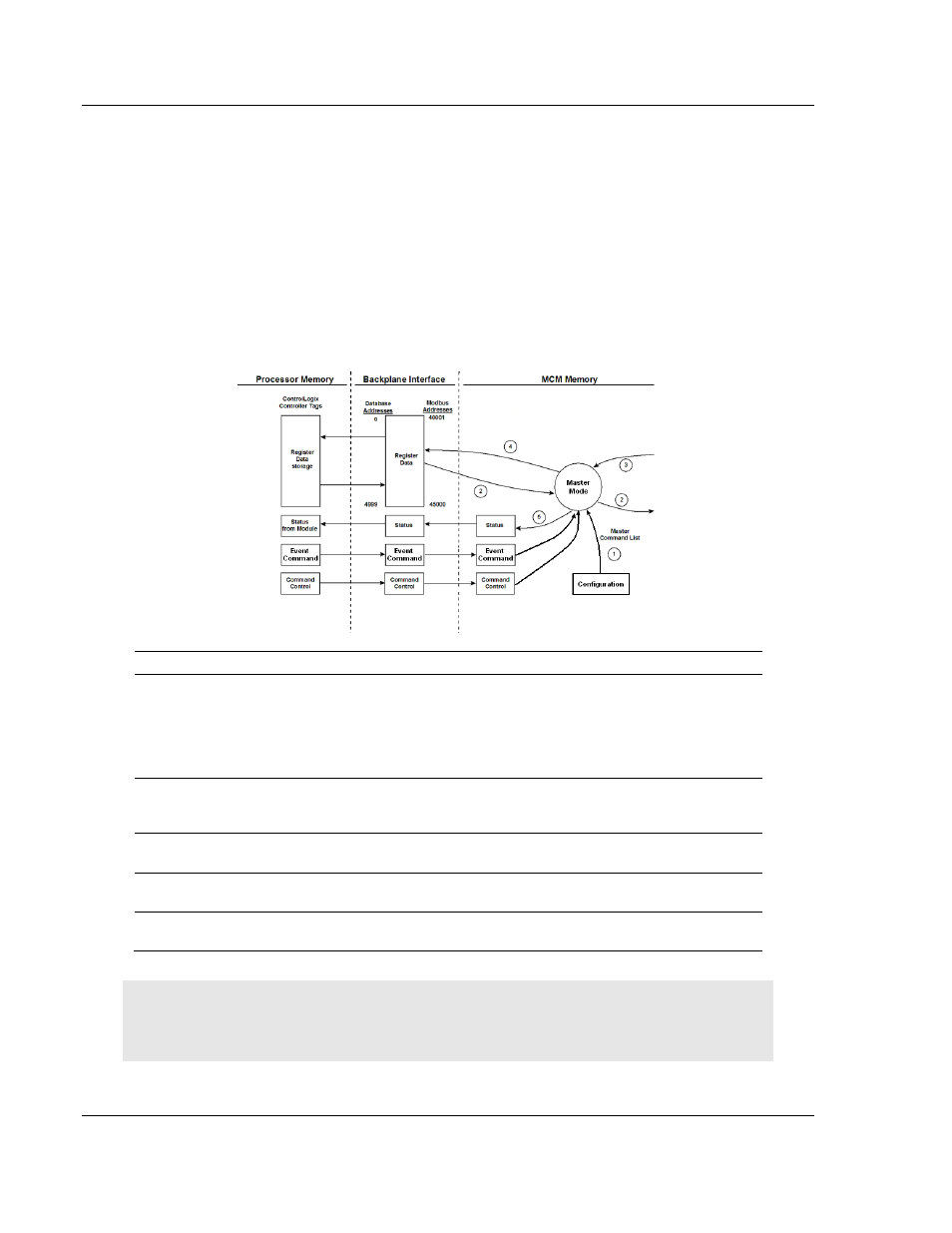
5.3.2 Master Driver Mode
In the Master mode, the MVI69-MCM module issues read or write commands to
slave devices on the MODBUS network. These commands are user configured in
the module via the Master Command List is received from the user defined
configuration file that is stored on the MVI69-MCM module or can be issued
directly from the CompactLogix or MicroLogix processor (Special Command
Blocks). Command status is returned to the processor for each individual
command in the command list. The location of this command status list in the
module’s internal database is user defined. The following flow chart and
associated table describe the flow of data into and out of the module.
Step
Description
1
The Master driver obtains configuration data from the user defined .CFG file that is
stored locally on the MVI69-MCM module itself. The configuration data obtained includes
port configuration and the Master Command List. Special Ccommands can be issued
directly from the CompactLogix or MicroLogix processor (using Event Commands and
Command Control). These configuration and command values are used by the Master
driver to determine the types and order of commands to send to slaves on the network.
2
After configuration, the Master driver begins transmitting read and/or write commands to
slave nodes on the network. If writing data to slave, the data for the write command is
obtained from the module’s internal database to build the command.
3
Once the specified slave has successfully processed the command, it will return a
response message to the Master driver for processing.
4
Data received from a slave in response to a read command is passed to the module’s
and stored in its internal database.
5
Status is returned to the CompactLogix or MicroLogix processor for each command in
the Master Command List.
Important: You must take care when constructing each command in the list to ensure predictable
operation of the module. If two commands write to the same internal database address of the
module, the results will be invalid. All commands containing invalid data are ignored by the module.
