ProSoft Technology MVI69-DNPSNET User Manual
Page 73
Reference MVI69-DNPSNET
♦ CompactLogix or MicroLogix Platform
Distributed Network Protocol Interface Module
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 73 of 119
November 3, 2008
How Data is Transferred
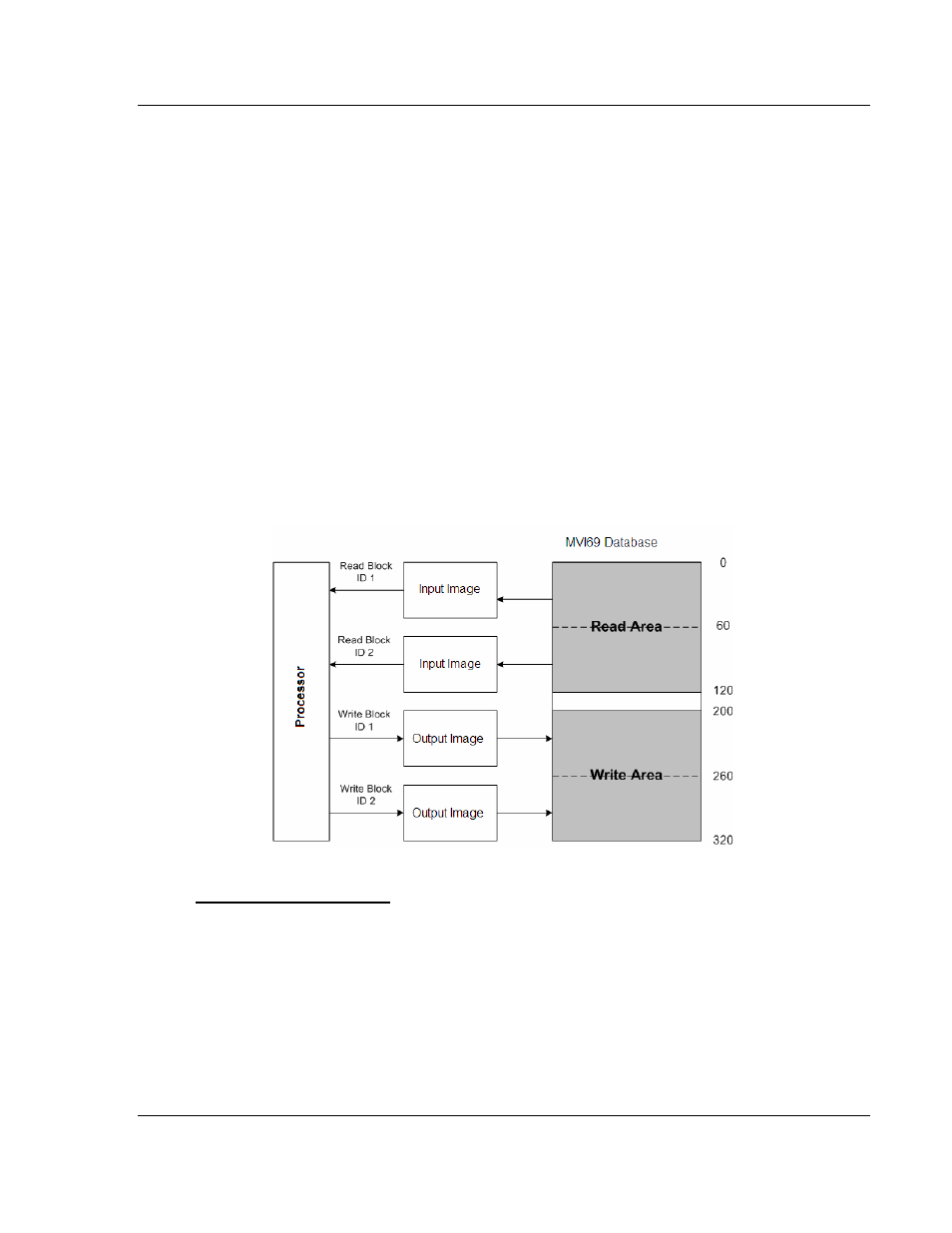
In order to understand how the data is transferred between the processor and the
module, you must understand the Read Data and Write Data area concept in the
module's database. The module's database can be partially, or totally divided into
Read Data Areas and Write Data Areas.
These areas are defined by the user when the configuration file is being edited.
The following parameters define the Read and Write data areas:
Read Register Start = 0
Read Register Count = 120
Write Register Start = 200
Write Register Count = 120
Each area is broken down into blocks of 60 words. Therefore, the Read Register
Count and Write Register Count parameters should be multiples of 60.
The Read Data Area will be transferred from the module to the CompactLogix or
MicroLogix processor. The Write Data Area will be transferred from the
CompactLogix or MicroLogix processor to the module.
The following example shows the resulting data flow:
Command Control Blocks
Command control blocks are special blocks used to control the module or
request special data from the module. The current version of the software
supports several command control blocks each of which is discussed in the
following topics:
Block 9958 - Processor Binary Input Event
If the processor sends a block 9958, the module will place the binary input event
data in the block into the event buffer and alter the data values for the points in
the DNP binary input database. The format for the message is shown in the
following table.
