1 hardware, 2 signal structure, Hardware – HEIDENHAIN SHB Data Interfaces for HEIDENHAIN User Manual
Page 10: Signal structure
June 2011
2 – 11
2.3.1 Hardware
The integrated Ethernet expansion card provides you with both the 10Base2 (BNC) port and the
10BaseT (twisted pair). You can only use one of the two connections at one time. Both
connections are electrically isolated from the control electronics.
Connection and wiring diagrams see chapter 7.2, pin layouts see chapter 3.2.
X26 Ethernet interface, BNC connection (coaxial cable, 10Base2)
The 10Base2 connection is also commonly known as ThinEthernet or CheaperNet.
You connect the TNC with your network via BNC-T connector. The maximum cable length is
185 m (coaxial cable). The network topology is a linear bus. The "open" ends of the bus must be
terminated with terminating resistors.
X25 Ethernet interface, RJ45 connection (10BaseT)
The twisted-pair cable of the 10BaseT connector may be either shielded or non-shielded.
Maximum cable length:
non-shielded:
100 m
shielded:
400
m
The network topology is a star connection. This means a central node establishes the connection
to the other participants.
2.3.2 Signal structure
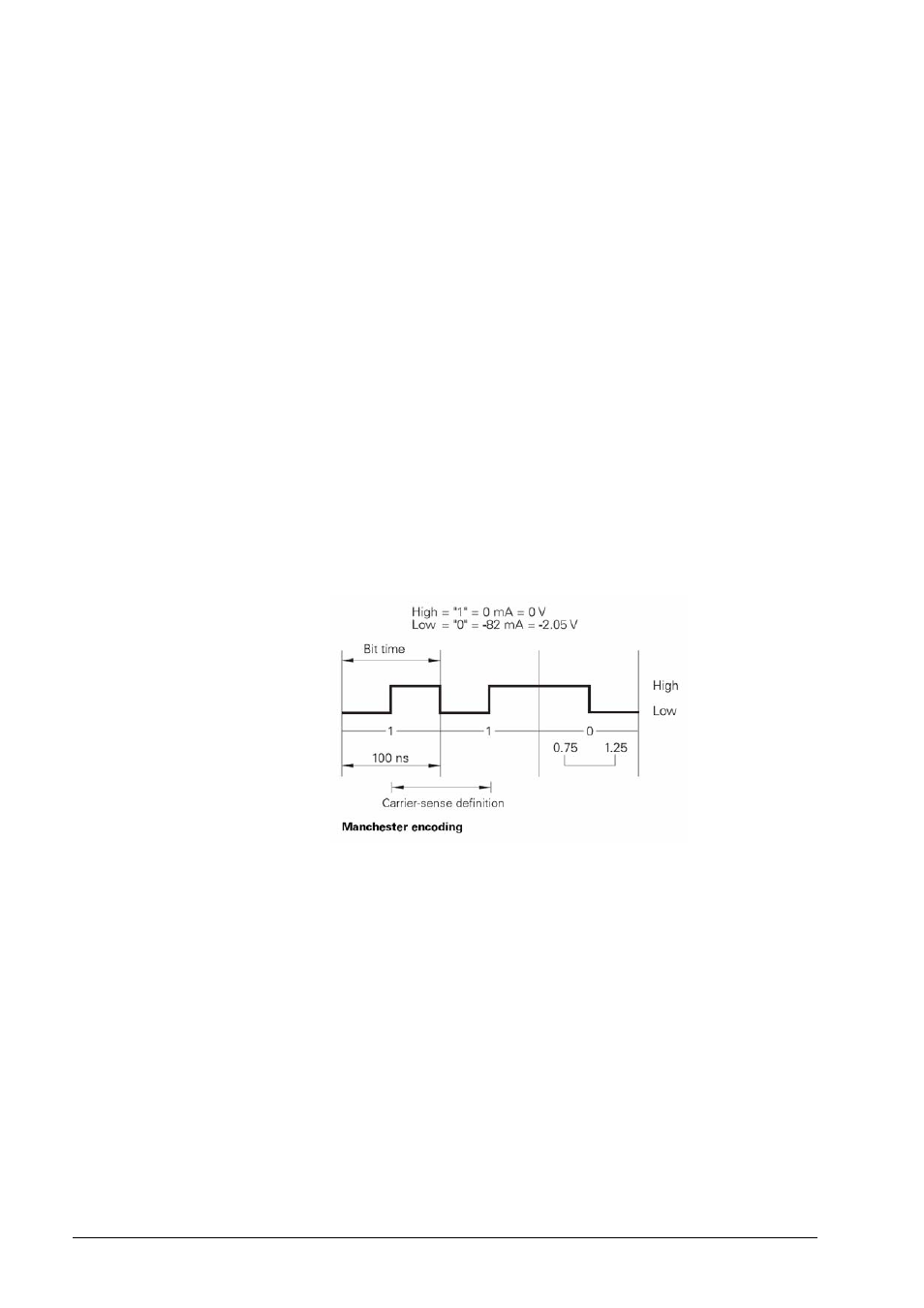
Ethernet frames are transferred in Manchester code which is a self-clocking code. The
synchronization or the transfer of a transmit clock pulse is executed such that each bit is
transmitted inverted in the first half of the transfer period, i.e. the bit rate is half the baud rate.
A data rate of 10 Mbps results in a bit time of 100 ns. Carrier detect (activity on the cable) is
indicated by the presence of signal level changes. If the signal level does not change in a bit time
interval between 0.75 and 1.25 after the last transition, no carrier is detected (see figure).
The network settings of the TNC are described in the Technical Manual and in chapter 7
(Ethernet) of this Service Manual.
