Cse60, How it works, Refrigeration – Scotsman CSE60 User Manual
Page 10
CSE60
June 2001
Page 10
HOW IT WORKS:
REFRIGERATION
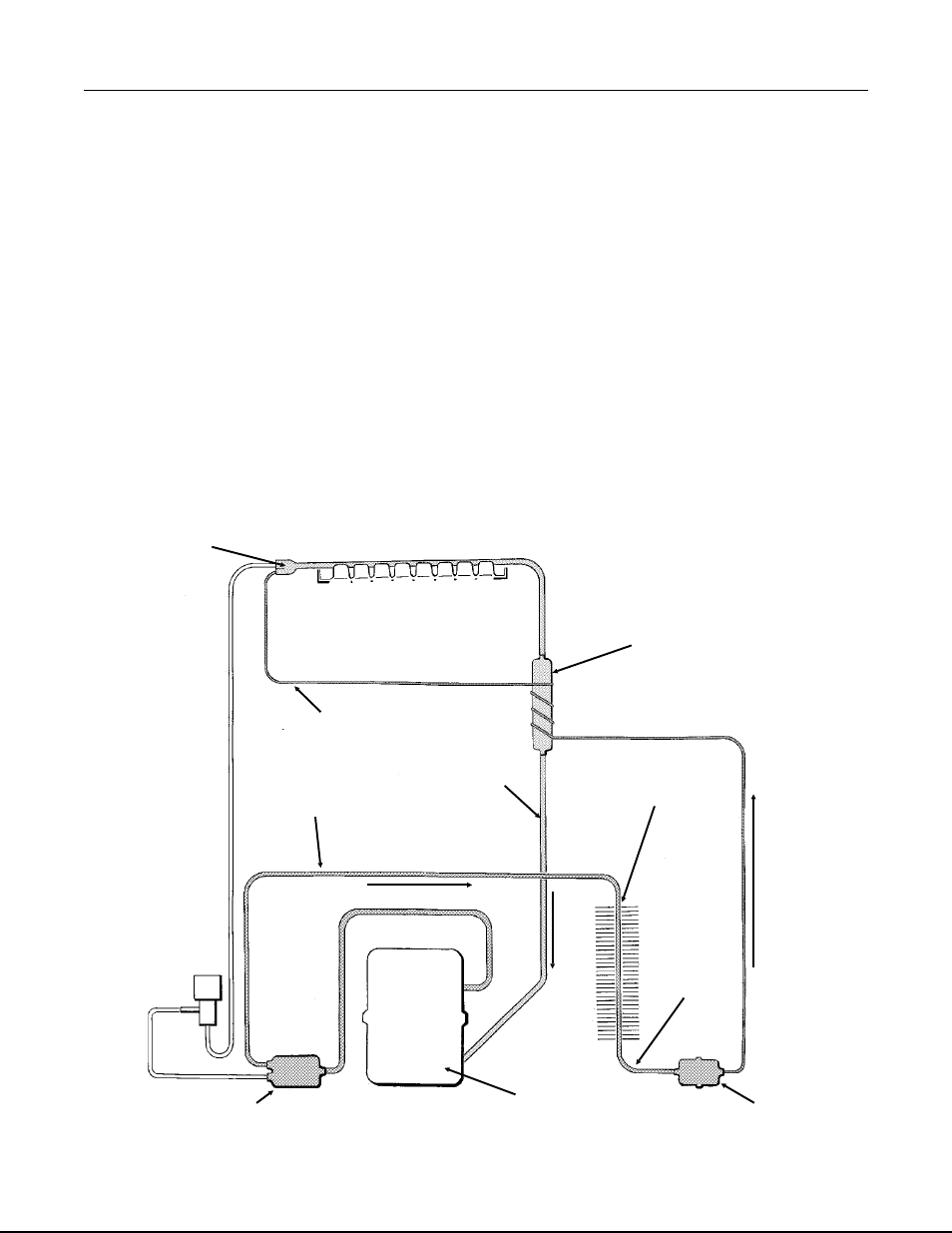
FREEZE CYCLE
The ice cubes are formed in an inverted mold
that is refrigerated.
The refrigeration process begins at the
compressor. There, refrigerant vapor is
compressed and flows from the compressor
through the discharge line as a high
temperature, high pressure gas. In the discharge
line there is a strainer with two outlets, one
leads to the condenser, and one to a solenoid
valve. Because the solenoid valve is closed, the
gas flows to the condenser, where heat is
transferred from the refrigerant to the air passing
through the condenser. The refrigerant then
condenses into a high pressure liquid.
From the condenser, the liquid refrigerant flows
through the liquid line, and the liquid line
filter-drier. After the filter drier, the liquid
refrigerant enters the metering device, a
capillary tube. After passing the restriction of
the capillary tube, the refrigerant enters an area
of relative low pressure, the evaporator. In the
tubing of the evaporator, the liquid refrigerant
expands and evaporates, absorbing heat from
the evaporator tubing and anything in contact
with it such as water sprayed against it.
The refrigerant, now a low pressure, low
temperature vapor, flows into the accumulator,
which traps excess liquid refrigerant. The vapor,
now primarily a gas, goes through the suction
line tube to the compressor where the cycle is
repeated.
EVAPORATOR
ACCUMULATOR
CAPILLARY TUBE
COMPRESSOR
STRAINER
CONDENSER
FILTER-DRIER
DISCHARG
E LINE
LIQUID
LINE
SUCTION
LINE
Refrigeration System Schematic
