Base address switch, Wait state jumper – Measurement Computing CIO-PDISO16 User Manual
Page 10
CIO-PDISO16 User's Guide
Installing the CIO-PDISO16
9
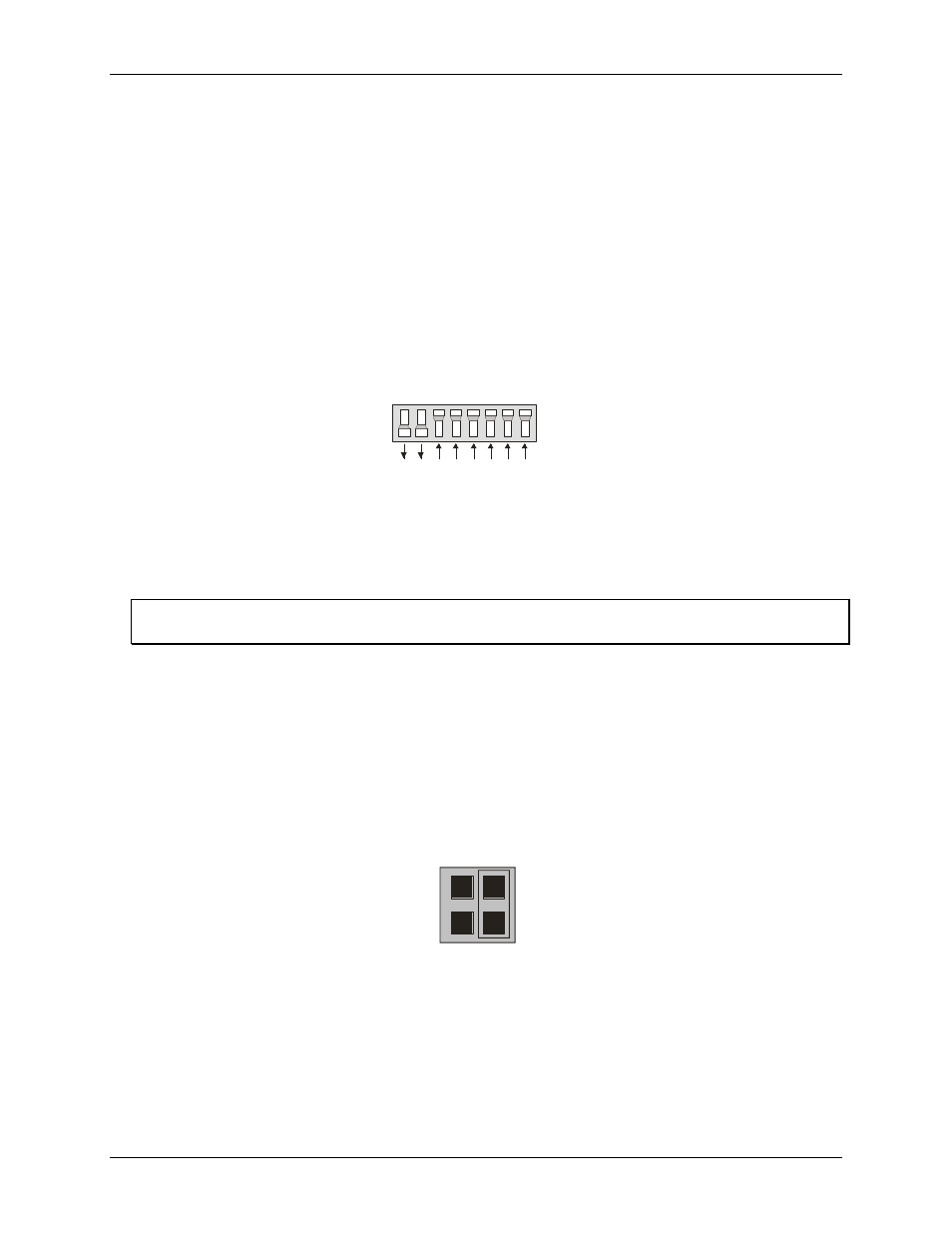
Base address switch
The base address switch sets the starting I/O location where the CPU can access the registers of the CIO-
PDISO16. The factory default is 300h (768 decimal).
Before you install the CIO-PDISO16 in your computer, set the base address by using the dip switch labeled
ADDRESS
located on the board. The easiest way to set the base address switch is to let InstaCal show you the
correct settings. However, if are already familiar with setting ISA base addresses, you may use the base address
switch description below to guide your base address selection.
Unless there is already another board in your system using address 300 hex (768 decimal), leave the switches as
they are set at the factory. The example shown in Figure 2 shows the settings for the factory-default base
address of 300 hex.
5 4 3 2
6
9 8 7
SW
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
HEX
200
100
80
40
20
10
08
04
Figure 2. CIO-PDISO16 base address switches
In the default configuration shown in Figure 2, addresses 9 and 8 are DOWN, and all others are UP.
Address 9 = 200 hex (512 decimal) and address 8 = 100 hex (256 decimal); when added together they equal 300
hex (768 decimal).
Disregard the numbers printed on the switch
When setting the base address, refer to the numbers printed in white on the printed circuit board.
Wait state jumper
The CIO-PDISO16 board has a wait state jumper which you can set to enable an on-board wait state generator.
A wait state is an extra delay injected into the processor's clock via the bus. This delay slows down the
processor when the processor addresses the CIO-PDISO16 board so that signals from slow devices (chips) will
be valid.
The factory default is wait state disabled (Off). You will probably never need the wait state because PC
expansion slot busses are limited to 8 or 10 MHz. If you get intermittent operation, try enabling the wait state to
see if that solves the problem.
O
N
O
F
F
Figure 3. Wait State jumper
