Greenheck Canopy Hoods (452413 IOM) User Manual
Page 22
Kitchen Hoods • Type I and Type II
22
®
Perforated Face Supply - Rotating Vane Method
1. Hood set up.
If the make-up air unit has a temperature control, it
should be used to keep the supply air at the desired
room discharge air temperature.
2. Measure velocities.
Divide the perforated face panel into a grid of equal
areas, each approximately 4 in. (101.6 mm) square.
Measure the velocity at the center of each grid
area. A digital 2.75 in. (69.85 mm) rotating vane
anemometer or equivalent is suggested. The center
of the anemometer should be held tight to the face
of the panel and parallel to the filter. Both squareness
and distance are important for accuracy. Calculate
the average velocity of the panel.
3. Measure the length and height of the perforated face
panel.
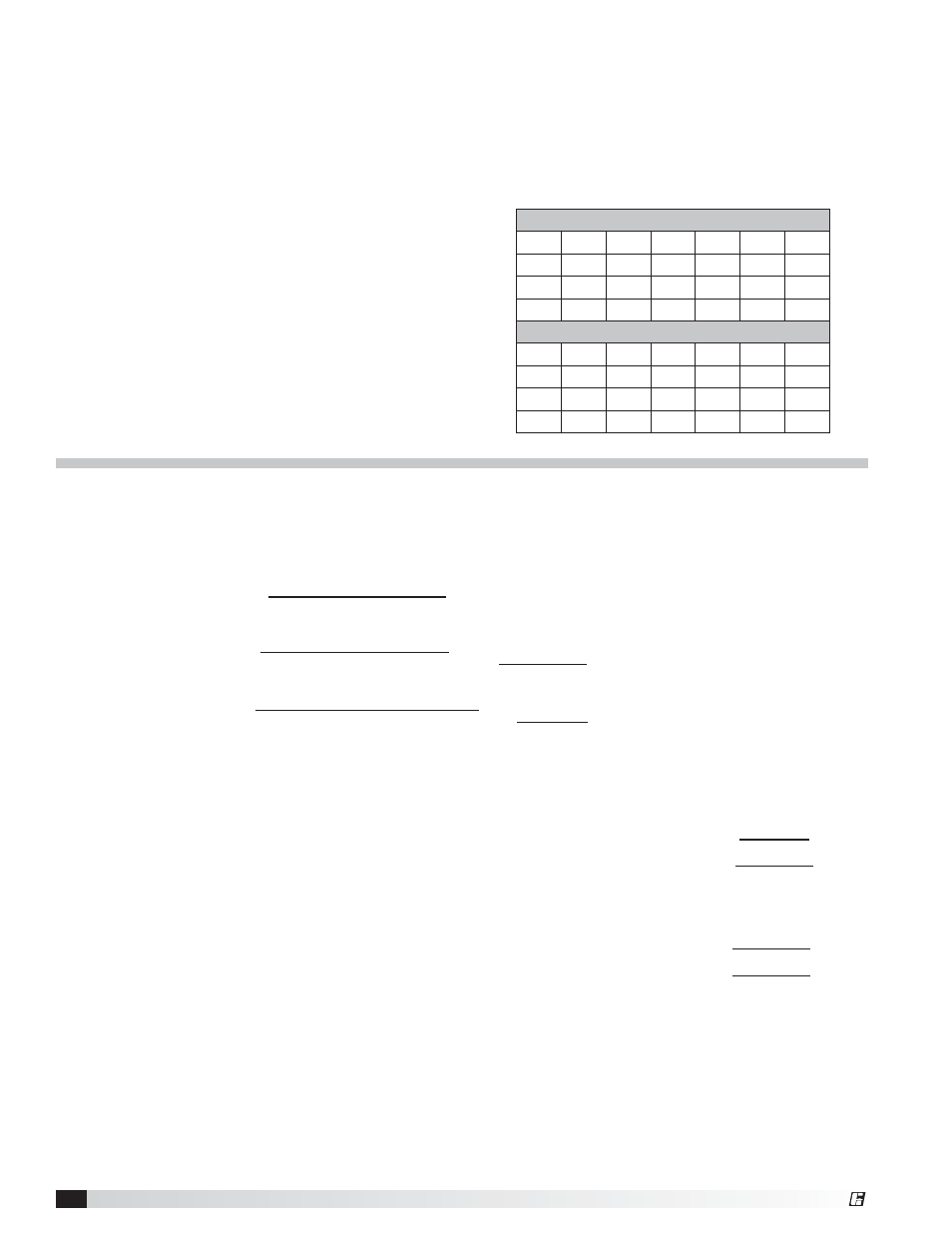
Filter Readings (ft/min.)
260
250
255
260
250
255
265
270
275
270
280
265
265
270
290
285
280
280
275
290
295
285
275
280
260
270
265
260
Filter Readings (m/hr)
4755
4572
4663
4755
4572
4663
4846
4938
5029
4938
5121
4846
4846
4938
5304
5212
5121
5121
5029
5304
5395
5212
5029
5121
4755
4938
4846
4755
Total system volume =
(Panel 1 Volume)
+
(Panel 2 Volume)
+
(Panel 3 Volume)
(Imperial)
=
606.4
+
614.3
+
593.8
=
1814.5 cfm
(Metric)
=
1029
+
1044
+
1009
=
3082 m
3
/hr
Measure length and height. 28 inches (.711 m) long perforated panel by 16 inches (.406 m) high
Volume for one panel =
Conversion Factor x
Average Velocity
x
Length
x Height
(Imperial)
=
0.005
x
270.7 ft/min.
x
28
x
16
=
606.4 cfm
(Metric)
=
0.72
x
4951 m/hr
x
.711
x
.406
=
1029 m
3
/hr
Example: Face supply hood with three 28 inch (.711 m) perforated panels
Measured velocities in ft/min. for one perforated panel
Average Velocity
=
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
(Imperial)
=
260 + 250 + ... + 265 + 260
28
= 270.7 ft/min.
(Metric)
=
4755 + 4572 + ... + 4846 + 4755
28
= 4951 m/hr
4. Calculate the perforated face panel volume using the
following formula:
CFM = avg. velocity x length (in.) x height (in.) x 0.005
m/hr = avg. velocity x length (m) x height (m) x 0.72
5. Calculate the system’s volume by repeating the
process for the remaining panels and adding the
individual panel volumes together.
