Sensor measuring principle, Mini cori-flow sensor, Valve principles – Bronkhorst Mini CORI-FLOW User Manual
Page 11: Solenoid valve, Vary-p valve, Pilot operated valve, 2 sensor measuring principle, 1 mini cori-flow sensor, 3 valve principles, 1 solenoid valve
BRONKHORST CORI-TECH B.V.
1.2 Sensor measuring principle
1.2.1 Mini CORI-FLOW sensor
Mini CORI-FLOW mass flow meters/controllers operate according to the Coriolis principle.
The instrument can be used to simultaneously measure the mass flow, temperature and density.
When a fluid flows through a vibrating tube, Coriolis forces are generated which bend or twist the tube.
The extremely small tube displacements are detected by optimally positioned sensors and evaluated
electronically.
Since the measured phase shift of the sensor signals is proportional to the mass flow, the mini CORI-FLOW
measures the mass flow directly. The measurement principle is independent of the density, temperature,
viscosity, pressure, heat-capacity or conductivity. The tubes always vibrate at their natural frequency, which is a
function not only of the tube geometry and the tube material properties but also the mass of the fluid in the
vibrating tubes.
1.3 Valve principles
Control valves are not designed to provide positive shut-off, although some models have excellent capabilities
for this purpose.
It is recommended to install a separate shut-off valve in the line if required. Also pressure surges, as may
occur during system pressurisation must be avoided. The following models can be distinguished:
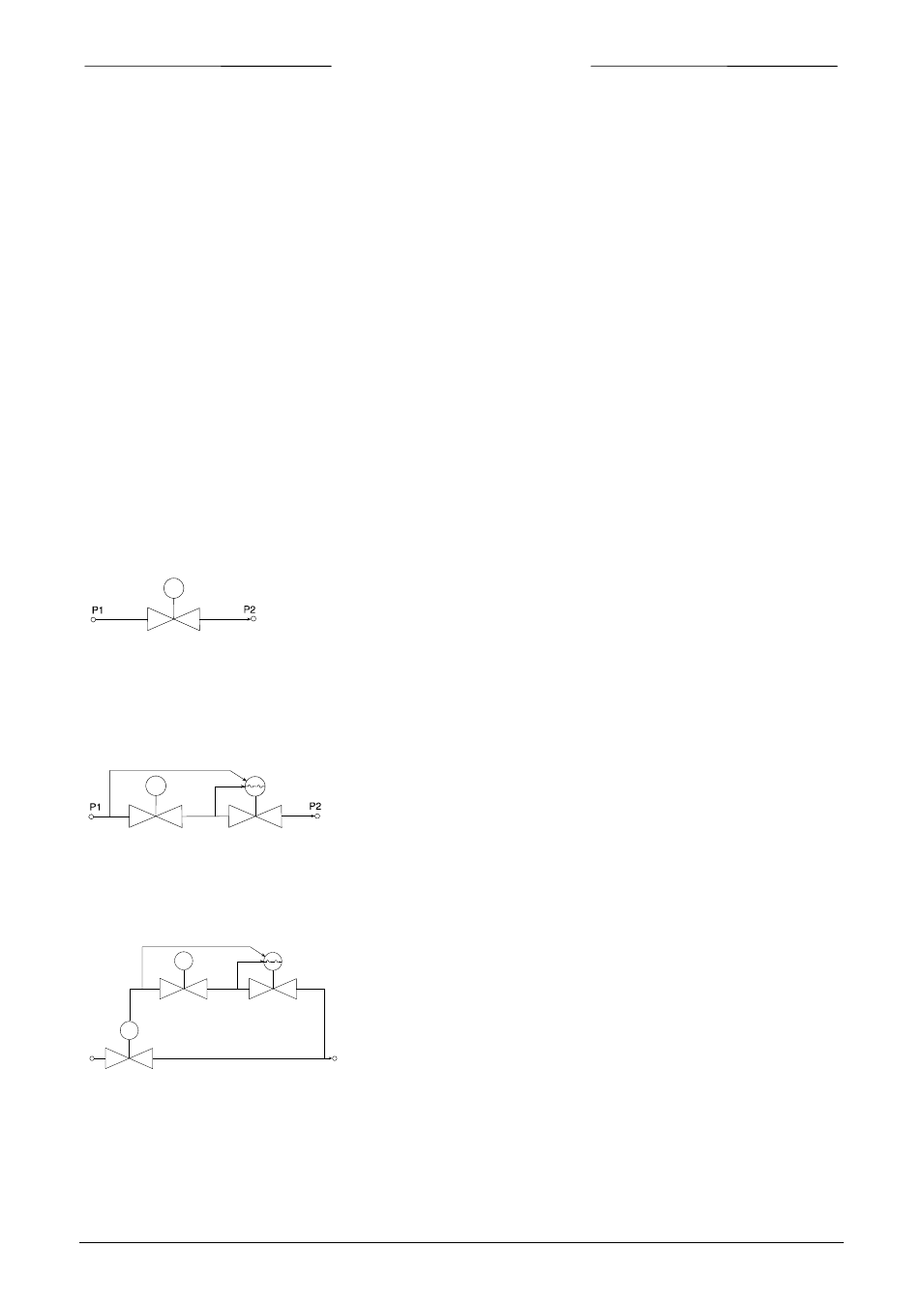
1.3.1 Solenoid valve
This is considered to be the standard (direct operated) control valve. In
general it is a normally closed solenoid valve. The plunger is lifted by the
force of the magnetic field of the coil. The orifice under the plunger is
removable for optimising the orifice diameter. Also a normally opened
solenoid valve is available.
1.3.2 Vary-P valve
For process conditions where up- and downstream pressure
varies much, a special type of valve, VARY-P has been designed.
This valve consists of two valves, a solenoid operated control
valve and a fixed adjusted pressure compensation valve.
1.3.3 Pilot operated valve
For high flow rates the pilot operated valve has been designed. A
solenoid driven control valve controls the pressure difference across a
piston, which lifts the main plunger.
Flow control
valve
pressure
compensating
valve
flow control
valve
P1
pilot valve
pressure
compensating
valve
P2
flow control valve
9.17.050
page 11
