1 fast regulator, 2 cpc, zero switching controller – CIRCUTOR FRE Series User Manual
Page 9
FRE / FRES
9 / 20
NOTES:
• Some elements of protection shown in Fig. 4-3 are optional and may not be present in your equipment
• In FRES equipment, capacitors are cylindrical type and static switches cut only two phases
Static switching equipment have a series of characteristic elements, which are very different from those in
equipment using contactors. Namely the main blocs are:
4.6.1 Fast regulator
Static capacitor banks are equipped with
computer Max f, computer Smart f or computer Plus TF fast
regulators. The outputs of these regulators are static; that is to say, instead of an output via relay contact
they have a semiconductor-based switch which allows them to perform operations in rapid succession,
practically every network cycle. This type of output is prepared to drive COM and ACT inputs on
CPCxx
zero switching controller
Fast regulators enable regulation with minimum delay, generally between 20 and 100 ms (see manual for
the specific regulator being used)
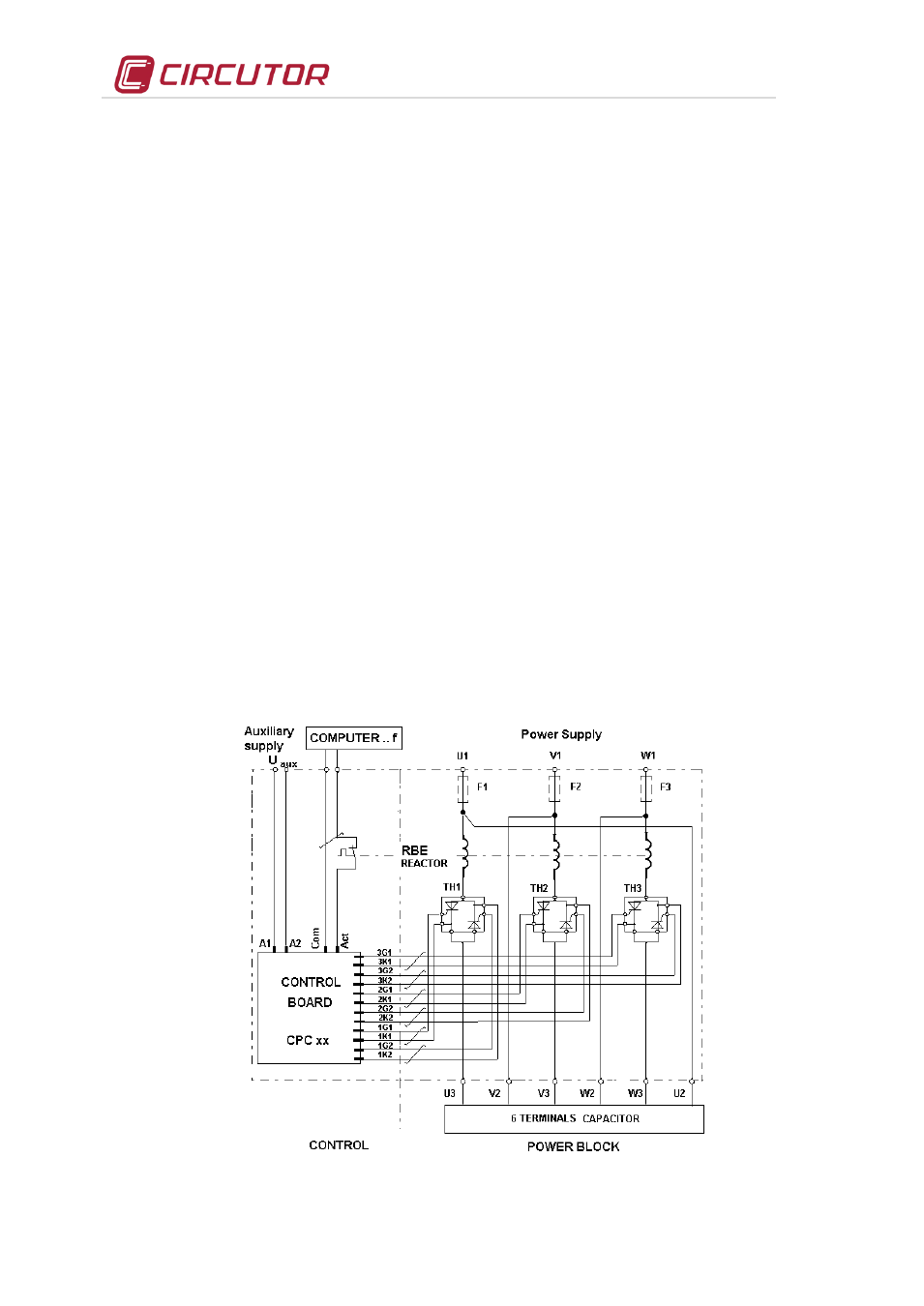
4.6.2 CPC, zero switching controller
Static capacitor banks are equipped with CPCxx controllers (xx means that there are different types
according to the network voltage, control voltage and control type).
The role of the CPCxx is to control the switching of the thyristors at zero voltage during the turn ON
operation, thus avoiding current transients. The typical connection diagram of a single step is shown in
Fig. 4-4 and in more detail in the simplified wire diagram in section 10.
CPC controllers are powered with an auxiliary voltage U
aux
. The standard CPCs are mainly used for
networks with U
max
= 440 V, nevertheless they have a dual-voltage supply circuit able to be supplied at a
rated voltage of 230 V or 400 V (±10%) . There are special controllers, type CPC3i, which are designed to
operate on networks up to 690 V. Notice that even for the latter case, the auxiliary control voltage, U
aux
must be 400 V or 230 V. The CPC3i controllers allow three-phase or individual phase-phase control,
thanks to an RS-485 bus. However, the standard control is through a voltage-free static contact
(semiconductor-based), which opens or closes the circuit between the controller's COM and ACT
terminals.
Fig. 4-4 .- Basic connection diagram of the
CPCxx to the power block
