Applications – ultrasonic insertion – Sonics H540 E User Manual
Page 33
A P P L I C A T I O N S – U L T R A S O N I C I N S E R T I O N
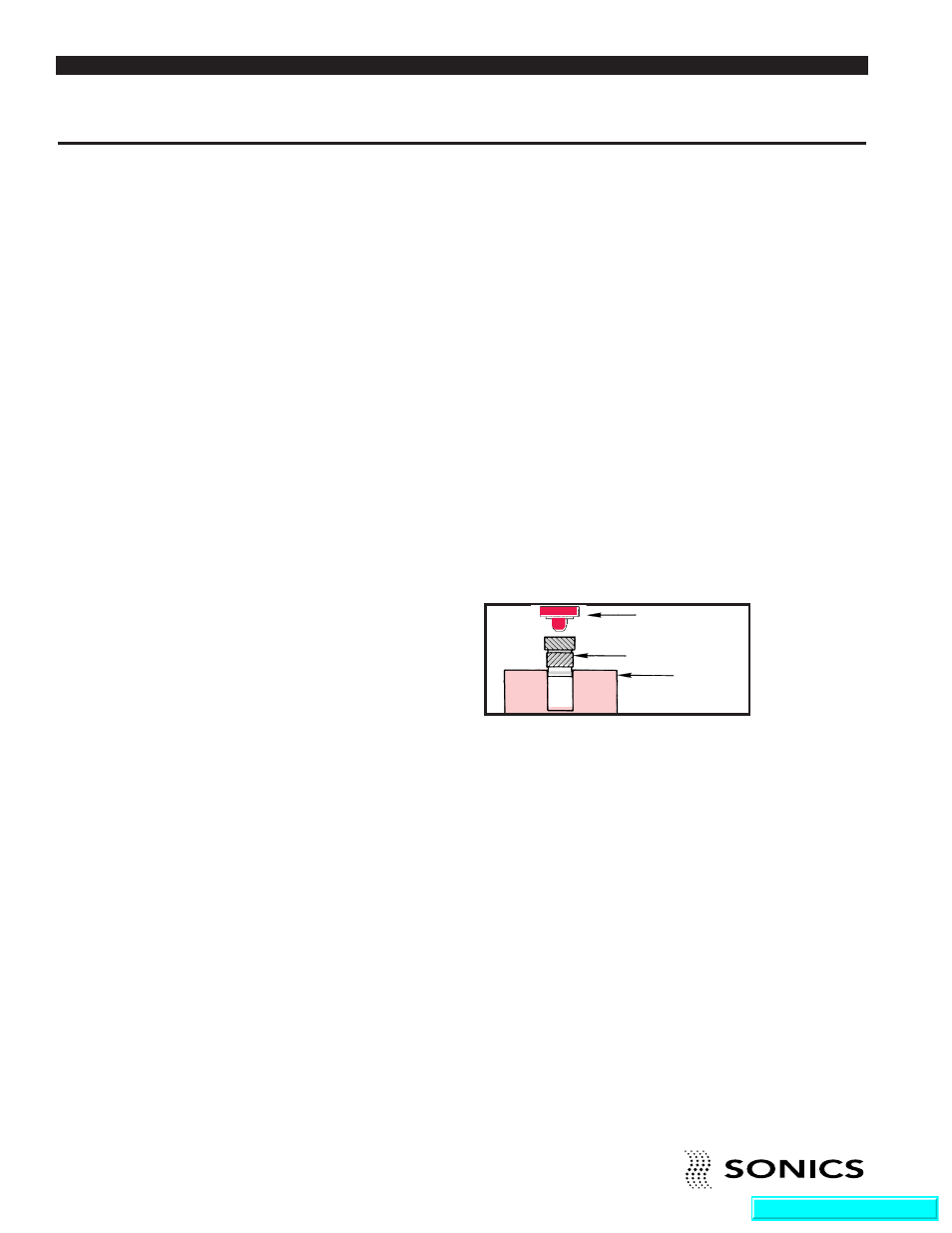
Ultrasonic insertion involves a metal insert to be placed in a cored or drilled
hole that is slightly smaller than the insert. This hole provides a certain
degree of interference and also serves to guide the insert into place. The
vibrating ultrasonic horn contacts the insert and the ultrasonic vibrations
travel through the insert to the interface of the metal and plastic. Heat,
generated by the insert vibrating against the plastic, causes the plastic to
melt, and as the horn advances, the insert is embedded into the component.
The molten plastic flows into the serrations, flutes, or undercuts of the inserts
and, when the vibrations terminate, the plastic resolidifies and the insert is
securely encapsulated in place. Inserts can be ultrasonically installed in most
thermoplastics.
Ultrasonic insertion provides the high performance strength values of a
molded-in insert while retaining all of the advantages of post-molded
installation. Some of the advantages of ultrasonic insertion over other
methods include rapid installation, minimal residual stresses in the
component following insertion, elimination of potential mold damage,
reduced mold fabrication costs and increased productivity as a result of
reduced mold cycle times.
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
32
I N S T R U C T I O N M A N U A L • H A N D H E L D W E L D E R S
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
PLASTIC
INSERT
HORN
Go To Top Of Document
