2 can protocols, Can protocols, Family reference and programming manual – ScanTool STN1100 FRPM User Manual
Page 15
Family Reference and Programming Manual
STN1100FRPMA www.obdsol.com
15 of 23
address of the receive (or transmit) node passed as
the parameter.
STM command uses all filters “as-set”: it does not
modify them in any way.
ATSR turns off the automatic filtering mode, and
sets up a pass filter to accept messages sent to the
receive address provided as the parameter to ATSR.
In order to directly manipulate the filters, use the
filtering ST commands described in section 6.6.
8.2 CAN Protocols
This section describes how message filtering works
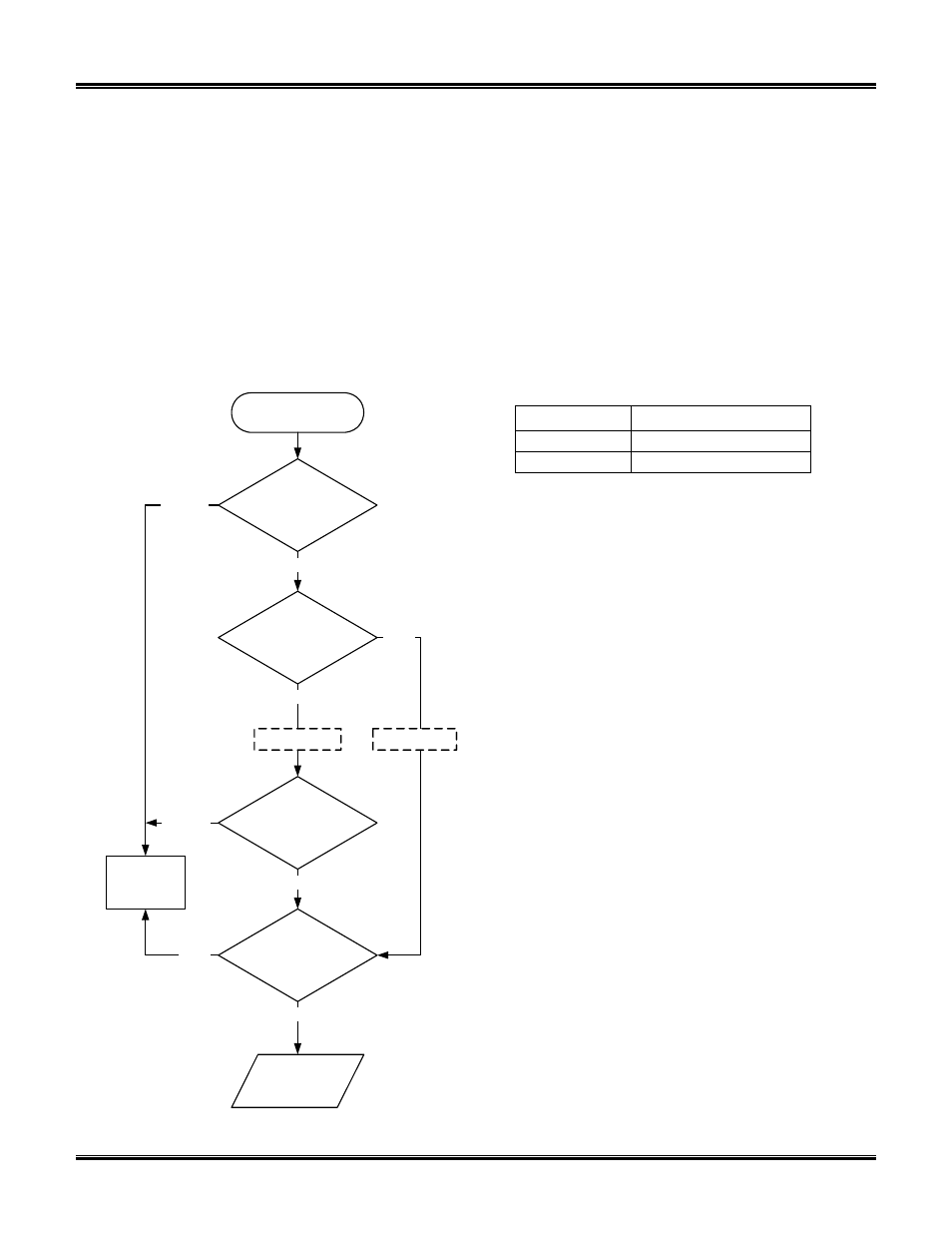
with CAN protocols (see ATSP, protocols 6 through 9).
When a CAN frame comes in from the network, it
must first go through the CAN hardware filter. If there is
no match, the frame is discarded. If there is a match,
the frame is compared against the flow control filters to
determine whether it is an ISO 15765 or an ISO 11898
(“raw”) CAN frame.
ISO 11898 frames are compared to the pass filters.
If there is no match, the frame is discarded. Otherwise,
the frame is compared to the block filters, and if there
is no match, it is transmitted on the UART.
ISO 15765 frames bypass the pass filters. As long
as the comparison with the block filters results in a “no
match”, the frame is transmitted on the UART.
In automatic filtering mode, flow control filters are
automatically set based on the currently set message
header. Table below lists the filters set up from the
default CAN headers:
CAN ID Type Filter (pattern, mask)
11-bit 7E8,7F8
29-bit 18DAF100,1FFFFF00
While in the automatic filtering mode, anytime the
user changes the headers using the ATSH command,
or by switching from 11-bit to 29-bit CAN IDs, the flow
control filter gets updated.
Automatic filtering mode is switched off when the
user clears the flow control filters, adds a flow control
filter, or sets the CAN hardware filter. To clear all
custom filters, and set up default filters, issue the
ATAR command.
The ATMA command sets the flow control, pass,
and block filters for “pass all, block none” operation.
When the command terminates, the old filters are
restored.
The STMA command works the same way as
ATMA, except that it also sets the CAN hardware filter
for “pass all” operation. Upon termination, the old CAN
hardware filter is restored.
ATMR and ATMT commands behave the same
way, except that instead of setting a “pass all” filter,
they set up a filter to accept messages based on the
address of the receive (or transmit) node passed as
the parameter.
STM command uses the filters “as-set”: it does not
modify them in any way.
ATSR turns off the automatic filtering mode, and
sets up a pass filter to accept messages sent to the
receive address provided as the parameter to ATSR.
In order to directly manipulate the filters, use the
filtering ST commands described in section 6.6.
CAN Frame from
Network
Flow Control Filters
added using STFAFC
Pass Filters
added using STFAP
Discard CAN
Frame
Block Filters
added using STFAB
Transmit
CAN Frame
on UART
CAN HW Filter
set via ATCF/ATCM
no match
match
match
ISO15765 Frame
no match
no match
no match
match
match
ISO11898 Frame
Figure 2 – Message Filtering: CAN Protocols
