0 obd requests, 0 obd message filtering, 1 non-can protocols – ScanTool STN1100 FRPM User Manual
Page 14: Obd requests, Obd message filtering, Non-can protocols, Stn1100
STN1100
14 of 23
www.obdsol.com STN1100FRPMA
7.0 OBD Requests
The STN11xx uses the same format for OBD
requests as the ELM327. Please refer to the “OBD
Commands” section of the ELM327 datasheet for
information.
See the following standards for more information
about legislated On-Board Diagnostics:
SAE J1979: E/E Diagnostic Test Modes. This
document describes data reporting requirements of
On-Board Diagnostic regulations in the United States
and Europe, and any other region that may adopt
similar requirements in the future. The ISO equivalent
of this standard is ISO 15031-5.
SAE
J2190: Enhanced E/E Diagnostic Test
Modes. This document describes the implementation
of Enhanced Diagnostic Test Modes, which are
intended to supplement the legislated Diagnostic Test
Modes defined in SAE J1979 standard. Modes are
defined for access to emission related test data beyond
what is included in SAE J1979, and for non-emission
related data.
SAE
J2178: Class B Data Communication
Network Messages. This document describes the
information contained in the header and data fields of
non-diagnostic messages for automotive serial
communications based on SAE
J1850 Class B
networks.
8.0 OBD Message Filtering
STN11xx supports pass, block, and flow control
filters. Their operation is backwards compatible with
the ELM327, however STN11xx filtering scheme is
much more powerful and flexible. It allows the user to
set up multiple filters and fine tune them to receive only
those messages that are of interest to the user.
8.1 Non-CAN Protocols
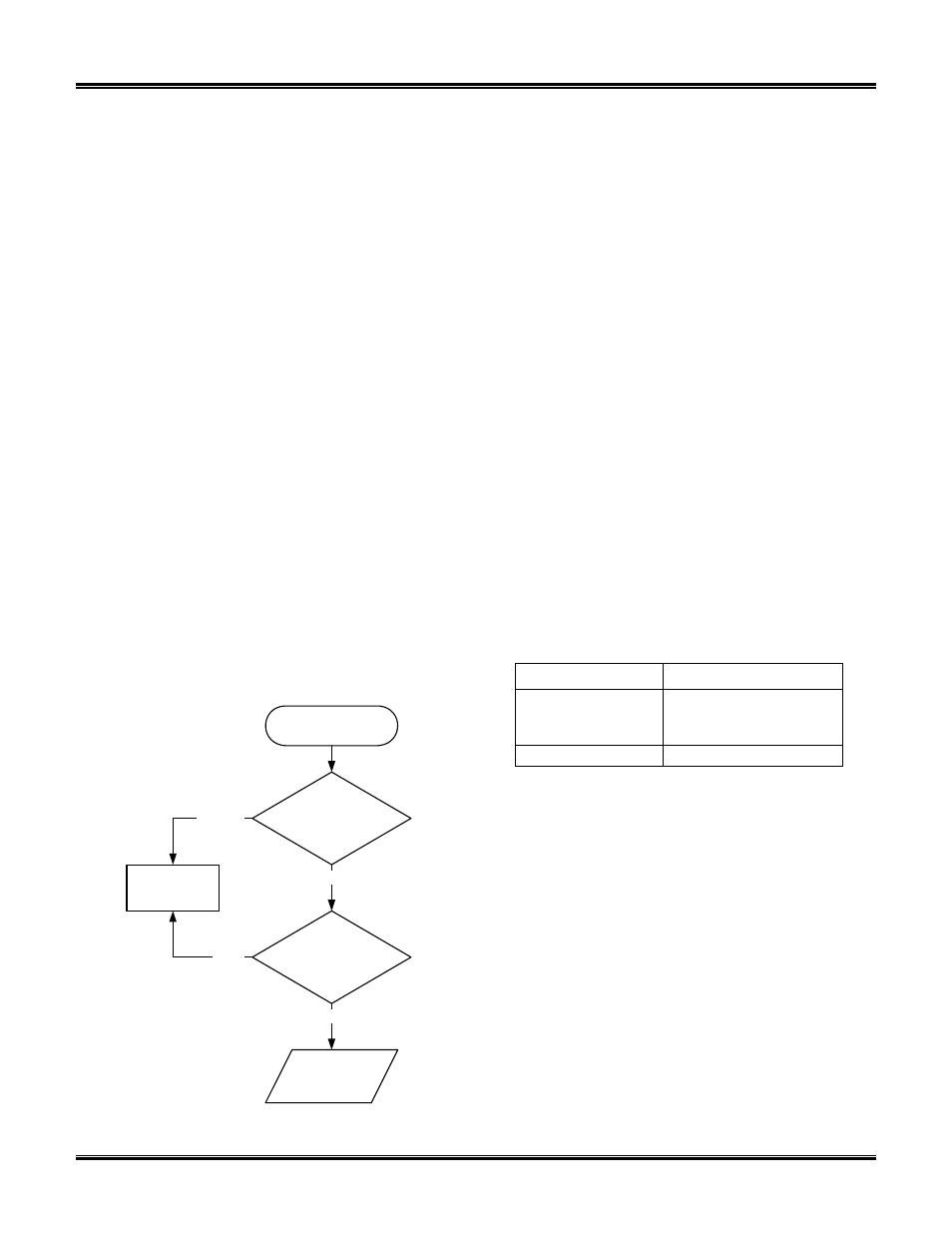
Non-CAN protocols (see ATSP, protocols 1 through
5) do not use flow control filters (refer to Figure 1).
When a message comes from the OBD bus, it is
compared to the pass filters. If the message does not
match one of the filters, it is discarded. Otherwise, the
message is compared to the block filters. If there is a
match, the message is discarded. Finally, if the
message goes through both the pass and block filters,
it is transmitted on the UART.
In automatic filtering mode, pass filters are
automatically set based on the currently set message
header. Table below lists the filters set up from the
default headers:
Protocol(s)
Filter (pattern, mask)
J1850 PWM
J1850 VPW
ISO 9141-2
006B00,14FF00
ISO 14230-4
80F100,C0FF00
While in the automatic filtering mode, anytime the
message header is changed, either by the user (ATSH
command) or because of a protocol change, the pass
filter gets updated.
As soon as the user clears the pass filters, or adds
a pass filter, automatic filtering mode is switched off.
Issue ATAR to clear all custom filters, set up default
filters, and turn on the automatic filtering mode.
Some commands temporarily alter the contents of
the pass filters.
For example, while the ATMA or STMA commands
are active, they temporarily delete any previously
added pass or block filters, and set up one “pass all”
filter. Upon termination of the command, the “pass all”
filter is removed, and the old pass/block filters are
restored.
ATMR and ATMT commands behave the same
way, except that instead of setting a “pass all” filter,
they set up a filter to accept messages based on the
Message from
OBD Bus
Pass Filters
added using STFAP
Discard OBD
Message
Block Filters
added using STFAB
Transmit
Message
on UART
no match
no match
match
match
Figure 1 – Message Filtering: Non-CAN Protocols
