Power monitor, Interrupts, Flags register – Cypress CY14B104M User Manual
Page 8
PRELIMINARY
CY14B104K, CY14B104M
Document #: 001-07103 Rev. *K
Page 8 of 31
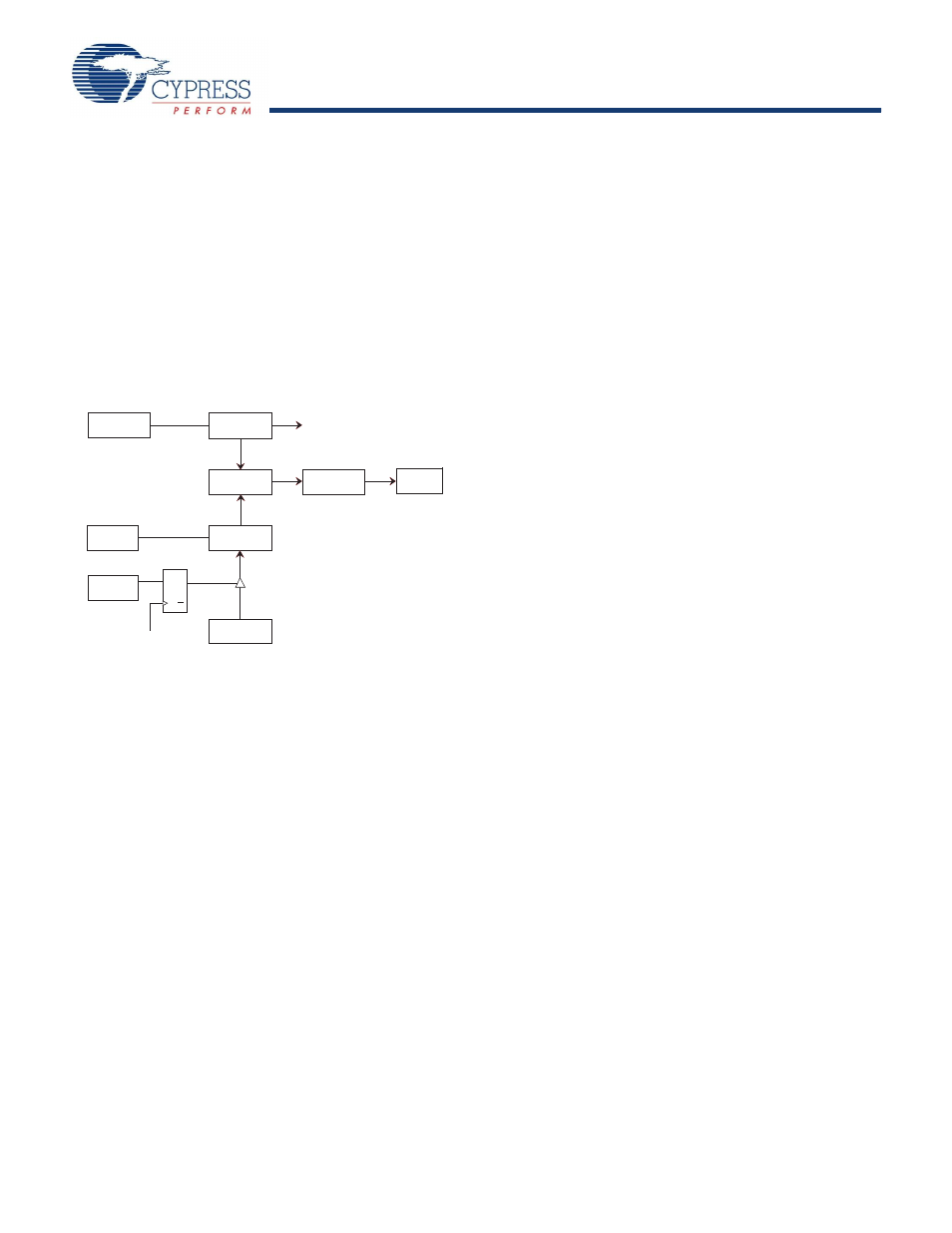
New time out values are written by setting the watchdog write bit
to ‘0’. When the WDW is ‘0’, new writes to the watchdog time out
value bits D5-D0 are enabled to modify the time out value. When
WDW is ‘1’, writes to bits D5-D0 are ignored. The WDW function
enables a user to set the WDS bit without concern that the
watchdog timer value is modified. A logical diagram of the
watchdog timer is shown in
. Note that setting the
watchdog time out value to ‘0’ disables the watchdog function.
The output of the watchdog timer is the flag bit WDF that is set if
the watchdog is allowed to time out. If the Watchdog Interrupt
Enable (WIE) bit in the Interrupt register is set, a hardware
interrupt on INT pin is also generated on watchdog timeout.
The
flag and the hardware interrupt are both cleared when user reads
the Flags registers.
Figure 3. Watchdog Timer Block Diagram
.
Power Monitor
The CY14B104K provides a power management scheme with
power fail interrupt capability. It also controls the internal switch
to backup power for the clock and protects the memory from low
V
CC
access. The power monitor is based on an internal band gap
reference circuit that compares the V
CC
voltage to V
SWITCH
threshold.
As described in the section
when V
SWITCH
is reached as V
CC
decays from power loss, a data
STORE operation is initiated from SRAM to the nonvolatile
elements, securing the last SRAM data state. Power is also
switched from V
CC
to the backup supply (battery or capacitor) to
operate the RTC oscillator.
When operating from the backup source, read and write opera-
tions to nvSRAM are inhibited and the clock functions are not
available to the user. The clock continues to operate in the
background. The updated clock data is available to the user
t
HRECALL
delay after V
CC
is restored to the device (see
Interrupts
The CY14B104K has Flags register, Interrupt register, and
Interrupt logic that can signal interrupt to the microcontroller.
There are three potential sources for interrupt: watchdog timer,
power monitor, and alarm timer. Each of these can be individually
enabled to drive the INT pin by appropriate setting in the Interrupt
register (0x7FFF6). In addition, each has an associated flag bit
in the Flags register (0x7FFF0) that the host processor uses to
determine the cause of the interrupt. The INT pin driver has two
bits that specify its behavior when an interrupt occurs.
An Interrupt is raised only if both a flag is raised by one of the
three sources and the respective interrupt enable bit in Interrupts
register is enabled (set to ‘1’). After an interrupt source is active,
two programmable bits, H/L and P/L, determine the behavior of
the output pin driver on INT pin. These two bits are located in the
Interrupt register and can be used to drive level or pulse mode
output from the INT pin. In pulse mode, the pulse width is
internally fixed at approximately 200 ms. This mode is intended
to reset a host microcontroller. In the level mode, the pin goes to
its active polarity until the Flags register is read by the user. This
mode is used as an interrupt to a host microcontroller. The
control bits are summarized in the following section.
Interrupts are only generated while working on normal power and
are not triggered when system is running in backup power mode.
Note CY14B104K generates valid interrupts only after the
Powerup Recall sequence is completed. All events on INT pin
must be ignored for t
HRECALL
duration after powerup.
Interrupt Register
Watchdog Interrupt Enable - WIE. When set to ‘1’, the
watchdog timer drives the INT pin and an internal flag when a
watchdog time out occurs. When WIE is set to ‘0’, the watchdog
timer only affects the WDF flag in Flags register.
Alarm Interrupt Enable - AIE. When set to ‘1’, the alarm match
drives the INT pin and an internal flag. When AIE is set to ‘0’, the
alarm match only affects the AF Flags register.
Power Fail Interrupt Enable - PFE. When set to ‘1’, the power
fail monitor drives the pin and an internal flag. When PFE is set
to ‘0’, the power fail monitor only affects the PF flag in Flags
register.
High/Low - H/L. When set to a ‘1’, the INT pin is active HIGH
and the driver mode is push pull. The INT pin drives high only
when V
CC
is greater than V
SWITCH
. When set to a ‘0’, the INT pin
is active LOW and the drive mode is open drain. The INT pin
must be pulled up to Vcc by a 10k resistor while using the
interrupt in active LOW mode.
Pulse/Level - P/L. When set to a ‘1’ and an interrupt occurs, the
INT pin is driven for approximately 200 ms. When P/L is set to a
‘0’, the INT pin is driven high or low (determined by H/L) until the
Flags or Control register is read.
When an enabled interrupt source activates the INT pin, an
external host reads the Flags registers to determine the cause.
Remember that all flags are cleared when the register is read. If
the INT pin is programmed for Level mode, then the condition
clears and the INT pin returns to its inactive state. If the pin is
programmed for Pulse mode, then reading the flag also clears
the flag and the pin. The pulse does not complete its specified
duration if the Flags register is read. If the INT pin is used as a
host reset, the Flags register is not read during a reset
Flags Register
The Flag register has three flag bits: WDF, AF, and PF, which can
be used to generate an interrupt. They are set by the watchdog
timeout, alarm match, or power fail monitor respectively.
The
processor can either poll this register or enable interrupts when
a flag is set. These flags are automatically reset once the register
is read. The flags register is automatically loaded with the value
0x00 on power up (except for the OSCF bit. See
1 Hz
Oscillator
Clock
Divider
Counter
Zero
Compare
WDF
WDS
Load
Register
WDW
D
Q
Q
Watchdog
Register
write to
Watchdog
Register
32 Hz
32,768 KHz
