Kenwood TS-430S User Manual
Page 16
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
Program scan operation
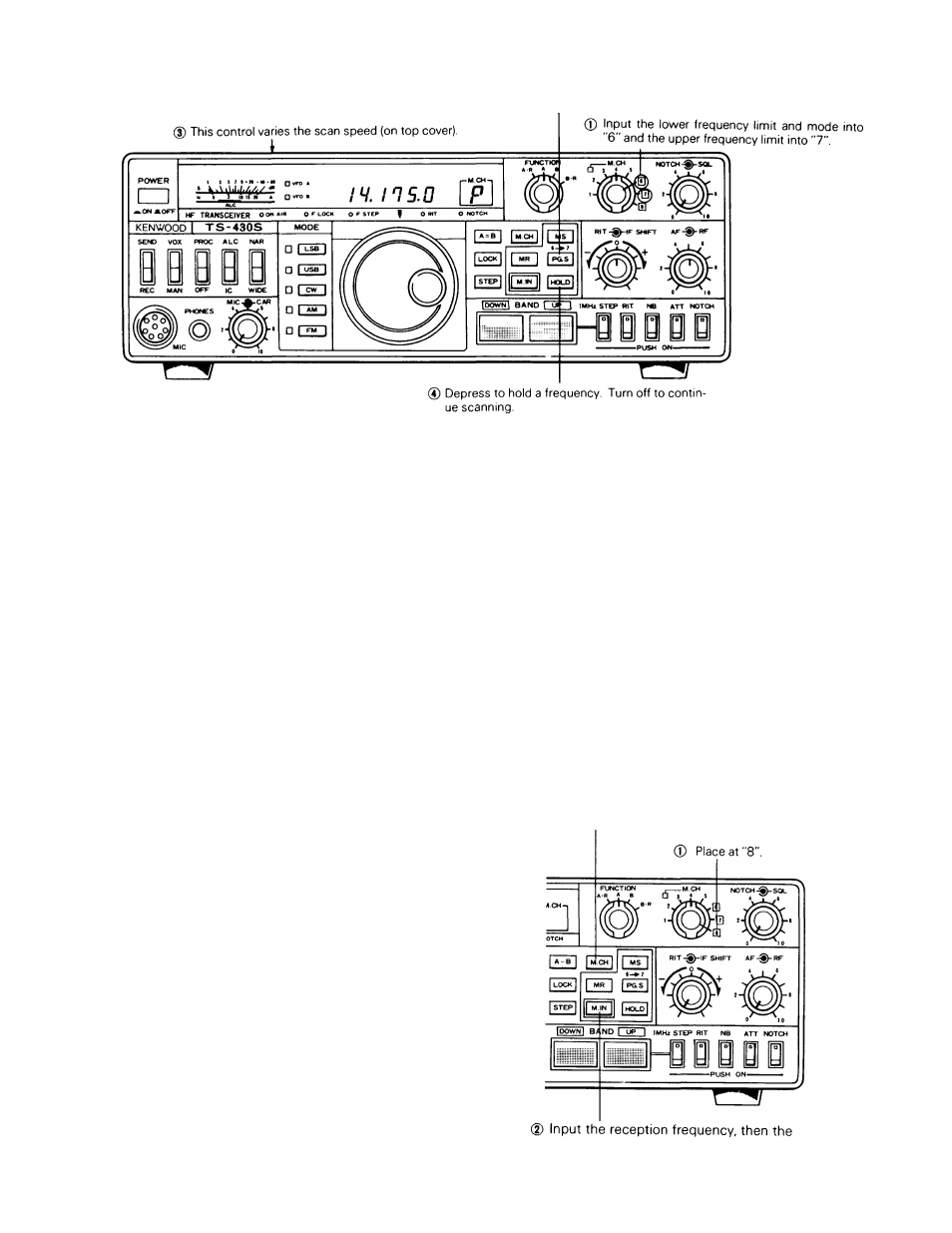
1. Program the scanning frequency range.
2. Input the lower (or upper) frequency limit and mode into
CH 6 (using the M.IN switch). Then, input the upper (or
lower) frequency limit into CH7.
3. Depress the PG.S switch to initiate scan. The letter P
will display during program scan.
4. The scan speed is adjustable using the speed control on
the top panel, along with the STEP switch. Select the
scan speed appropriate for the selected frequency and
mode.
5. When the desired station is received and that frequency
is to be held, depress the HOLD switch. Then, adjust
the VFO for best tuning. During hold, the mode may be
temporarily changed. When Hold is released, the mode
will revert to the original programmed mode setting
after one scan cycle.
6. After the CH 7 upper (or lower) frequency limit has been
reached, a "beep" sounds and the scan repeats from
the CH 6 frequency.
NOTE: --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Program scan is from CH 6 to CH 7, only.
2. During scan, only the CH 6 mode is used.
3.
During scan or scan hold, a frequency can be stored
into a memory channel selected by the M.CH switch by
depressing the M.IN switch.
4. When the scan is on and the STEP switch is depressed,
the step is 100 Hz.
5. When CH 6 and CH 7 are empty, there can be no scan.
6. Scanning is stopped during transmit and resumed after
return to the receive mode.
• Memory CH 8 reception and transmission operation
1. Place the M.CH switch to "8".
2. Input the reception frequency and mode using the M.IN
switch.
3. The usual data entry "beep" is emitted as a pulse train.
Input the transmission frequency (and mode).
4. The "beep" ceases.
5.
Depress the M.CH switch. "Split" frequency operation
(transmission
and
reception
on
different
frequencies
are programmed into CH 8.)
NOTE: --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Different modes and/or bands can also be programmed
for transmission and reception.
2. If the M.IN switch is depressed twice in succession, this
memory can be used as an ordinary memory, now hav
ing the same frequency for both transmission and re
ception.
(D
Pressing this switch TWICE allows
transmission and reception on different
frequencies.
16
