A simple bridging example, Multiport bridges/switches and “bridge groups – Compatible Systems 5.4 User Manual
Page 295
Appendices
289
In all other respects, spanning tree bridges operate in the same fashion as
simple learning bridges.
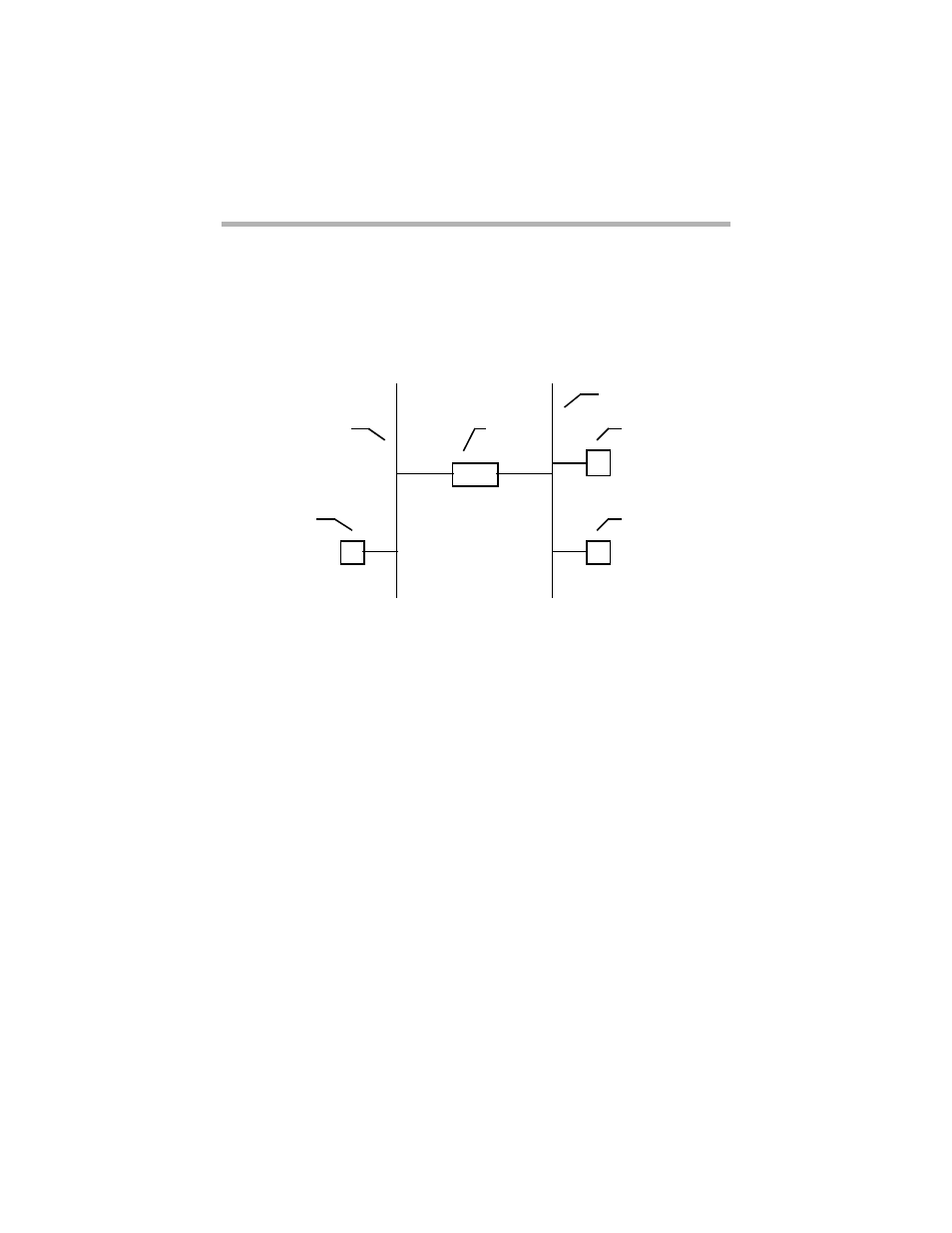
A Simple Bridging Example
Bridging Example
In the diagram above, the bridge develops a table by listening to both the Port
0 net and the Port 1 net. Through the listening process, it associates Worksta-
tion A with Port 0 and Workstations B and C with Port 1. A simplified
bridging table is shown below:
A -> Port 0
B -> Port 1
C -> Port 1
When a packet with A as a destination address arrives at Port 0, the packet is
dropped (A is on the same interface). When a packet with a destination
address of C arrives at Port 0, the packet is forwarded to Port 1. When a packet
with a destination address which isn’t in the table (or a broadcast address)
arrives at Port 1, it is forwarded to Port 0.
Multiport Bridges/Switches and “Bridge Groups”
When a router has multiple interfaces, and also supports bridging/switching,
some new concepts are required to understand the organization of the avail-
able functions.
Backbone
Local
Net
Bridge
Workstation C
Workstation A
Port 0 Net
Port 1 Net
Workstation B
