Cub Cadet U-Channel Beam Style User Manual
Page 21
Hydrualic Diagnosis
17
C.
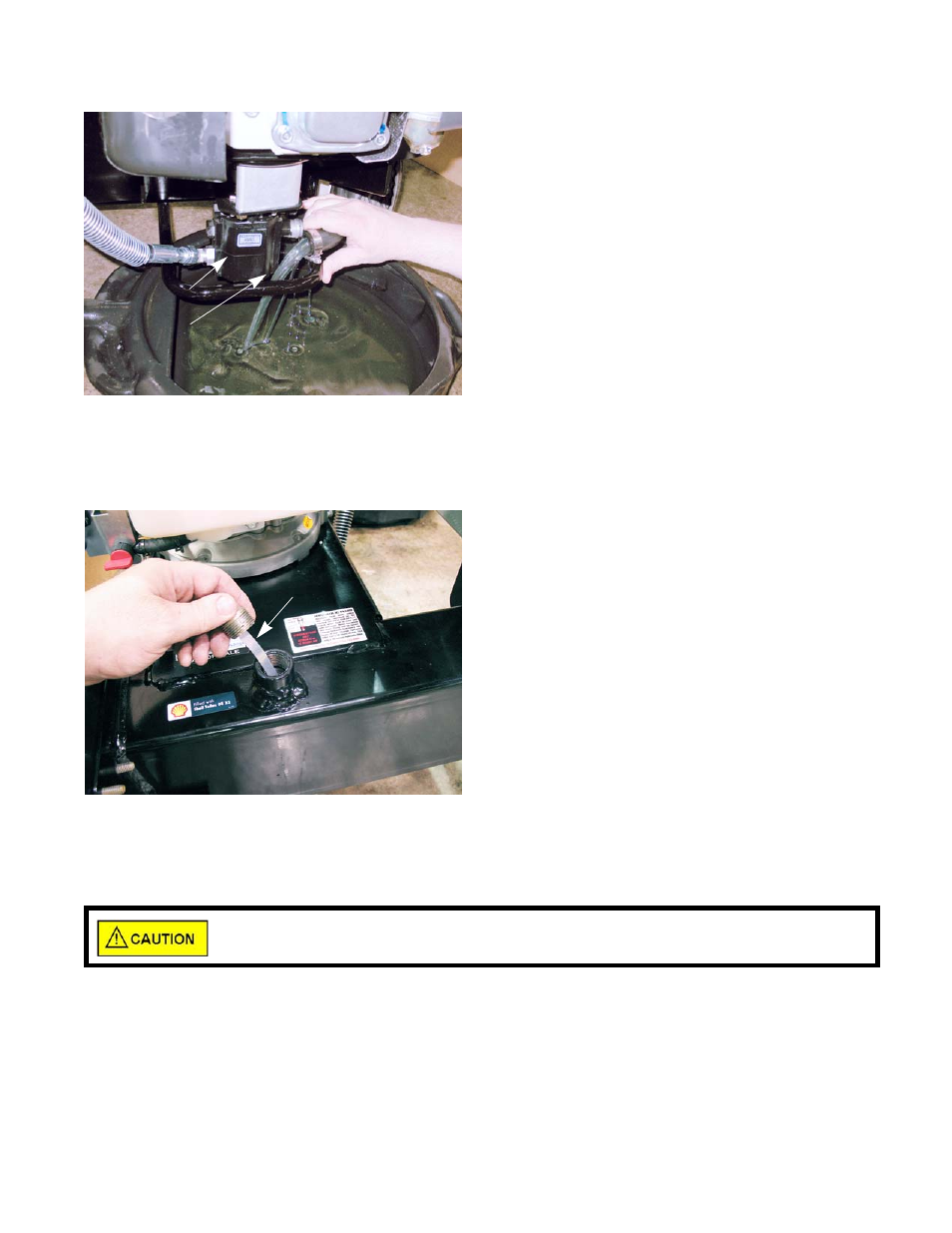
Fluid not getting to the pump See Figure 3.11.
• If fluid is not reaching the pump, the log splitter will
not work
• Continued running with a dry pump will destroy the
pump. This is not warrantable damage.
• To check the fluid supply to the pump:
a.
Place a drain pan under the pump.
b.
Disconnect the suction hose from the pump.
c.
Fluid should flow freely from it.
• Watch the hose that feeds the pump while the ram
is in motion. If the hose is collapsing, it will block-
off the supply of fluid to the pump.
• Entrained air from a suction hose leak will cause a
loss of splitting force and a noisy pump.
D.
Low fluid / wrong fluid: See Figure 3.12.
• With the log splitter on level ground, remove the
dipstick from the tank to check the fluid.
• Check fluid cold. It expands when it gets hot.
• Read the fluid level on the dipstick.
• The reservoir will hold 3 or 5 gallons depending on
the model.
• Use either Dexron III ATF or SAE 10WAW (ISO 32
viscosity grade) hydraulic fluid. Do not mix the two.
NOTE: Models that are produced pre-filled, are filled with
10WAW (ISO 32).
• If in doubt, drain it out; replace the fluid with known
correct hydraulic fluid.
• Too little fluid will starve the pump.
• Too much fluid will slow performance and spill from
the vent.
E.
Cold temperatures
•
Hydraulic fluid gets thick at low temperatures; the splitter should not be used with hydraulic fluid tempera-
ture below 20
°
F. (-6.66
°
C.)
•
Hydraulic tests should be performed with the fluid warmed-up to 120
°
F. (49
°
C.) to get accurate results.
•
When the fluid is too cold, pressure will be high and flow will be low.
•
When the fluid is too cold, log splitter operation will be sluggish.
Figure 3.11
Pump
Oil free flowing
Figure 3.12
Dip stick
Hot hydraulic fluid can cause burns. Do not check the fluid until the hydraulic system has
cooled to ambient temperature after use.
