3 calculating fiber link attenuation, Calculating fiber link attenuation, Maintenance 9145elb nid hardware user’s manual – CANOGA PERKINS 9145ELB Network Interface Device Hardware User Manual
Page 47: Checking optical power levels
Maintenance
9145ELB NID Hardware User’s Manual
Checking Optical Power Levels
33
web site. The power level must be lower than the saturation level. If not, contact Canoga
Perkins Technical Support.
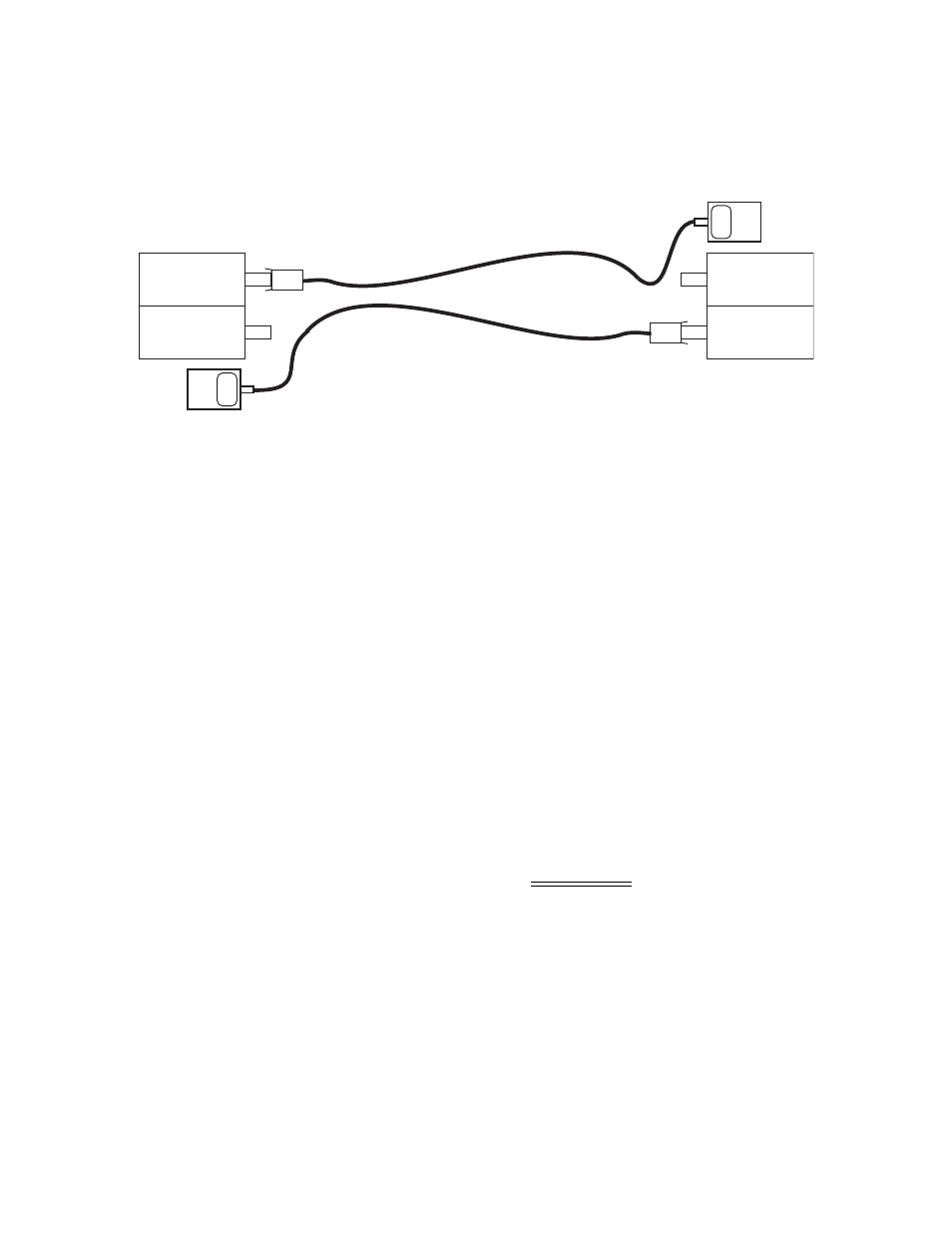
Figure 6-2 Measuring Receiver Input Power
6.2.3 Calculating Fiber Link Attenuation
Link attenuation measurement identifies potential problems with links that are on the threshold of
receiver sensitivity. Measure optical fiber links at the shortest wavelength of operation, as it is the
limiting factor in the loss budget. Use a power meter calibrated for the laser source, then factor in
approximately 1 dB for the connector loss from the patch cables between the 9145ELB and the
local device. (Each fiber connection can generate 0.5 dB of additional loss.)
If you cannot determine the Rx sensitivity, contact Canoga Perkins Technical Support for
assistance.
Follow these steps to calculate fiber link attenuation:
1. Determine transmitter output power as described in section 6.2.1.
2. Determine receiver input power as described in section 6.2.2.
3. Subtract receiver input power from transmitter output power. The result is the fiber link
attenuation.
Transmit Output Power
-7.0 dBm
Receiver Sensitivity
-28.2 dBm
Fiber Link Attenuation
21.2 dB
FIBER OPTIC
TRANSMITTER
FIBER OPTIC
RECEIVER
OPT
IC
A
L
P
O
WE
R
ME
TER
-2
4
dB
m
λ
= 1
300
nm
FIBER OPTIC
TRANSMITTER
FIBER OPTIC
RECEIVER
OPT
IC
A
L
P
O
WE
R
ME
TER
-2
4
dB
m
λ
= 1
300
nm
LOCAL SITE
REMOTE SITE
