Compaq COBOL AAQ2G1FTK User Manual
Page 188
Processing Files and Records
6.1 Defining Files and Records
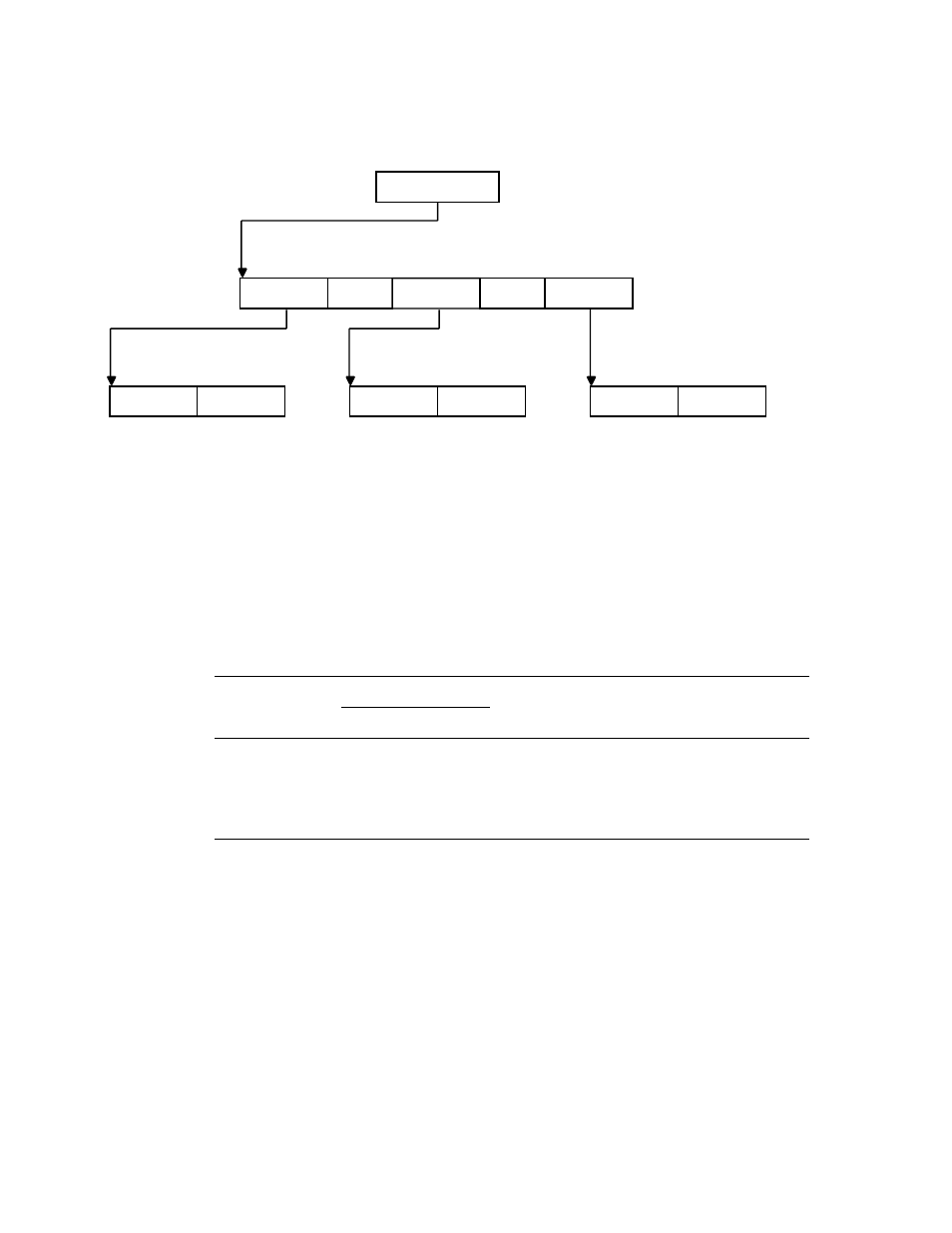
Figure 6–5 Indexed File Organization
record
Key Definition
...
...
Primary key index (employee name)
...
...
ABLE
SMITH
JONES
ABLE
ELM AVE
JONES
MAIN ST
COLT RD
SMITH
record
record
ZK−6058−GE
For a more detailed explanation of indexed file structure on OpenVMS Alpha
systems, see the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications.
♦
For information about specifying file organization in your program, see
Section 6.2.2.
6.1.2 Record Format
Compaq COBOL provides four record format types: fixed, variable, print-control,
and stream. Table 6–2 shows the record format availability.
Table 6–2 Record Format Availability
Sequential
Line
Sequential
Relative
Indexed
Disk
Tape
Fixed length
yes
yes
no
yes
yes
Variable length
yes
yes
no
yes
yes
Print control
yes
no
no
no
no
Stream
no
no
yes
no
no
The compiler determines the record format from the information that you specify
as follows:
•
Fixed record format—Use the RECORD CONTAINS clause. This is the
Compaq COBOL default.
•
Variable record format—Use the RECORD CONTAINS TO clause or the
RECORD VARYING clause.
•
Print-control (VFC on OpenVMS Alpha systems or ASCII on Tru64 UNIX
and Windows NT systems)—use the Procedure Division ADVANCING phrase,
the Environment Division APPLY PRINT-CONTROL or (on Tru64 UNIX and
Windows NT systems) ASSIGN TO PRINTER clauses, or the Data Division
LINAGE clause, or use Report Writer statements and phrases.
•
Stream—Use the FILE-CONTROL ORGANIZATION IS LINE SEQUENTIAL
clause. On OpenVMS Alpha you also get this format with /NOVFC.
6–8 Processing Files and Records
