2 communication protocols, 1 escape protocol, Escape protocol – Rice Lake RL550 Digital Chair Scale Technical and Operating Instructions User Manual
Page 24
20
Rice Lake 550 Digital Chair Scale Technical Manual
7.2
Communication Protocols
The Rice Lake Digital Chair Scale has two communication protocols, escape and maintenance protocol.
7.2.1
Escape Protocol
An escape protocol is where the escape (0X1B or ASCII 27) is used to indicate that there is a command
following. On the PC side there must be a listener created by the vendor that will interpret this protocol. This
listener must also take care of all the issues regarding data integrity, etc. to make sure that the data that was sent
and received is valid.
Two examples include:
•
Scale initiated communication
•
PC initiated communication
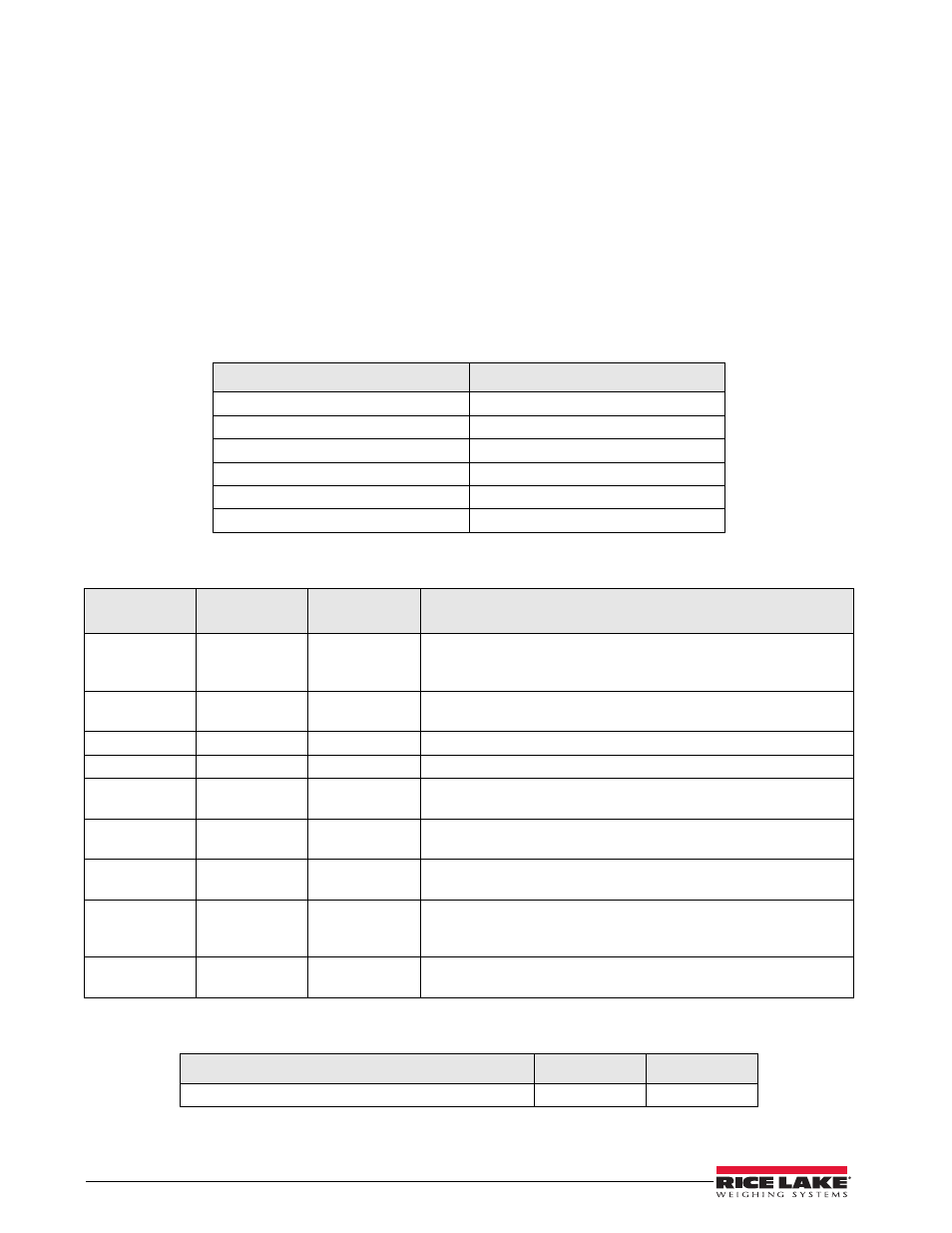
Table 7-1 is what can be sent across communications lines.
Table 7-1. Escape Protocol Commands
PC Initiated
ESC Value
Request current values/settings
R
Diagnostics
A
Send scale control messages
C
PC Initiated
ESC Value
Send single reading
R
Send diagnostic response
Table 7-2 lists the ESC characters that will be used.
Table 7-2. ESC Characters
Name
ESC character
ESC value with
parameters
Description
Reading
R
R
Tells the PC that the scale is sending a reading. Immediately following
this is the value that is sent. Example:
Weight
W
Wnnn.n
Is the patient weight (example: W02000 means 200.0). If the scale is
overloaded or under loaded, the scale will return the value 999.99.
Height
H
Hnnn.n
Patient height
BMI
B
Bnn.n
Patient BMI
Units
N
Nc
Indicates in which unit the values have been taken (m=metric,
c=constitutional).
End of Packet
(EOP)
E
E
Indicates that the end of the command has been reached.
Diagnostics
(request)
A
Accc
A request for a diagnostic test on certain parts of the scale (such as
battery life, load cells).
Diagnostics
(response)
Z
Zccc
This will be the response of the diagnostics done on the scale. Values
will include error codes to indicate what is wrong with the scale, or all
zeros (Z000) to indicate that all is well.
Control (set a
value)
C
Cccc=c
Sets the value of the scale’s global settings. Example: Table 7-3. Scale Global Values List and Identifiers Name of Control Identifier Unit Unit of Measure (metric or constitutional) UOM c (m or c)
