HP 10B User Manual
Page 51
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
m
шш
ш
Ш]
(ЁУ)
Number of periods or payments.
Annual percentage interest rate (usually the annual nomi
nal rate).
Present value (the cash flow at the beginning of the time
line).
Periodic payment.
Future value (the cash flow at the end of the cash flow
diagram, in addition to any regular periodic payment).
You can calculate any value after entering the other four. Cash flow
diagrams for loans, mortgages, leases, savings accounts, or any contract
with regular cash flows of the same amount arc normally treated as TVM
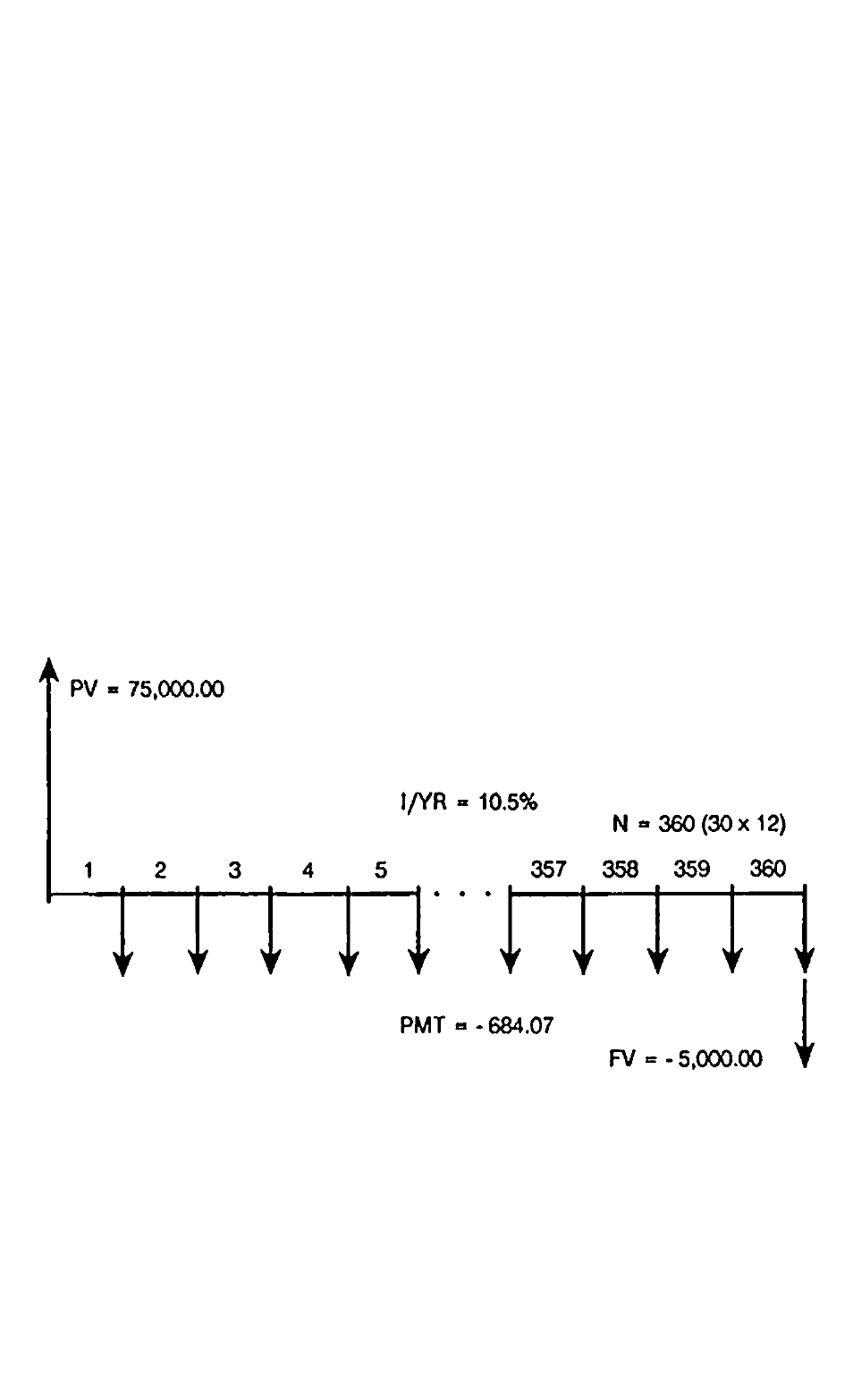
problems. For example, following is a cash flow diagram, from the
borrower’s perspective, for a 30-ycar, $75,000.00 mortgage, with a pay
ment of $-684.07, at 10.5% annual interest, with a $5,000 balloon pay
ment.
One of the values for
PV^
PA/T,
FV
can be zero. For example, following is
a cash flow diagram (from the saver’s perspective) for a savings account
with a single deposit and a single withdrawal five years later. Interest
compounds monthly. In this example, PA/r is zero.
4в 4: Picturing Financial Problems
