I/o ports and connectors, Serial and parallel connectors – Dell PowerEdge 1500SC User Manual
Page 4
Back to Contents Page
I/O Ports and Connectors
Dell™ PowerEdge™ 1500SC Systems User's Guide
Serial and Parallel Connectors
Integrated Network Interface Controller Connector
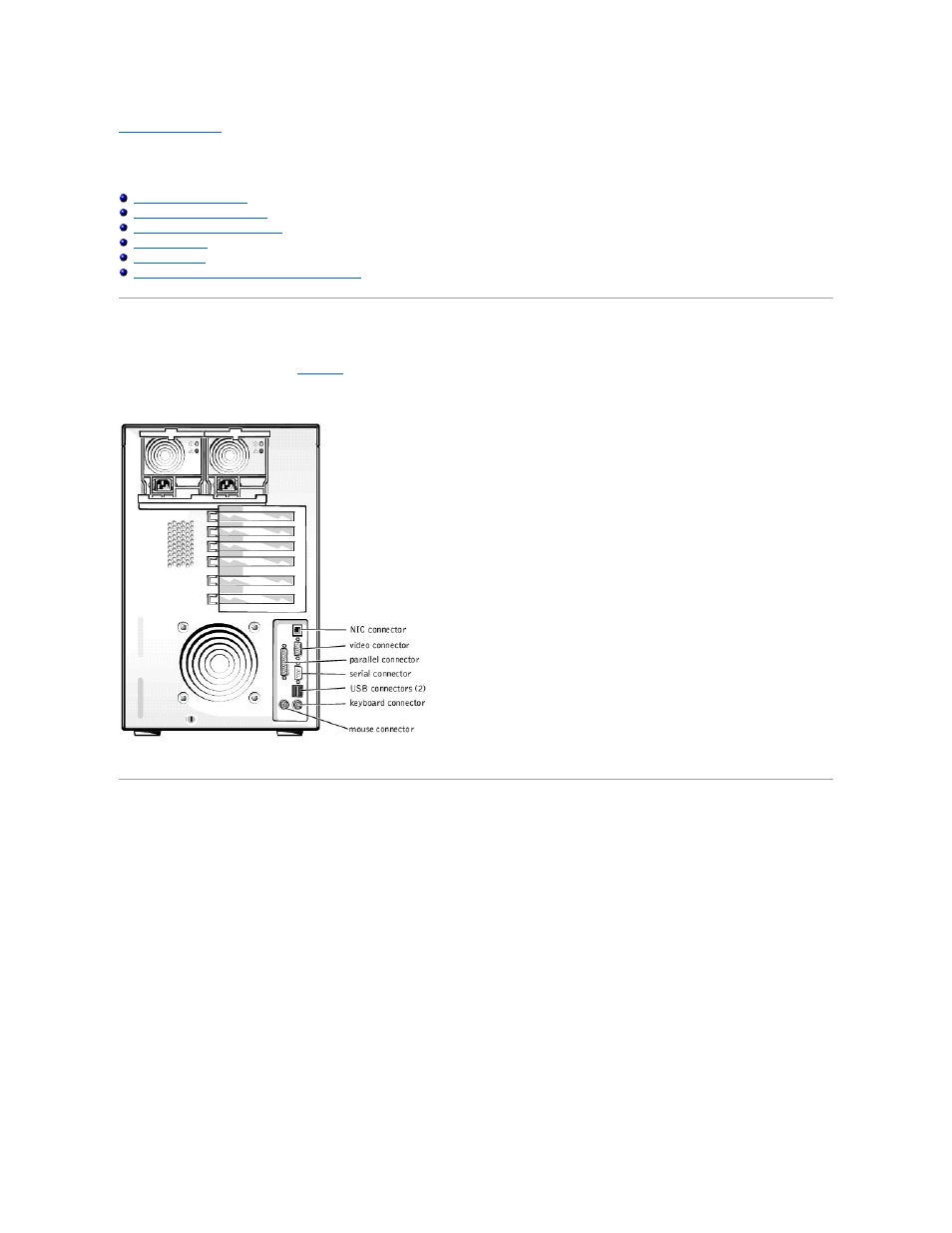
I/O Ports and Connectors
The I/O ports and connectors on the back panel of the system are the gateways through which the system communicates with external devices, such as a
keyboard, mouse, printer, and monitor.
identifies the I/O ports and connectors for your system.
Figure B-1. I/O Ports and Connectors
Serial and Parallel Connectors
The integrated serial connector uses a 9-pin D-subminiature connector on the back panel. This connector supports devices such as external modems, printers,
plotters, and mice that require serial data transmission (the transmission of data one bit at a time over one line).
Most software uses the term COM (for communications) plus a number to designate a serial connector (for example, COM1 or COM2). The default designation
of your system's integrated serial connector is COM1.
The integrated parallel connector uses a 25-pin D-subminiature connector on the system's back panel. This I/O port sends data in parallel format (where eight
data bits, or one byte, are sent simultaneously over eight separate lines in a single cable). The parallel connector is used primarily for printers.
Most software uses the term LPT (for line printer) plus a number to designate a parallel connector (for example, LPT1). The default designation of the system's
integrated parallel connector is LPT1.
Port designations are used, for example, in software installation procedures that include a step in which you identify the connector to which a printer is
attached, thus telling the software where to send its output. (An incorrect designation prevents the printer from printing or causes scrambled print.)
Expansion Cards Having a Serial or Parallel Connector
The system has an autoconfiguration capability for the serial connectors. This feature lets you add an expansion card containing a serial connector that has
the same designation as one of the integrated connectors, without having to reconfigure the card. When the system detects the duplicate serial connector on
the expansion card, it remaps (reassigns) the integrated connector to the next available designation.
Both the new and the remapped COM connectors share the same interrupt request (IRQ) setting, as follows:
l
COM1, COM3: IRQ4 (shared setting)
