Bio-Rad Nonmagnetic Beads and Related Reagents User Manual
Page 6
Section 2
Principle
Amine Coupling
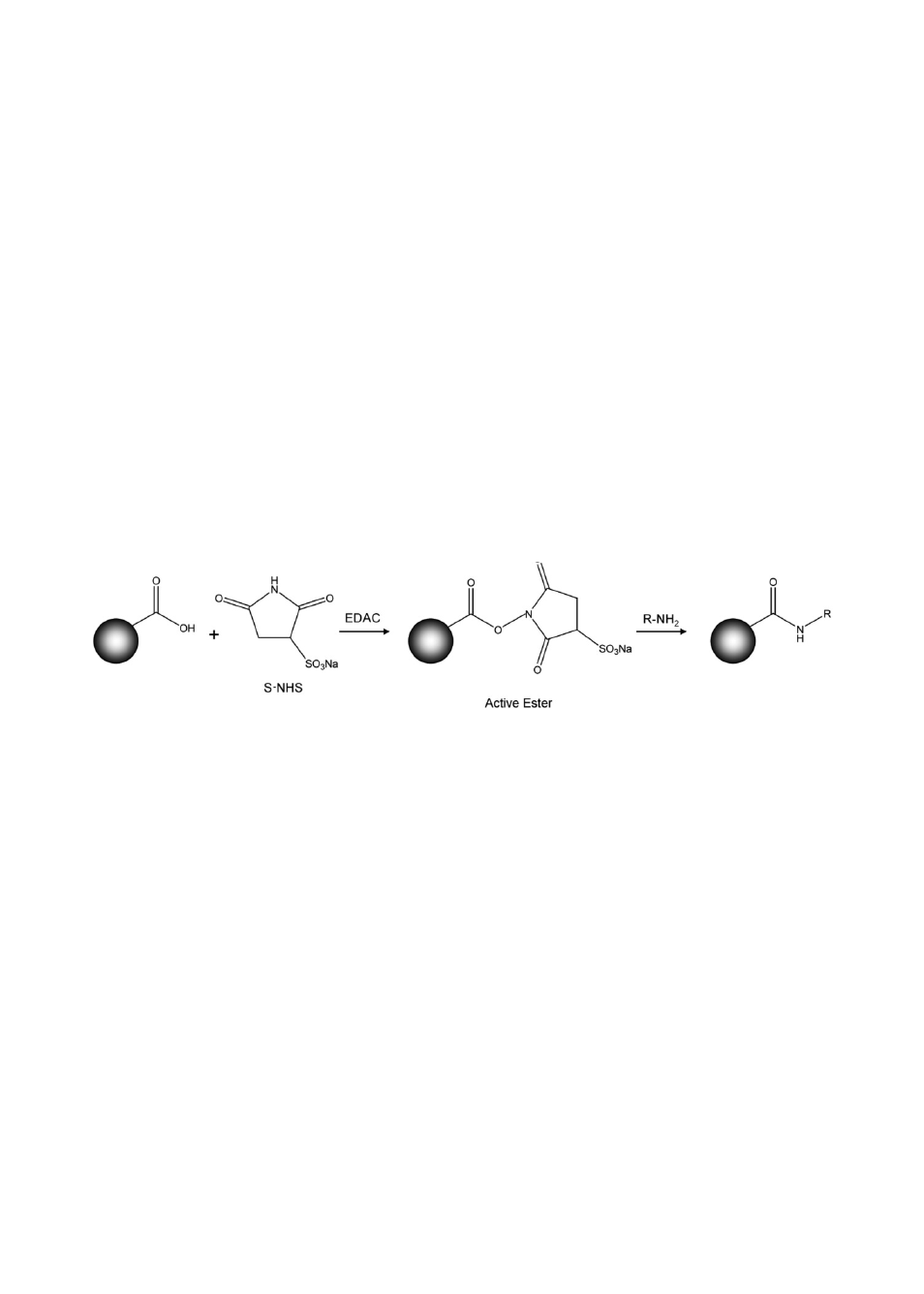
The coupling procedure involves a two-step carbodiimide reaction. The carboxyl
groups on the surface of the polystyrene beads must first be activated with a
carbodiimide derivative prior to coupling the protein. EDAC (1-ethyl-3-[3-
dimethylaminopropyl] carbodiimide hydrochloride) reacts with carboxyl groups
on the surface of the beads to form an active O-acylisourea intermediate. This
intermediate forms a more stable ester using S-NHS (N-
hydroxysulfosuccinimide). The ester reacts with the primary amines (NH
2
groups)
of proteins or amine-modified oligonucleotides to form a covalent bond (amide
linkages).
A number of buffers can be used successfully in this coupling reaction. As no
buffer is ideal for every ligand, the protocols provided in this manual do not
contain recommendations for specific buffers. Generally the pH at which a
coupling reaction occurs should be compatible to the solubility of the ligand of
interest. PBS and MES buffers are two popular choices mentioned in this
manual. PBS buffer is provided in the kit. MES buffer can be prepared according
to the formulation provided in Section 8 for the coupling of oligonucleotides.
Protein Preparation
This coupling procedure can be used to covalently couple water soluble
proteins ranging in size from 6–150 kD via carboxyl groups on the surface of
the beads. The protein sample must be free of sodium azide, BSA, glycine, Tris,
or amine-containing additives and must be suspended in PBS, pH 7.4. Optimal
protein coupling conditions must be established. First determine how much
protein will be required for the coupling reaction to promote optimal binding
4
