Bio-Rad SsoAdvanced™ Universal Probes Supermix User Manual
Page 23
| 17
SsoAdvanced
™
Universal Probes Supermix Instruction Manual
| 17
2. Either remove this data point or dilute your sample so that it does not show amplification earlier
than cycle 15. This ensures that the software’s algorithm has enough background to subtract
from the signal. Early amplification may cause the algorithm to fail due lack of background data.
If you notice high standard deviations for technical replicates or inconsistent gene
expression data, this could be due to the threshold being positioned either too high or
too low. Consider the following corrective action:
When setting the threshold, you should choose a position that is in the middle of the geometric
(exponential) phase of PCR. Setting the threshold too high or too low places the threshold in a less
than ideal region of amplification where greater noise is present and PCR is not 100% efficient.
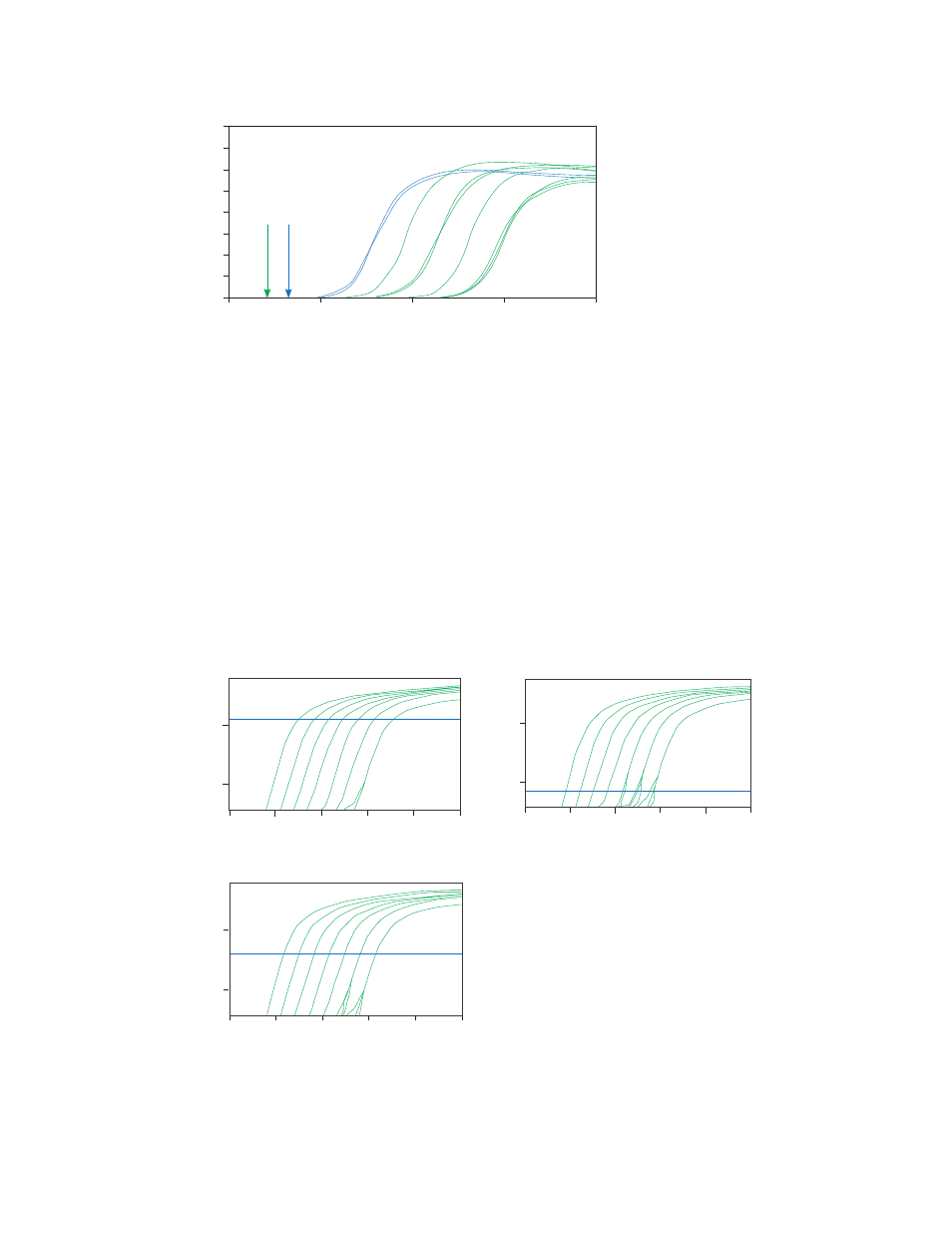
Fig. 12. Baseline setting is best completed in the linear view. In this example,
the amplification starts around cycle 8; therefore, setting the end baseline two
cycles prior at cycle 6 is best.
Fig. 13. Illustrations of baseline settings. A, when the threshold is set too high, the data collected are often
from the linear phase of PCR, where the reaction is not the most efficient; B, the threshold is set too low. When
set too low, the data collected are often within the background noise of the reaction; C, a correct threshold
setting where the data collected are within the geometric (exponential) phase of PCR.
Amplification
Cycles
R
FU
0
10
20
30
40
50
10
2
10
3
Amplification
Cycles
R
FU
0
10
20
30
40
50
10
2
10
3
Amplification
Cycles
R
FU
0
10
20
30
40
50
10
2
10
3
A B
C
(R
FU
)(10
^
3)
16
Cq 6 Cq 8
14
12
10
10
40
30
20
8
6
4
2
0
0
Amplification
Cycles
