Remedies, Duplexer problems and remedies – Bird Technologies 28-88-04B User Manual
Page 14
TXRX Systems Inc. Manual 7-9176-4 06/23/04 Page
10
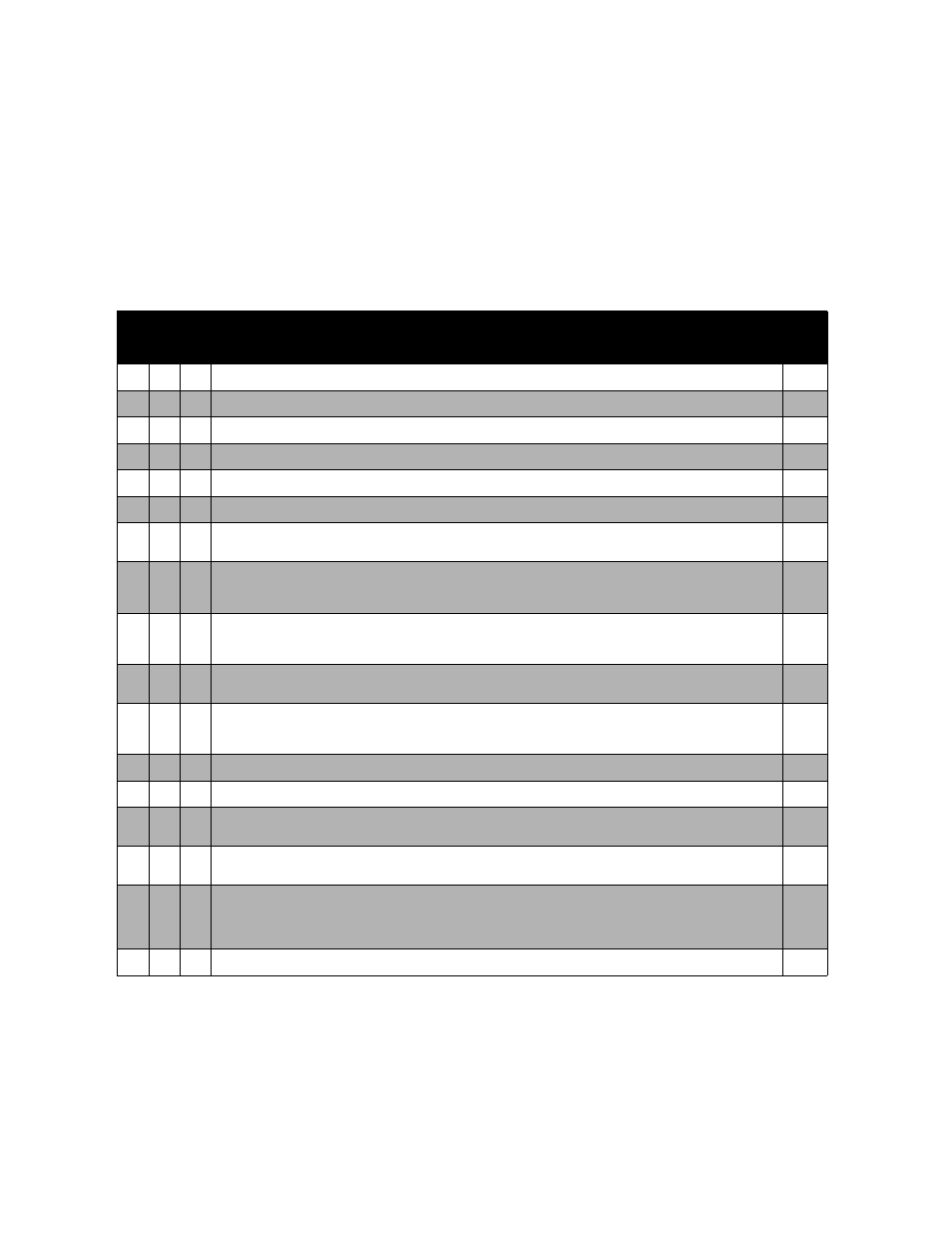
PROBLEM
POTENTIAL CAUSE
The number at right corresponds to the appropriate numbered remedy paragraph
A
B
C
•
•
Reverse labeling of Tx and Rx terminals.
1
•
•
Unit tuned to wrong frequencies.
2
•
Bad antenna or interconnect cables.
3
•
•
Use of between series adapter, especially UHF types.
4
•
•
•
Duplexer detuned in shipment.
5
•
•
Water has entered the Duplexer antenna connector from the antenna feed line.
6
•
•
Spurious Tx output is being reflected by the selective Duplexer input terminal and observed on the wattmeter, the
wattmeter being unable to discriminate between on-frequency and off-frequency energy.
7
•
Bad joint in a cable or antenna system beyond the antenna of the Duplexer. All lines may show zero reflected power,
but noise can still be produced when a corroded or indefinite metal-to-metal contact is exposed to RF energy. When
this occurs beyond the Duplexer, it cannot be filtered out, and the noise backs up into the receiver.
8
•
Adverse cable length between Duplexer and transmitter using varactor or broadband hybrid combining type trans-
mitter outputs. Even though the Duplexer VSWR is flat on frequency, the reflected impedance of the Duplexer off
resonance, transformed by changing cable lengths, can cause parasitics to be generated.
9
•
Duplexer transmitter mixing with another outside transmitter, producing intermodulation on or near the receiver fre-
quency.
10
•
Transmitter cable leading to Duplexer in close proximity to Duplexer antenna or receiver cable. This is usually only a
problem on close separation Duplexers, (1.0 MHz or less) where the 85 to 100 dB isolation is decreased by adverse
coupling, created by running these cables too close together for too great a distance.
11
•
Inadequate shielding of transmitter and receiver modules in the repeater.
12
•
Insufficient duplex isolation for the application.
12
•
A spurious transmitter response outside of the normal Duplexer isolation band or inadequacy of notch filter type
Duplexers to suppress a wide enough band of Tx noise to protect the receiver.
14
•
Impedance change in antenna due to icing. VSWR increase may be sufficient to reflect back through the Duplexer
and upset transmitter tuning, causing parasitics, which are not suppressed by the Duplexer.
15
•
The addition of a broadband power amplifier to a low power transmitter. The noise floor of the low power radio is
raised by an amount equal to the gain of the power amplifier, and in addition, the power amplifier will contribute its
own noise. Power amplifiers are just as prone to the generation of parasitics as transmitters, and may be triggered
by an adverse cable length between power amplifier and Duplexer, a problem covered above.
16
•
Excessive loss with changing temperature and apparent Duplexer detuning.
17
1. Tune a signal generator to the receive frequency and inject it into the antenna terminal, sampling for the signal at each equipment terminal.
Reverse the labels if necessary. It may be that the unit was ordered to the reverse frequencies. If so, the label will indicate this. If the duplexer is
symmetrical in design (usually indicated by the same number of Tx and Rx sections) just reverse the equipment labels and operate. Generally, no
damage will be done to the duplexer when operated in reverse for a short period. If other adverse symptoms appear, contact the factory.
REMEDIES
Duplexers are passive devices requiring little or no service once installed in a system. The proper design and application of a given Duplexer will give
years of trouble free service. When problems do occur in a duplex system it is necessary to identify as many abnormal conditions as possible to zero in
on the specific cause of the problem. Unfortunately,there are only a few measurable or observable performance indicators at the disposal of the field
serviceman, and any number of conditions may exist, even simultaneously, which are responsible for the observed phenomena. Most Duplexer installa-
tion problems fall into three categories. Each of these three conditions will be treated separately, using the typical cause and remedy approach.
DUPLEXER PROBLEMS AND REMEDIES
A. High input VSWR
B. Excessive loss
C. Desensitization of the receiver
