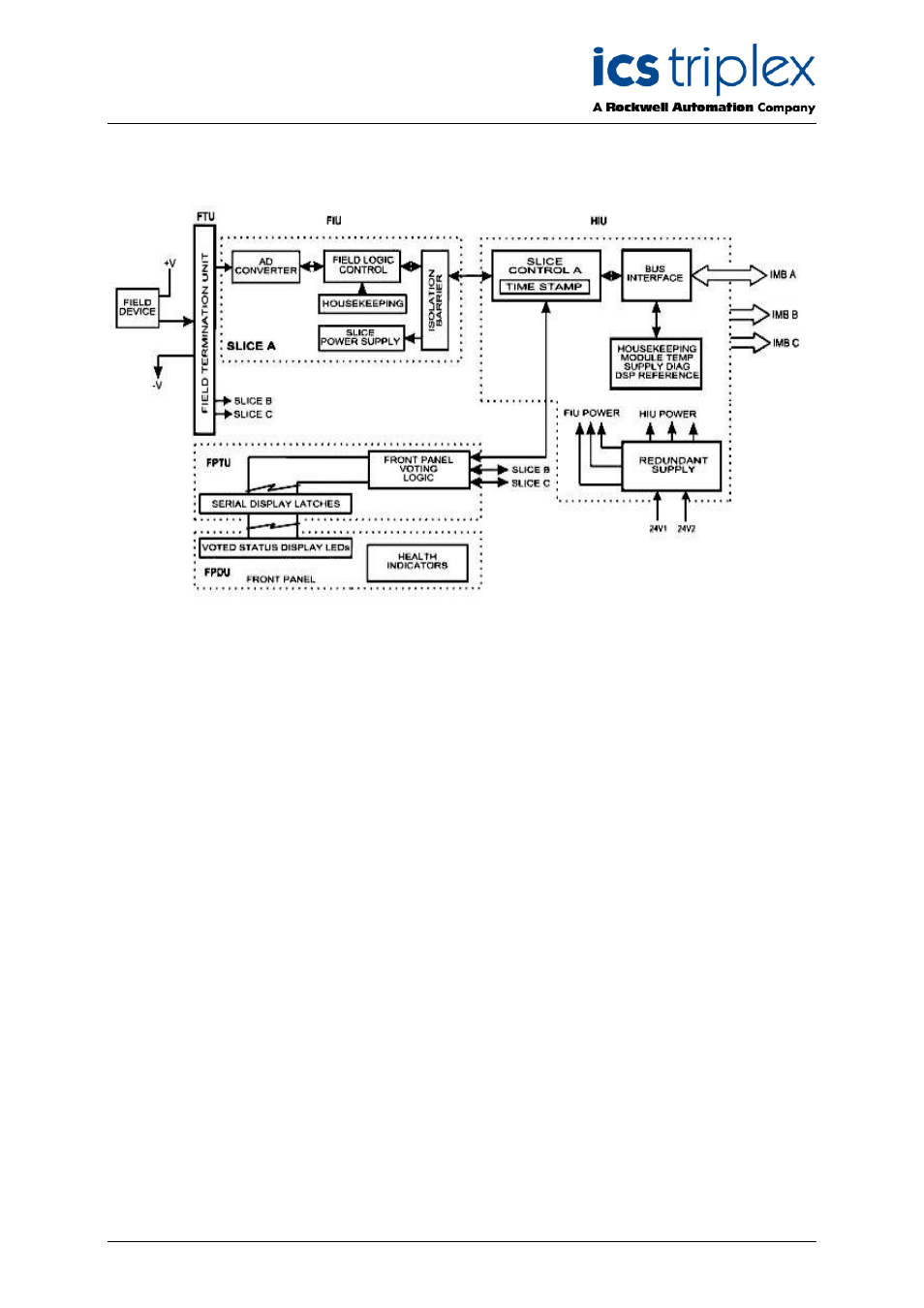
Field termination unit (ftu), Field interface unit (fiu), Figure 2 functional block diagram – Rockwell Automation T8432 Trusted Dual Vdc Analogue Input Module - 60 Channel User Manual
Page 9
Trusted
TM
Module T8432
Issue 16 Apr 10
PD-T8432
9
Figure 2 shows a simplified functional block diagram of the Trusted
TM
Dual 24V dc Analogue Input
module.
Figure 2 Functional Block Diagram
1.1.
Field Termination Unit (FTU)
The Field Termination Unit (FTU) is the I/O module assembly that connects all three FIUs to a field
connector. The FTU primarily contains passive components necessary for front-end signal
conditioning. When installed in a Trusted
TM
Controller or Expander Chassis, the FTU field connector
mates to the Field I/O Cable Assembly attached at the rear of the chassis.
The SmartSlot link is passed from the HIU to the field connections via the FTU. These signals go
directly to the I/O cable assembly and maintain isolation from the I/O signals on the FTU. The
SmartSlot link is the intelligent connection between active and standby modules for co-ordination
during module replacement.
1.2.
Field Interface Unit (FIU)
The Field Interface Unit (FIU) is the section of the module that contains the specific circuits necessary
to interface to the particular types of field I/O signals. Each module has three FIUs, one per slice. For
the Dual 24V dc Analogue Input module, two of the three FIUs allocate an analogue to digital (A/D)
converter for each of the 60 field inputs.
The FIU receives isolated power from the HIU for logic. The FIU provides additional power
conditioning for the operational voltages required by the FIU circuitry. An isolated 6.25Mbit/sec serial
link connects each FIU to one of the HIU slices.
The FIU also measures a range of on-board “house-keeping” signals that assist in monitoring the
performance and operating conditions of the module. These signals include power supply voltages,
current consumption, on-board reference voltages, board temperature, and condensation.
