Calculating bending strain—flat thick specimens, Calculating bending strain—flat thick specimens 38, Where – MTS Series 609 Alignment Fixture User Manual
Page 38
Series 609 Alignment Fixture Product Information
38
Calculating Bending Strain—Flat Thick Specimens
Specimen Preparation
Calculating Bending Strain—Flat Thick Specimens
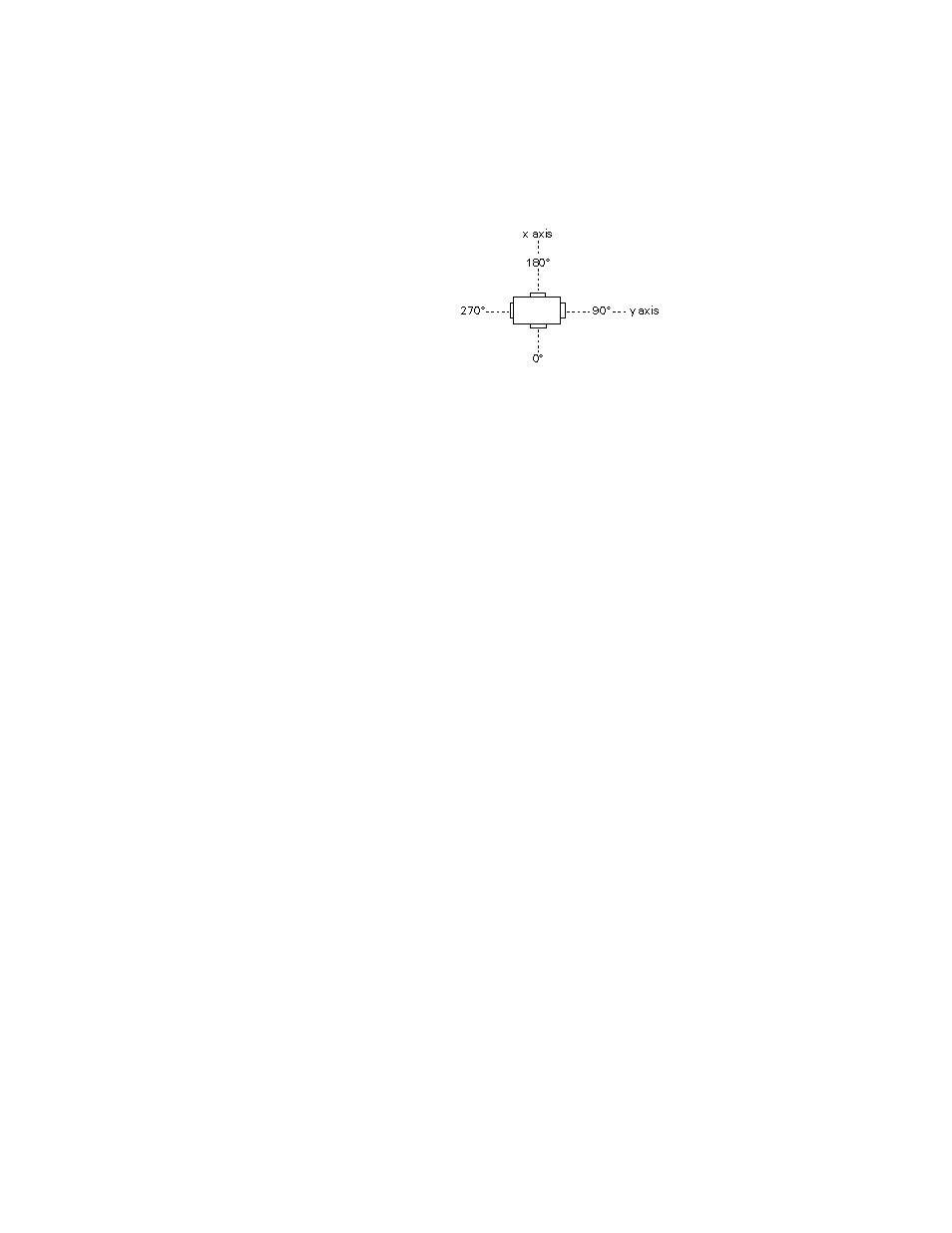
This section shows how to calculate the bending strain for flat specimens with
four gages at each level.
Gage Placement
1. Calculate the bending strains for each level.
Use these formulas to find the x axis (B
x
) and y axis (B
y
) bending strains of
each level:
Where:
ε
1
through
ε
12
are the strain readings from gages 1 through 12
Bu
x
is the bending strain of the x axis of the upper gages
Bm
x
is the bending strain of the x axis of the middle gages
Bl
x
is the bending strain of the x axis of the lower gages
Bu
y
is the bending strain of the y axis of the upper gages
Bm
y
is the bending strain of the y axis of the middle gages
Bl
y
is the bending strain of the y axis of the lower gages
Do not ignore the sign of negative numbers.
2. Calculate the average axial strain for each level.
Use this formula to find the average axial strain (A):
Where:
ε
1
through
ε
12
are the strain readings from gages 1 through 12
Au is the average strain of the upper gages
Am is the average strain of the middle gages
Al is the average strain of the lower gages
Bu
x
ε
1
ε
3
–
2
----------------
=
Bu
y
ε
2
ε
4
–
2
----------------
=
Bm
x
ε
5
ε
7
–
2
----------------
=
Bm
y
ε
6
ε
8
–
2
----------------
=
Bl
x
ε
9
ε
11
–
2
------------------
=
Bl
y
ε
10
ε
12
–
2
---------------------
=
Upper Gages
Middle Gages
Lower Gages
Au
ε
1
ε
2
ε
3
ε
4
+
+
+
4
---------------------------------------
=
Am
ε
5
ε
6
ε
7
ε
8
+
+
+
4
---------------------------------------
=
Al
ε
9
ε
10
ε
11
ε
12
+
+
+
4
----------------------------------------------
=
Upper Gages
Middle Gages
Lower Gages
