Carbolite GVC Series User Manual
Page 9
G range
MF48 -1.18
9
to the progressive shrinkage of the insulation materials. Cracks are not usually detrimental to the
functioning or the safety of the furnace.
3.4 Operator Safety
The ceramic materials used in furnace manufacture become electrically conductive to some extent
at high temperatures. Also, there are partially exposed heating coils in the chamber. DO NOT use
any conductive tools within the work tube without isolating it. If a metal work tube is used, it must
be earthed (grounded).
Switch off the Heater switch whenever loading or unloading the furnace. The elements are isolated
when the Heater switch is OFF. This switch cuts both sides of the circuit directly or via a contactor
(a contactor is used in models where the rated current exceeds 16 Amps).
3.5 Tube Life
A ceramic work tube may be cracked if workpieces are inserted
too quickly or at temperatures below 900°C when the tube is
more brittle. Large pieces should also be heated slowly to ensure
that large temperature differences do not arise.
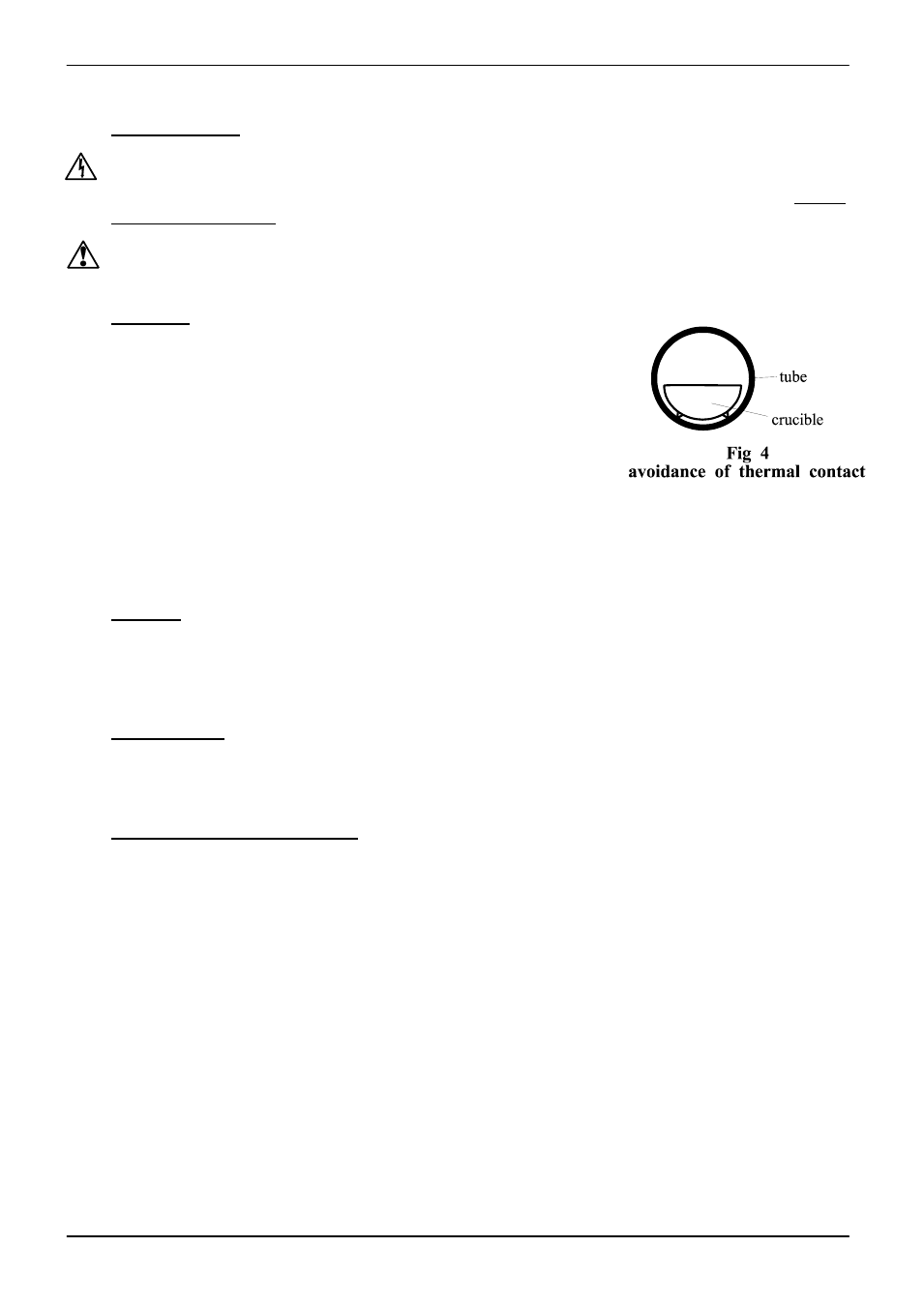
Poor thermal contact should be encouraged between the
workpiece and the tube; crucibles or boats should be of low
thermal mass and should have feet to reduce the contact with the
tube (fig. 4).
Do not set too high a heating rate. Large diameter tubes are more susceptible to thermal shock than
smaller. Tubes that extend beyond the heated part of the furnace are more at risk. A general rule
for maximum heating rate is 400/internal diameter (°C/min); for 75mm i/d tubes this comes to 5°C
per minute. The controller can be set to limit the heating rate.
3.6 Pressure
Work tubes are not able to accept high internal pressure. When gas seals or similar fittings are in
use, the gas pressure should be restricted to a maximum of 0.2 bar (3 psi). A pressure of about half
of that should normally be sufficient to achieve the desired flow rate. The customer must ensure
that the exhaust path from the tube is not blocked, so that excess pressure does not occur.
3.7 Gas Tightness
Work tubes of IAP material are impervious. Sillimanite may look similar but is porous. Ensure
that the correct tube material is in use before connecting and using gases, other than inert gases
such as nitrogen.
3.8 Running at Low Temperatures
Better control when running the furnace at a low temperature may often be achieved by adjusting
the power limit to a low level. No hard and fast rules can be given, but, as an example, to run at
temperatures only up to 600°C try a power limit of 50%. Control stability may fall off again if a
setting below about 40% is used.
Before changing the power limit, record its factory setting for possible future use. T o change the
power limit, see sections 8.2.
