Manually configuring your modem – Belkin High Speed ADSL2+ Modem F5D5730au User Manual
Page 14
25
24
Manually Configuring your Modem
Manually Configuring your Modem
25
se
ct
io
n
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
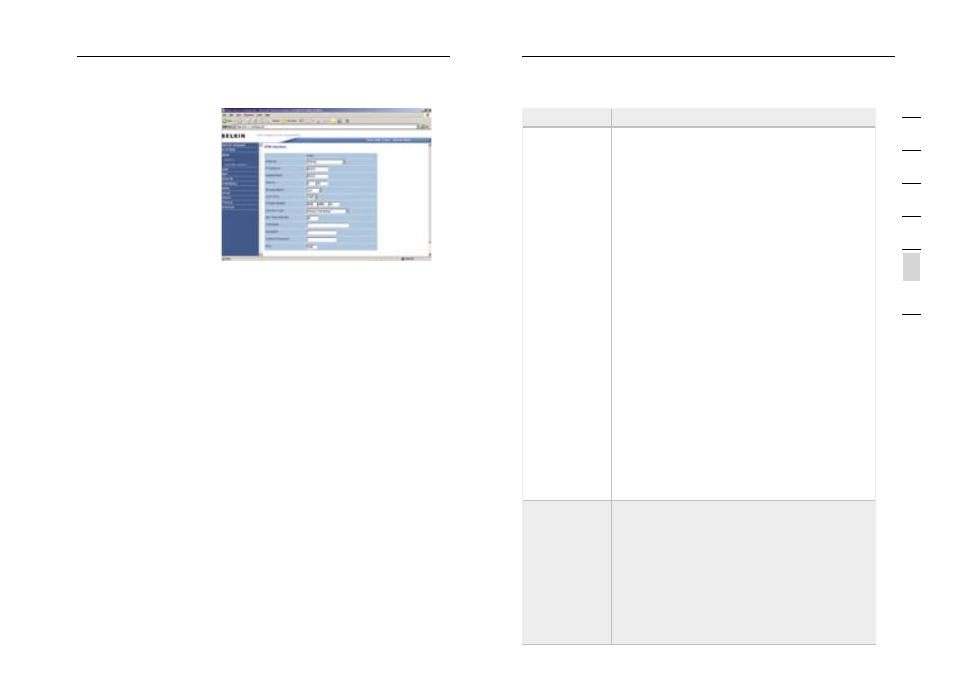
ATM Interface
Clicking on the ATM VC
brings up the following
screen. The Modem
uses ATM as its WAN
interface. Protocols
including 1483 Routing,
1483 Bridging, MAC
Encapsulated Routing
(MER), PPPoA and PPPoE
with LLC-SNAP and VC-
Mux encapsulations are
supported for each ATM
PVC.
When you have finished
entering your connection parameters, click “SAVE SETINGS”. You
can verify that you have established an ADSL connection by clicking
Status at the bottom of the left-hand menu.
See the table for a description of the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Protocol
•
Disable: Disables the connection.
•
1483 Bridging: Bridging is a standardized layer
2 technology. It is typically used in corporate
networks to extend the physical reach of a single
LAN segment and increase the number of stations
on a LAN without compromising performance.
Bridged data is encapsulated using the RFC1483
protocol to enable data transport.
•
PPPoA: Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM is a
method of encapsulating data for transmission to
a far point.
•
1483 Routing: 1483 Routing allows a simple, low-
cost connection to the Internet via a standard
Ethernet port. The Modem looks up the network
address for each packet seen on the LAN port. If
the address is listed in the routing table as local, it
is filtered. If the address is listed under the ADSL
port, it is forwarded. Or if the address is not found,
then it is automatically forwarded to the default
Modem (i.e., the Modem at the head end).
•
PPPoE: Point-to-Point over Ethernet is a common
connection method used for xDSL.
•
MAC Encapsulated Routing: If your ADSL service
is a Bridged mode service and you want to share
the connection to multiple PC’s, please select
MAC Encapsulated Routing. MER is a protocol
that allows you do IP routing with NAT enabled.
VPI/VCI
See Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) and Virtual Circuit
Identifier (VCI). Data flows are broken up into fixed
length cells, each of which contains a Virtual Path
Identifier (VPI) that identifies the path between two
nodes, and a Virtual Circuit Identifier (VCI) that
identifies the data channel within that virtual path.
Each virtual circuit maintains a constant flow of
cells between the two end points. When there is
no data to transmit, empty cells are sent. When
data needs to be transmitted, it is immediately
inserted into the cell flows.
