Oops! jumper (bios recovery), Serial console, Oops! jumper (bios recovery) serial console – Ampro Corporation CoreModule 420 5001692A User Manual
Page 47: Figure 3-2. oops! jumper
Chapter 3
Hardware
CoreModule 420
Reference Manual
41
Table 3-18. User GPIO Signals Pin/Signal Descriptions (J8)
Pin #
Signal
Description
1
GPIO8
User defined
2
GPIO9
User defined
3
GPIO10
User defined
4
GPIO11
User defined
5
GPIO12
User defined
6
GPIO13
User defined
7
GPIO14
User defined
8
GPIO15
User defined
9
GND
Ground
10
GND
Ground
Notes: The shaded area denotes ground.
Oops! Jumper (BIOS Recovery)
The Oops! jumper is provided in the event you’ve selected BIOS settings that prevent you from booting
the system. By using the Oops! jumper you can stop the current BIOS settings in the CMOS from being
loaded, allowing you to proceed, using the default settings. Connect the DTR pin to the RI pin on Serial
port 1 (COM 1) prior to boot up to prevent the present BIOS settings from loading. After booting with
the Oops! jumper in place, remove the Oops! jumper and go into BIOS Setup.
To restore your BIOS setting changes without the errors, you must first select Load Factory Default
Settings, which will automatically load and save the defaults and reboot the system. Then you can
modify the default settings to your desired values. Ensure you save the changes before rebooting the
system.
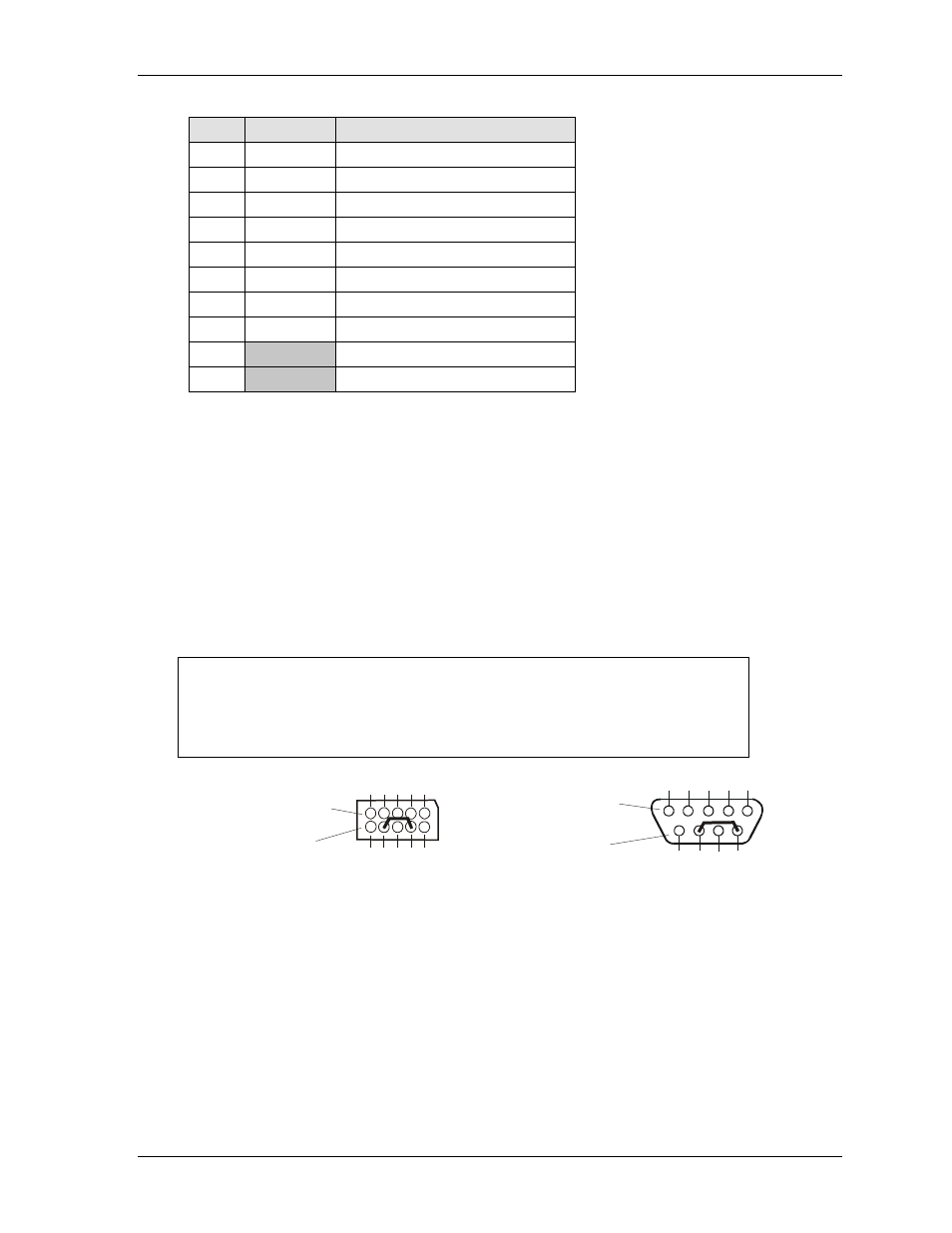
NOTE
The CoreModule 420 Serial Port 1 (J3) is a 10-pin header and uses
pin 7 = DTR and pin 8 = RI. At Serial Port 1, short pin 7 to 8, as
shown in Figure 3-2. Alternatively, you may short the equivalent
pins on the DB9 connector attached to Serial Port 1 as shown in
Figure 3-2.
Serial Ports (J3, J9)
(COM1 or COM2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Side View
Or
Standard DB9 Serial
Port Connector (Female)
Rear View
5
4
3
2
1
9
8
7
6
C
M
420se
rc
o
n
ju
m
p
Figure 3-2. Oops! Jumper
Serial Console
The CM 420 BIOS supports the serial console (or console redirection) feature. These I/O functions are
provided by an ANSI-compatible serial terminal, or the equivalent terminal emulation software running
on another system. This can be very useful when setting up the BIOS on a production line for systems
that are not connected to a keyboard and display.
