Calibration example (scaling), Troubleshooting, Installation – Red Lion IFMA User Manual
Page 8: Application, 0 calibration (cont’d)
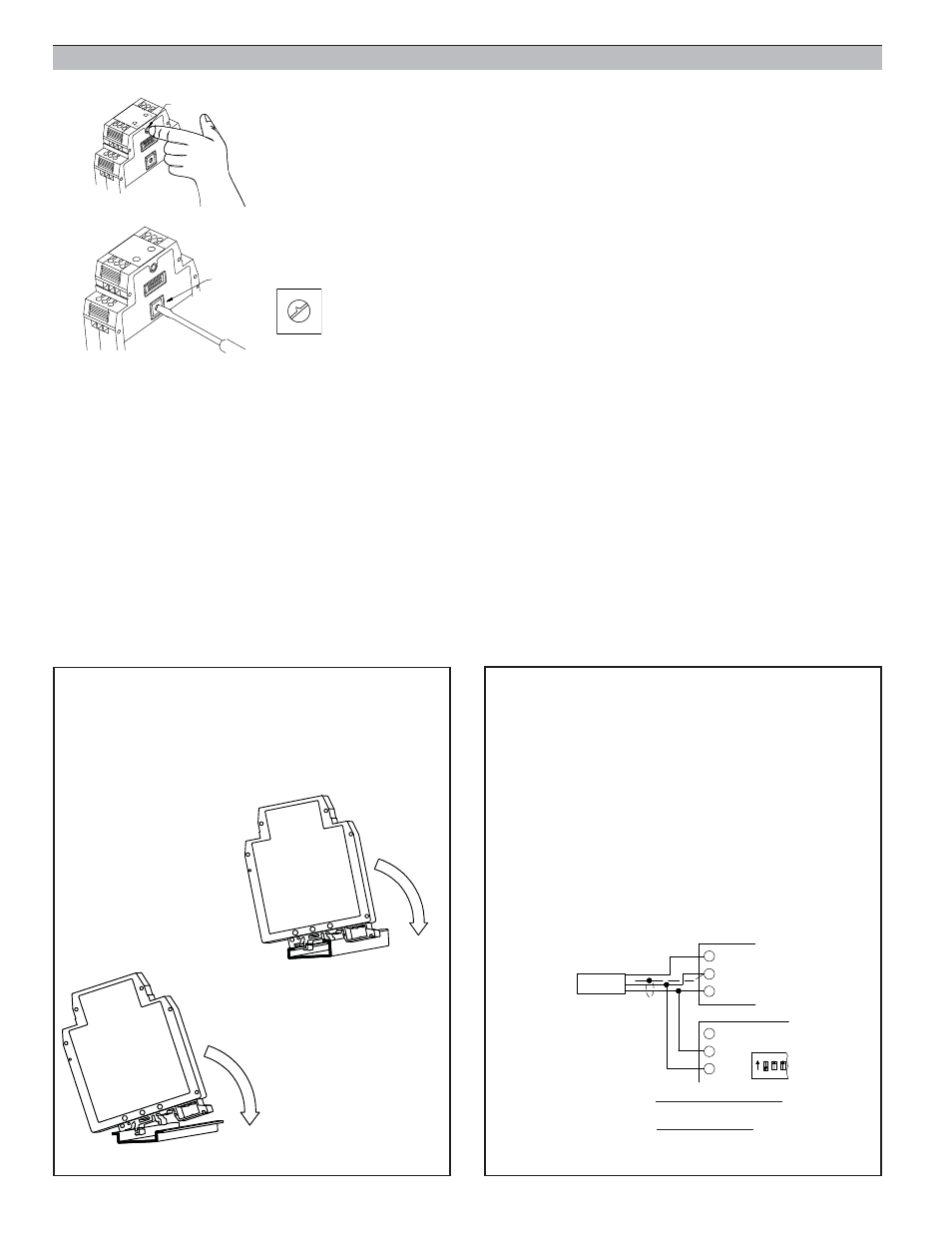
6.3 Press the push-button to enable the rotary switch. The Green input LED now blinks at a faster
rate, indicating that calibration values are accessible.
6.4 Turn rotary switch to appropriate numerical setting for calibration (see list in Step 6.0), while
monitoring the output signal. Press the push-button. Calibration is raised or lowered by this
approximate value, depending on calibration direction.
If this setting meets your requirements, go to step 6.5. If more calibration is required, repeat
step 6.4 until the calibration meets your requirements.
If you overshoot your desired value, reverse calibration direction as shown in 6.0 and
continue calibration until the value meets your requirements.
6.5 Turn the rotary switch to 0 and press the push-button. This saves the new user calibration setting.
If you want to return to factory calibration, exit Calibration and then re-enter. Turn rotary
switch to 0 and press push-button twice. This reloads the factory calibration setting for the
selected mode of operation.
When calibrating the Minimum output value, if the red output LED blinks while in the down
direction, the requested calibration setting is beyond the output’s absolute minimum value.
The calibration setting is held at the absolute minimum value. Reverse calibration direction
and repeat from step 6.4.
When calibrating Full Scale, if the red output LED blinks while in the up direction, the
requested calibration setting is beyond the output’s absolute maximum value. The calibration
setting is held at the maximum value. Reverse calibration direction and repeat from step 6.4.
If an attempt is made to calibrate the Full Scale value lower than the Minimum value, or
conversely, the Minimum value higher than the Full Scale value, the red output LED blinks,
and the IFMA sets the two values equal. Reverse calibration direction and repeat from step 6.4.
Calibration Example (Scaling):
A customer using the 0 to 10 VDC output range of the IFMA wants the Minimum value to be at 1 VDC. To do this,
connect a voltmeter to the output of the IFMA to monitor the output voltage. Access Configuration Mode by placing DIP
switch 4 to the ON (up) position. Access Analog Output Minimum value by placing DIP switches 5 and 7 up, and DIP
switch 6 down. Press the push-button to enable changes to the calibration value. Turn the rotary switch to position 8 and
press the push-button. The voltmeter should reflect an increase of about 400 mV. With the rotary switch still at position
8, press the push-button again. The voltmeter should now read approximately 800 mV. Turn the rotary switch to a
position lower than 8 to effect a smaller change in calibration. Continue adjusting the rotary switch and pressing the
push-button until 1 VDC is displayed on the voltmeter. Turn the rotary switch to position 0 and press the push-button.
This action saves the new calibration setting for the Minimum value.
TROUBLESHOOTING
For further technical assistance, contact technical support at the appropriate company numbers listed.
6.0 Calibration (Cont’d)
INSTALLATION
The unit is equipped with a universal mounting foot for attachment to
standard DIN style mounting rails, including G profile rail according to
EN50035 - G32 , and top hat (T) profile rail according to EN50022 - 35 x 7.5
and 35 x 15. The unit should be installed in a location that does not exceed
the maximum operating temperature and provides good air circulation.
Placing the unit near devices that generate excessive heat should be avoided.
G Rail Installation
To install the IFMA on a “G”
style DIN rail, angle the module so
that the upper groove of the “foot”
catches under the lip of the top rail.
Push the module toward the rail
until it snaps into place. To remove
a module from the rail, push up on
the bottom of the module while
pulling out and away from the rail.
T Rail Installation
To install the IFMA on a “T”
style rail, angle the module so
that the top groove of the “foot”
is located over the lip of the top
rail. Push the module toward the
rail until it snaps into place. To
remove a module from the rail,
insert a screwdriver into the slot
on the bottom of the “foot”, and
pry upwards on the module until
it releases from the rail.
APPLICATION
A customer needs a unit to output a signal to a chart recorder for a flow
rate system. There is an existing APLR rate indicator receiving an input
from a PSAC inductive proximity sensor. The IFMA Frequency to Analog
Converter is connected in parallel with the APLR to output the signal to the
chart recorder.
The flow rate is measured in gal/min. and needs to be converted to a 0 to
10 VDC signal. The Operating Mode of the IFMA is set for a 0 to 10 VDC
output signal. The PSAC measures 48 pulses/gal. with a maximum flow rate
of 525 gal/min. The Maximum Response Time is set to setting ‘9’ (10 sec).
The chart recorder will record 0 VDC at 0.125 gal/min, and 10 VDC at 525
gal/min.
The Input Range can be set one of two ways. By entering the calculated
maximum frequency with the rotary switch, or by applying the maximum
frequency signal of the process to the input of the IFMA. To set the input
with the rotary switch, first determine the maximum frequency generated by
the maximum output of the sensor using the following formula:
Max. Freq. = unit/measure x pulses/unit
seconds/measure
Max. Freq. = 525 GPM x 48 PPG = 420 Hz
60 sec.
Set the Input Range with the rotary switch to 420 Hz.
SNK
LOGIC
SRC
ON 1 2 3
7
8
9
+12V
INPUT
COMM.
COMM.
INPUT
+12V
8
9
7
APLR
PSAC
IFMA
0
9
8
7 6 5 4
3
2
1
Setting ‘9’
Selected
PUSH-BUTTON
OUT
IN
STATUS
Step 6.3
OUT
IN
ROTARY
SWITCH
Step 6.4
