Adding drives – HP Smart Array P431 Controller User Manual
Page 30
Drive procedures 30
o
If a 1724 or 1727 POST message appears, drive positions were changed successfully and the
configuration was updated. Continue with step 7.
6.
If the array did not configure properly, do the following:
a.
Power down the system immediately to prevent data loss.
b.
Return the drives to their original locations.
c.
Restore the data from backup, if necessary.
7.
Verify the new drive configuration by running HP SSA ("
" on page
Adding drives
You can add drives to a system at any time, if you do not exceed the maximum number of drives that the
controller supports. You can then either build a new array from the added drives or use the extra storage
capacity to expand the capacity of an existing array.
If the drives that you intend to add to the system are already configured into logical drives, you must meet
certain conditions before adding drives to the system. For more information, see "Moving drives and arrays
(on page
)." When you have successfully added the drives, reset the server so that the controller can
recognize the logical drives.
To perform an array capacity expansion, use HP SSA. If the system uses hot-pluggable drives and HP SSA
runs in the same environment as the normal server applications, you can expand array capacity without
shutting down the operating system. For more information, see the HP Smart Storage Administrator User
Guide on the HP website
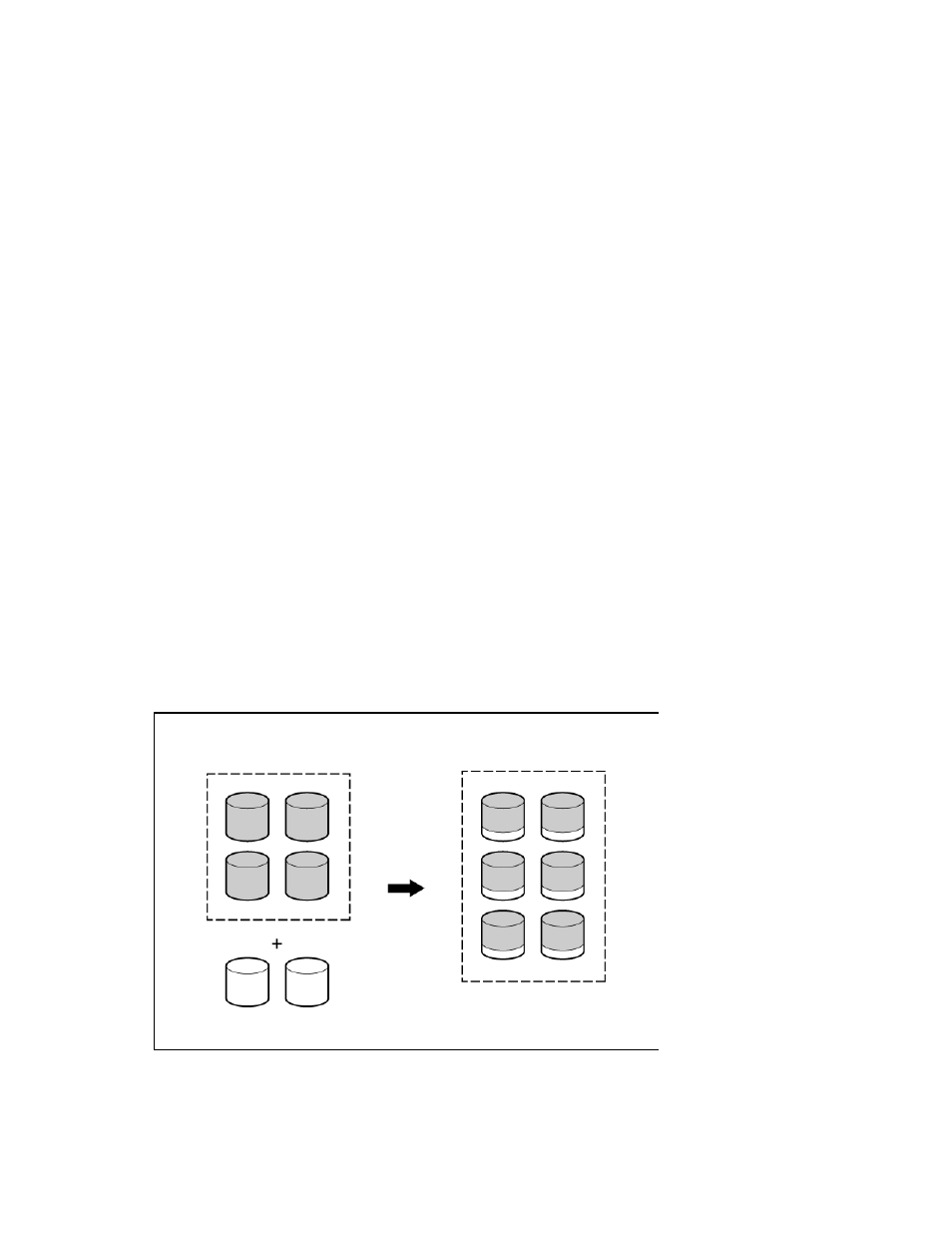
The expansion process is illustrated in the following figure, in which the original array (containing data) is
shown with a dashed border, and the newly added drives (containing no data) are shown unshaded. The
array controller adds the new drives to the array and redistributes the original logical drives over the
enlarged array one logical drive at a time. This process liberates some storage capacity on each physical
drive in the array. Each logical drive keeps the same fault-tolerance method in the enlarged array that it had
in the smaller array.
