Hp remote graphics software and use, Location for application execution and control, 1 using a single sva node from local desktop – HP Scalable Visualization Array Software User Manual
Page 32
The
SVA Software Installation Guide has specific RGS installation instructions that you must use to supplement
the HP RGS installation instructions.
HP Remote Graphics Software and Use
HP RGS is an advanced utility that makes it possible to remotely access and share 3D graphics workstation
desktops. This can be done across Windows and Linux platforms. With RGS, you can:
•
Remotely access 3D graphics workstations.
•
Access applications running on SVA from a Linux or Windows desktop.
•
Perform multiuser remote collaborations.
A link to the HP RGS documentation is available from the SVA Documentation Library.
Location for Application Execution and Control
This example requires that you configure the SVA so that it can run your application while you control it from
your local desktop. Additionally, display output is routed to your local desktop using HP RGS.
See
for examples of using the installed RGS script. A summary of the overall process
follows.
1.
An SVA Kit installed RGS launch script allocates resources on the SVA based on the Display Surface
you specify. In the case of the RGS script, you must use a Display Surface with a single display node
that has the RGS Sender installed.
Your application runs on the same display node denoted by the Display Surface.
2.
The RGS Receiver starts on your local desktop (Linux or Windows). Configure it by manually entering
the external name for the display node defined by the Display Surface you chose.
3.
The RGS Receiver and Sender connect.
4.
A desktop environment (for example, KDE or Gnome) appears on your local desktop in the same way
it would appear if you were directly logged into an individual SVA node.
5.
You control your application, that is, provide input to the application while it is running, using the local
desktop keyboard and mouse. Display output from the application appears on your local desktop.
Display output simultaneously appears on the display device in the SVA as determined by the Display
Surface you chose when you started the launch script.
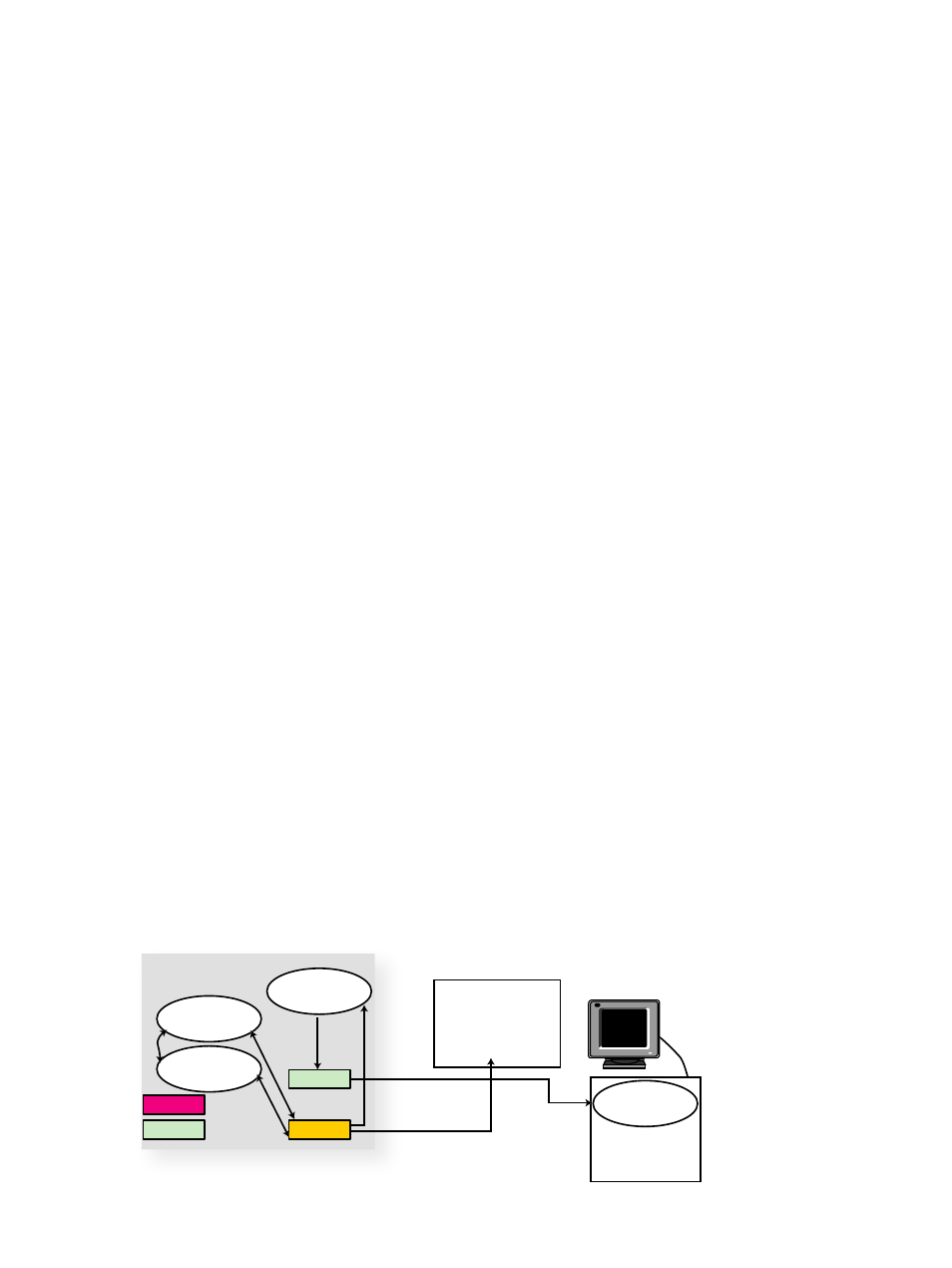
shows the relationships among the various processes that run when you launch visualization
jobs.
There are four processes that must run when a remote visualization session begins.
•
The X Server.
•
RGS Sender on the SVA display node.
•
RGS Receiver on your local desktop.
•
Your visualization application.
Figure 5-1 Using a Single SVA Node from Local Desktop
G F X
G igE
G igE
S I
User
Application
X Server
Display Node
RGS
Sender
RGS
Receiver
Local Desktop
Display Device
(attached to SVA)
32
Application Examples
