Commonality of interface – HP Integrity NonStop J-Series User Manual
Page 118
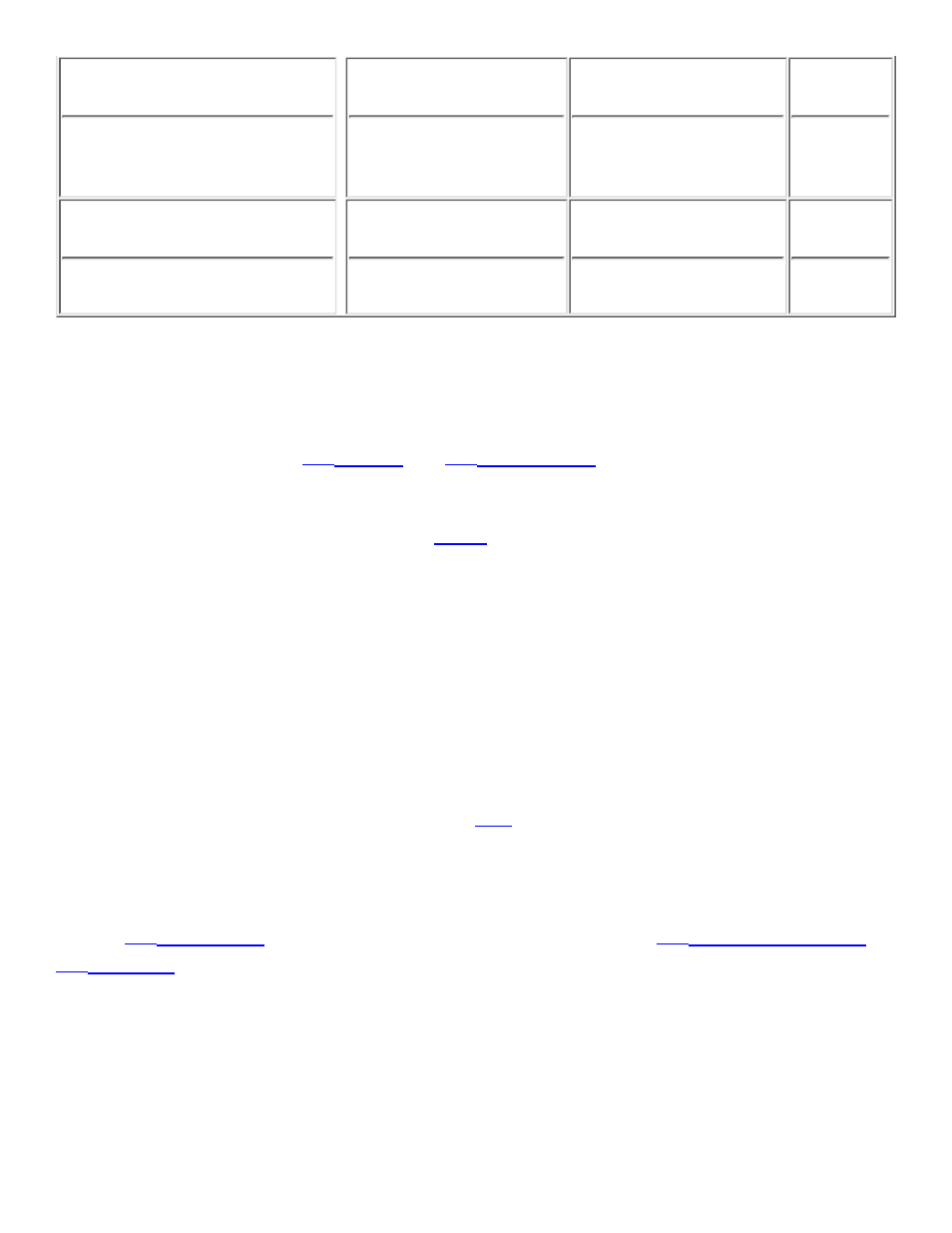
Associative container-based
(set-based)
(map-based)
//Internal ordering, access by
key
RWTValSet
RWTValMultiSet
RWTValMap
RWTValMultiMap
RWTPtrSet
RWTPtrMultiSet
RWTPtrMap
RWTPtrMultiMap
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Associative hash-based
(set-based)
(map-based)
//No ordering, access by key
RWTValHashSet
RWTValHashMultiSet
RWTValHashMap
RWTValHashMultiMap
RWTPtrHashSet
RWTPtrHashMultiSet
RWTPtrHashMap
RWTPtrHashMultiMap
No
No
No
Yes
Commonality of Interface
To keep things simple and allow you to program with more flexibility, we have implemented
common interfaces within the various divisions of standard-library based collection class
templates. For example, the
RWTPtrSet
and
RWTPtrMultiSet
templates have interfaces
identical to their value-based cousins; so do the map-based collection classes. All of the
Sequence-based collections have nearly identical interfaces within the value and pointer-based
subgroups. (An exception here is the set of
deque
-based classes, which contain push and pop
member functions designed to enhance their abstraction of the queue data structure.)
There are pluses and minuses to this approach. The downside is that it puts slightly more of the
burden on you, the developer, to choose the appropriate collection class. Had we chosen not to
provide the insertAt(size_type index) member function for class RWOrderedVectorVal
we could have enforced the idea that vector-based templates are not a good choice for inserting
into the middle of a collection class. Instead, it is up to you to be aware of your choices and use
such member functions judiciously.
On the plus side, the common interface lowers the learning curve, allows flexibility in
experimenting with different collections, and provides the capability of dealing with the Rogue
Wave templates polymorphically via genericity.
[14]
Real-life programming is seldom as neat as the exercises in a data structures textbook. You may
find yourself in a situation where it is difficult to balance the trade-offs and determine just
which collection class to use. With the common interface, you can easily benchmark code that
uses an
RWTValDeque
and later benchmark it again, substituting an
RWTValOrderedVector
or
RWTValDlist
. You can also write class and function templates that are parameterized on the
collection class type. For example:
template
void tossHiLo(RWSeqBased& coll) {
// throw out the high and low values:
assert(coll.entries() >= 2); // precondition
coll.sort();
coll.removeFirst();
